Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 janeiro 2025
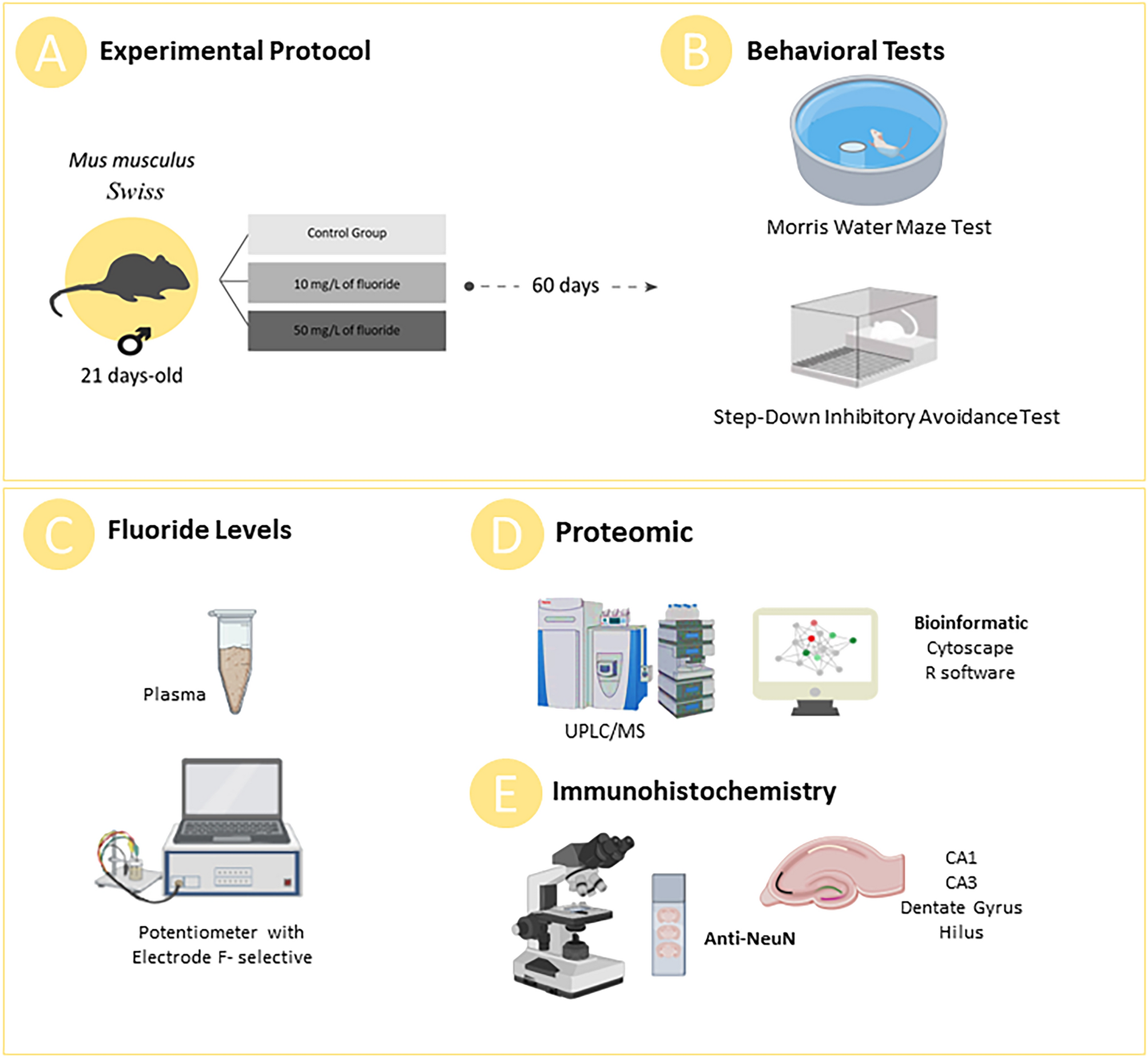
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

eNAMPT actions through nucleus accumbens NAD+/SIRT1 link increased adiposity with sociability deficits programmed by peripuberty stress
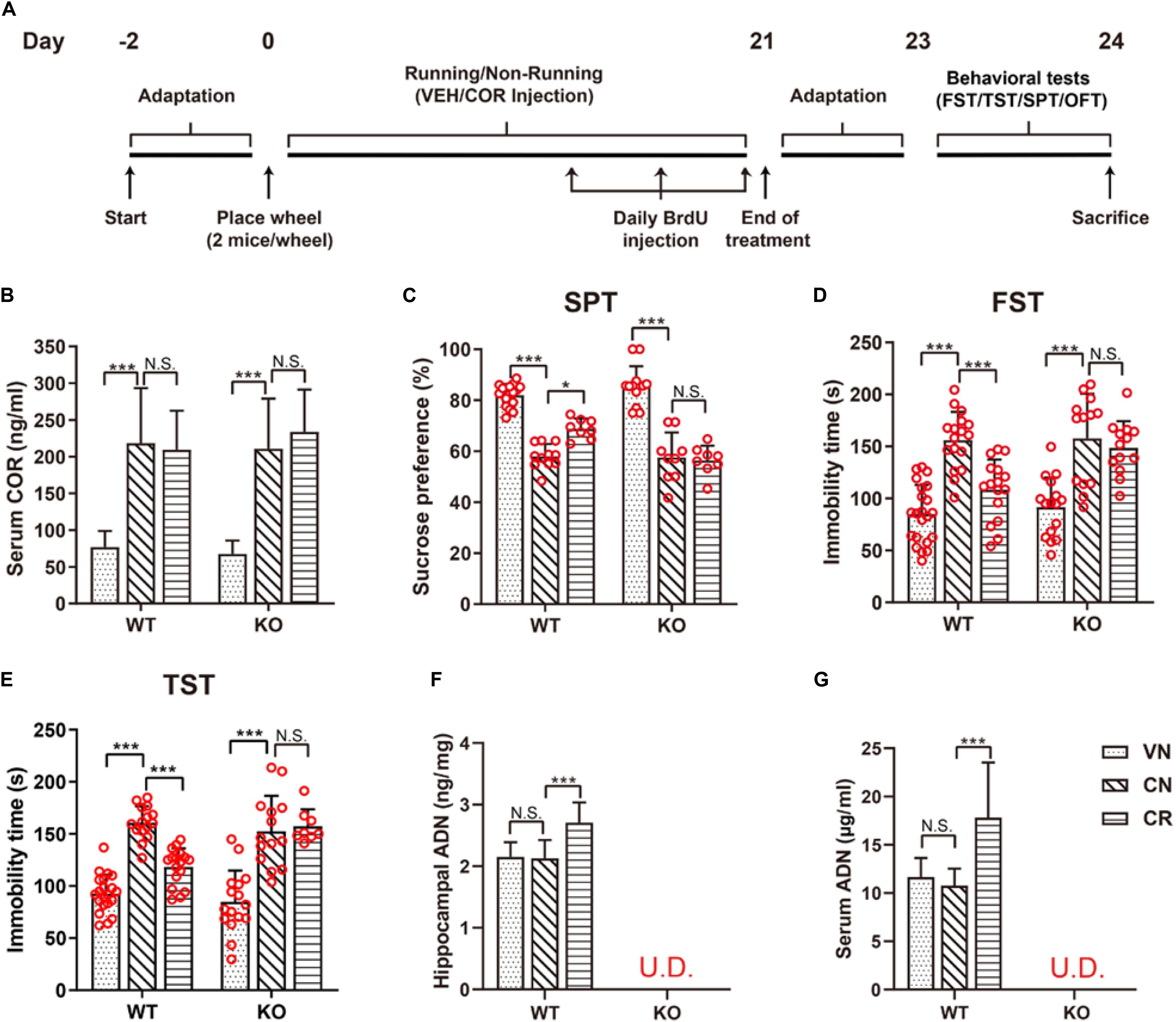
Frontiers Potential Involvement of Adiponectin Signaling in Regulating Physical Exercise-Elicited Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Dendritic Morphology in Stressed Mice
Effects of long-term fluoride exposure are associated with oxidative biochemistry impairment and global proteomic modulation, but not genotoxicity, in parotid glands of mice
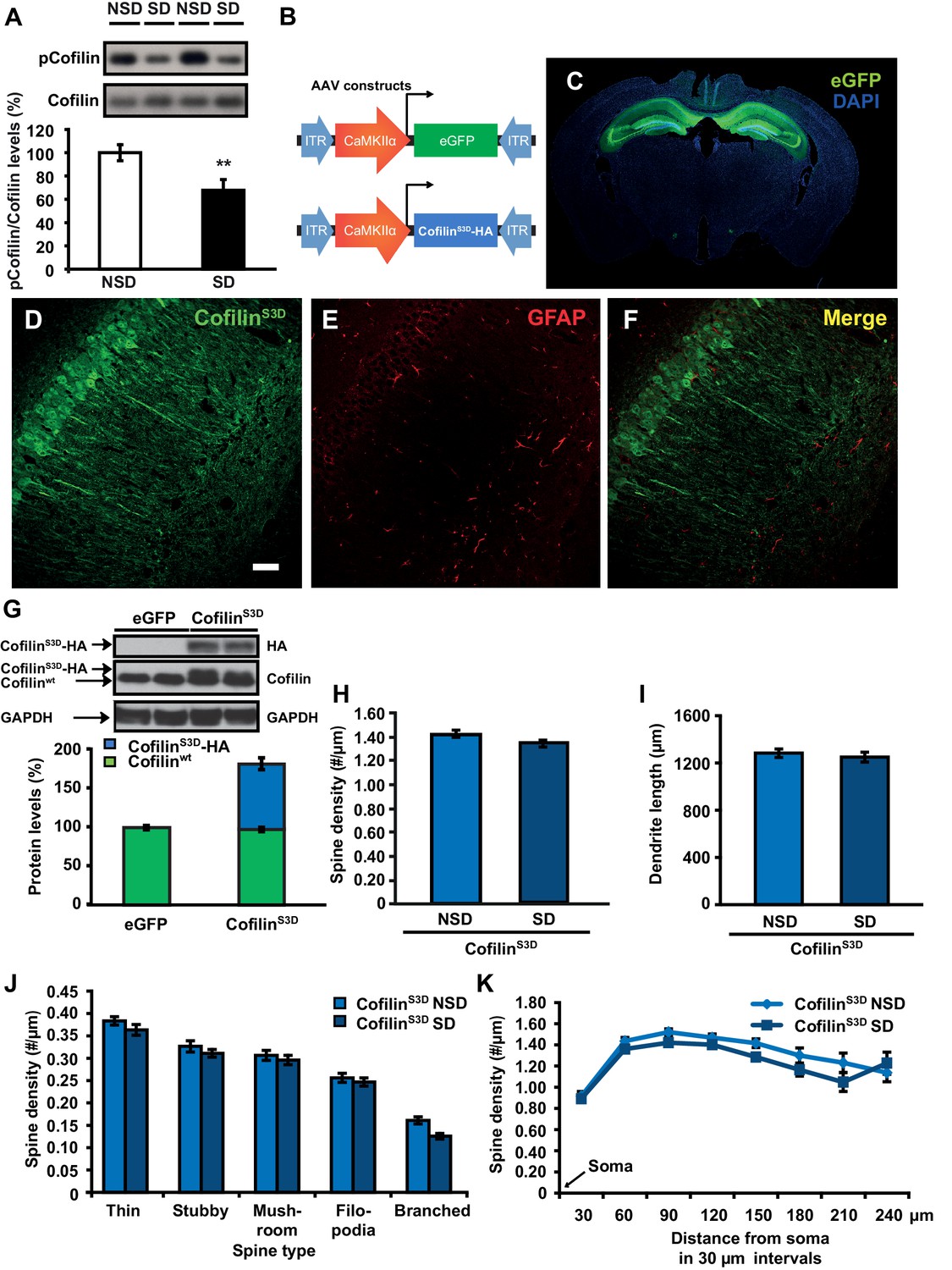
Sleep deprivation causes memory deficits by negatively impacting neuronal connectivity in hippocampal area CA1

Bisphenol S Impairs Behaviors through Disturbing Endoplasmic Reticulum Function and Reducing Lipid Levels in the Brain of Zebrafish

Early‐life stress affects the structural and functional plasticity of the medial prefrontal cortex in adolescent rats - Chocyk - 2013 - European Journal of Neuroscience - Wiley Online Library

Goods and Bads of the Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target: Lessons Learned after 30 Years

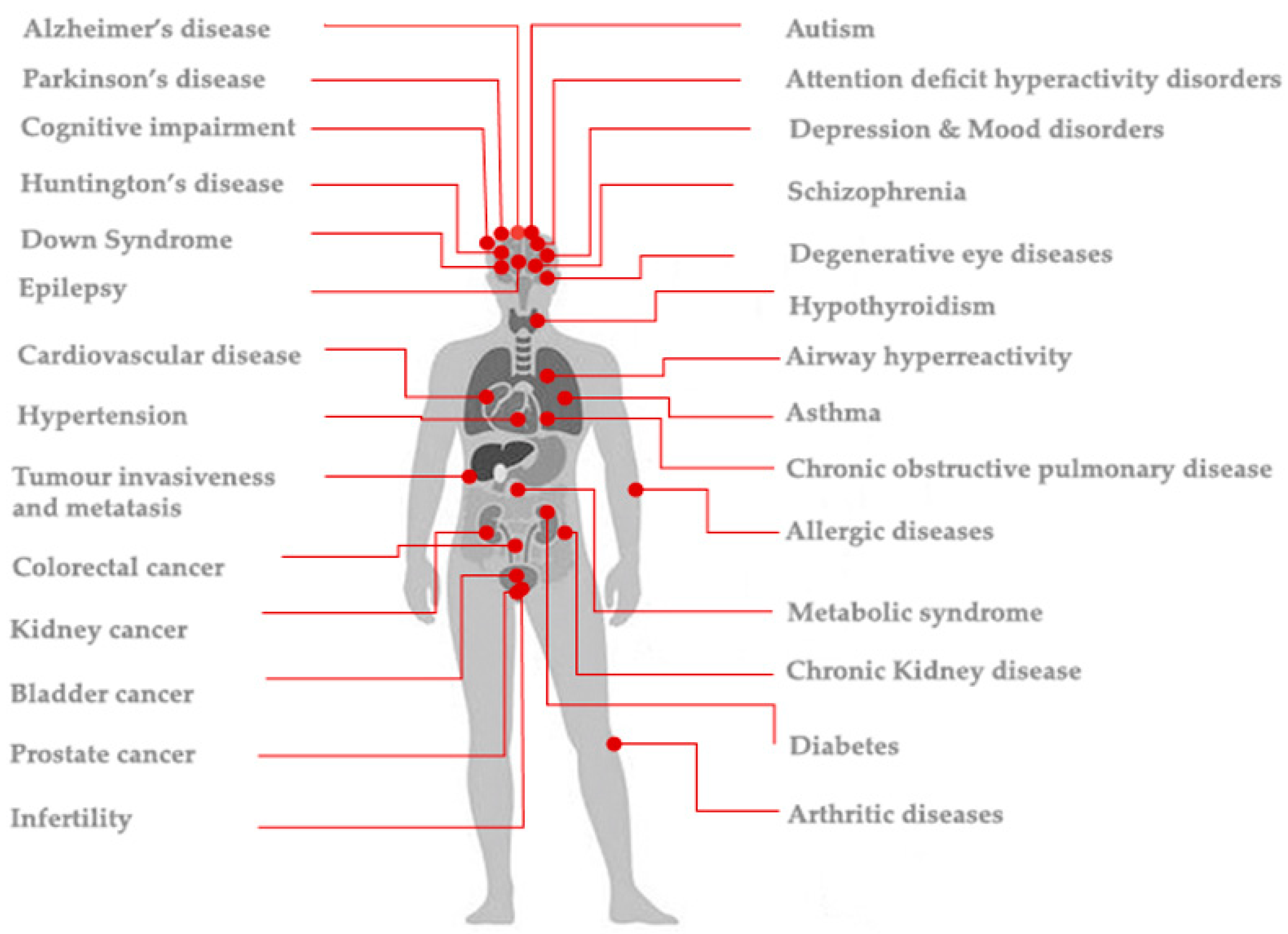
High Fluoride Levels May Affect Child Cognition - Neuroscience News

Nys Cof

Frontiers Unraveling molecular characteristic of fluoride neurotoxicity on U87 glial-like cells: insights from transcriptomic and proteomic approach
Vitamins

Progesterone activates GPR126 to promote breast cancer development via the Gi pathway
Recomendado para você
-
 BLOCO FLORK DIVERSOS 10x15 Capa Dura01 janeiro 2025
BLOCO FLORK DIVERSOS 10x15 Capa Dura01 janeiro 2025 -
 Brain test 8801 janeiro 2025
Brain test 8801 janeiro 2025 -
 Brain test nivel 88 deja entrar al gato por favor se esta congelando01 janeiro 2025
Brain test nivel 88 deja entrar al gato por favor se esta congelando01 janeiro 2025 -
 Brain Test Level 86 87 88 89 90 Walkthrough #Short #Shorts01 janeiro 2025
Brain Test Level 86 87 88 89 90 Walkthrough #Short #Shorts01 janeiro 2025 -
 Convite Digital Charlie e Lola01 janeiro 2025
Convite Digital Charlie e Lola01 janeiro 2025 -
:strip_icc()/pic7783885.png) BoardGameGeek01 janeiro 2025
BoardGameGeek01 janeiro 2025 -
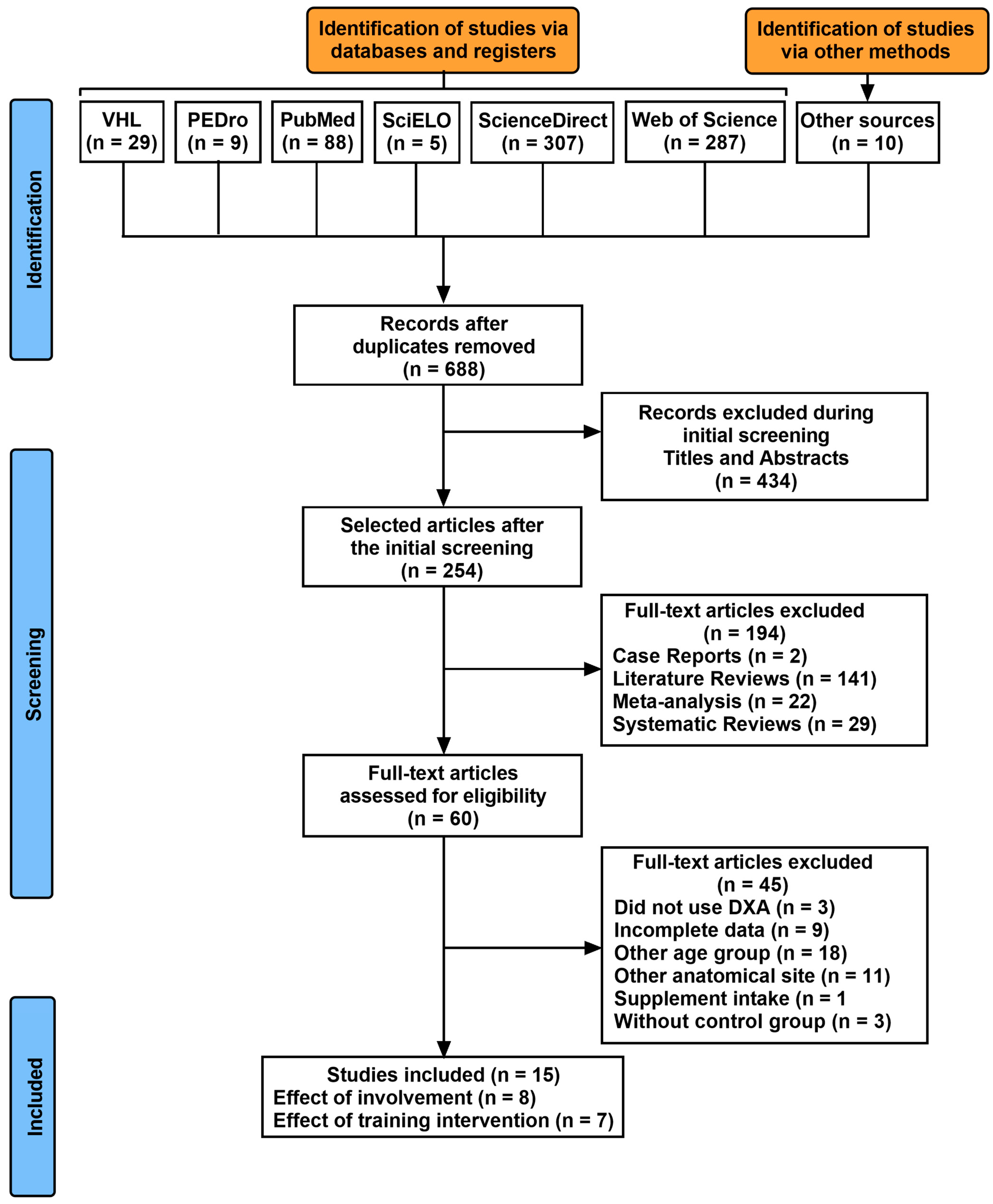 IJERPH, Free Full-Text01 janeiro 2025
IJERPH, Free Full-Text01 janeiro 2025 -
braintest4 #level51 #viral #foryoupage #very #funny01 janeiro 2025
-
brain test level 266|TikTok Search01 janeiro 2025
-
 Brain Test 4 Level 88 Granny Amy is forcing Uncle Bubba to run on the treadmill, help him Answers and Solutions01 janeiro 2025
Brain Test 4 Level 88 Granny Amy is forcing Uncle Bubba to run on the treadmill, help him Answers and Solutions01 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
![Melanie Martinez - Mad hatter [Nightcore] Roblox ID - Music Code](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2s9u0F_5DUw/maxresdefault.jpg) Melanie Martinez - Mad hatter [Nightcore] Roblox ID - Music Code01 janeiro 2025
Melanie Martinez - Mad hatter [Nightcore] Roblox ID - Music Code01 janeiro 2025 -
 Old Stranger Things Characters Who Return In Season 401 janeiro 2025
Old Stranger Things Characters Who Return In Season 401 janeiro 2025 -
 Black Dot Digital Gift Card01 janeiro 2025
Black Dot Digital Gift Card01 janeiro 2025 -
 Jogo de cores por números para crianças página para colorir com01 janeiro 2025
Jogo de cores por números para crianças página para colorir com01 janeiro 2025 -
 Streamer Ludwig Sets a Couple Goal by Fulfilling01 janeiro 2025
Streamer Ludwig Sets a Couple Goal by Fulfilling01 janeiro 2025 -
 bangla street ping pong show|TikTok Search01 janeiro 2025
bangla street ping pong show|TikTok Search01 janeiro 2025 -
music #tripleb #partyinpinegrove #pooltournament #livemusic #freefood01 janeiro 2025
-
 Netflix's 'Special' Creator Reflects on Man-on-Man Sex on TV – The Hollywood Reporter01 janeiro 2025
Netflix's 'Special' Creator Reflects on Man-on-Man Sex on TV – The Hollywood Reporter01 janeiro 2025 -
 Mapa De Portugal E Cor Branca Das Estradas Ilustração do Vetor - Ilustração de porto, terra: 14576222001 janeiro 2025
Mapa De Portugal E Cor Branca Das Estradas Ilustração do Vetor - Ilustração de porto, terra: 14576222001 janeiro 2025 -
 Do It Yourself!! TRAILER OFICIAL01 janeiro 2025
Do It Yourself!! TRAILER OFICIAL01 janeiro 2025


