Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 30 março 2025
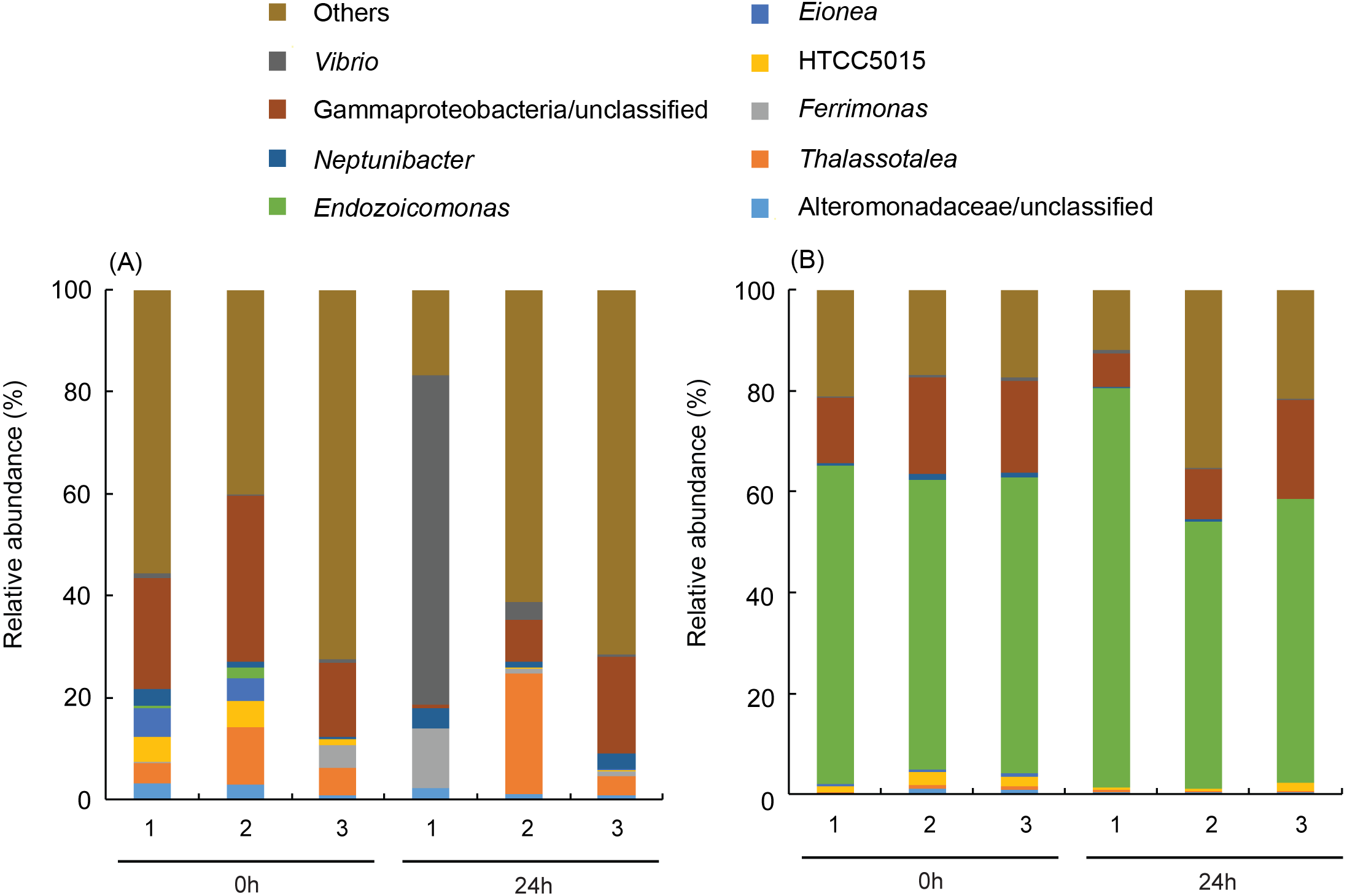
Global warming threatens reef-building corals with large-scale bleaching events; therefore, it is important to discover potential adaptive capabilities for increasing their temperature resistance before it is too late. This study presents two coral species (Platygyra verweyi and Isopora palifera) surviving on a reef having regular hot water influxes via a nearby nuclear power plant that exhibited completely different bleaching susceptibilities to thermal stress, even though both species shared several so-called “winner” characteristics (e.g., containing Durusdinium trenchii, thick tissue, etc.). During acute heating treatment, algal density did not decline in P. verweyi corals within three days of being directly transferred from 25 to 31 °C; however, the same treatment caused I. palifera to lose < 70% of its algal symbionts within 24 h. The most distinctive feature between the two coral species was an overwhelmingly higher constitutive superoxide dismutase (ca. 10-fold) and catalase (ca. 3-fold) in P. verweyi over I. palifera. Moreover, P. verweyi also contained significantly higher saturated and lower mono-unsaturated fatty acids, especially a long-chain saturated fatty acid (C22:0), than I. palifera, and was consistently associated with the symbiotic bacteria Endozoicomonas, which was not found in I. palifera. However, antibiotic treatment and inoculation tests did not support Endozoicomonas having a direct contribution to thermal resistance. This study highlights that, besides its association with a thermally tolerable algal symbiont, a high level of constitutive antioxidant enzymes in the coral host is crucial for coral survivorship in the more fluctuating and higher temperature environments.

Small-molecule superoxide dismutase (SOD)1 inhibitors. Shown are three
Frontiers Emerging Antioxidant Paradigm of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Therapy

Chemical Warfare at the Microorganismal Level: A Closer Look at the Superoxide Dismutase Enzymes of Pathogens
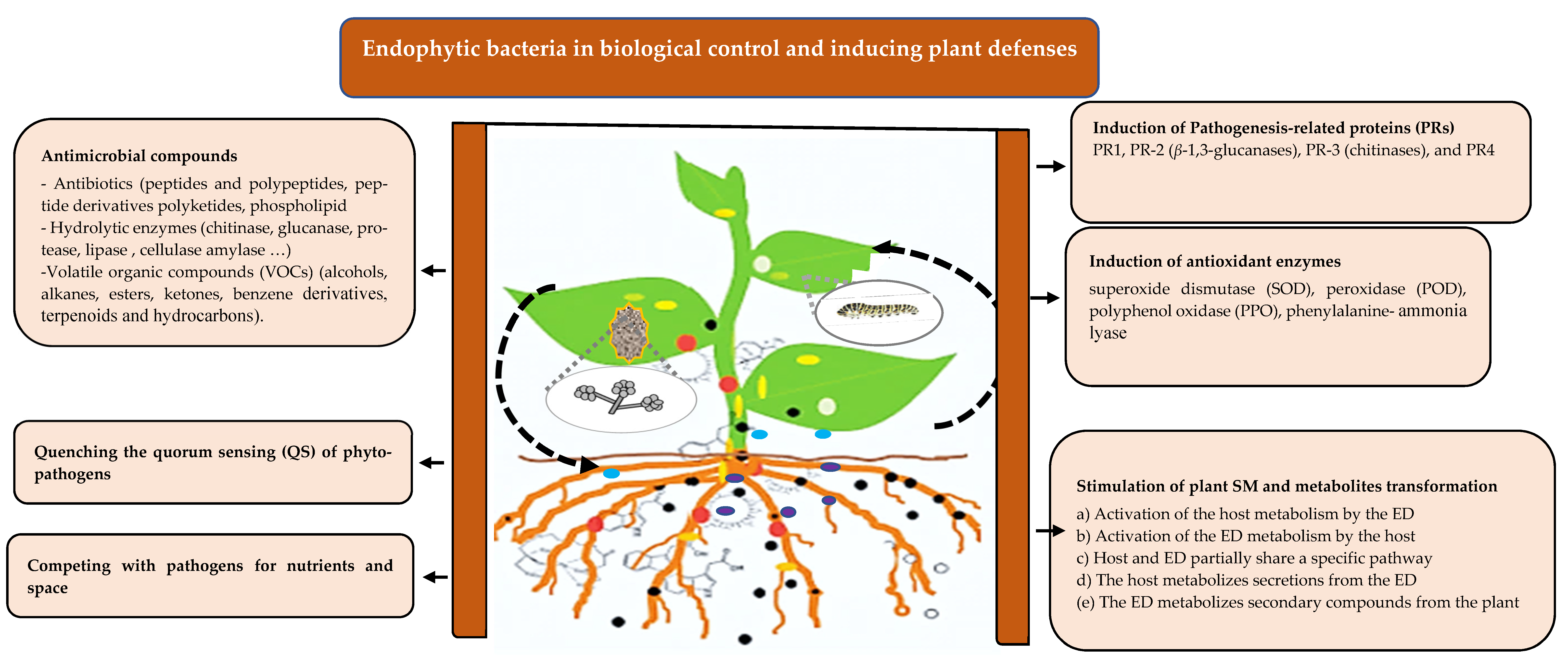
Plants, Free Full-Text

Superoxide dismutase 3 is expressed in bone tissue and required for normal bone homeostasis and mineralization - ScienceDirect
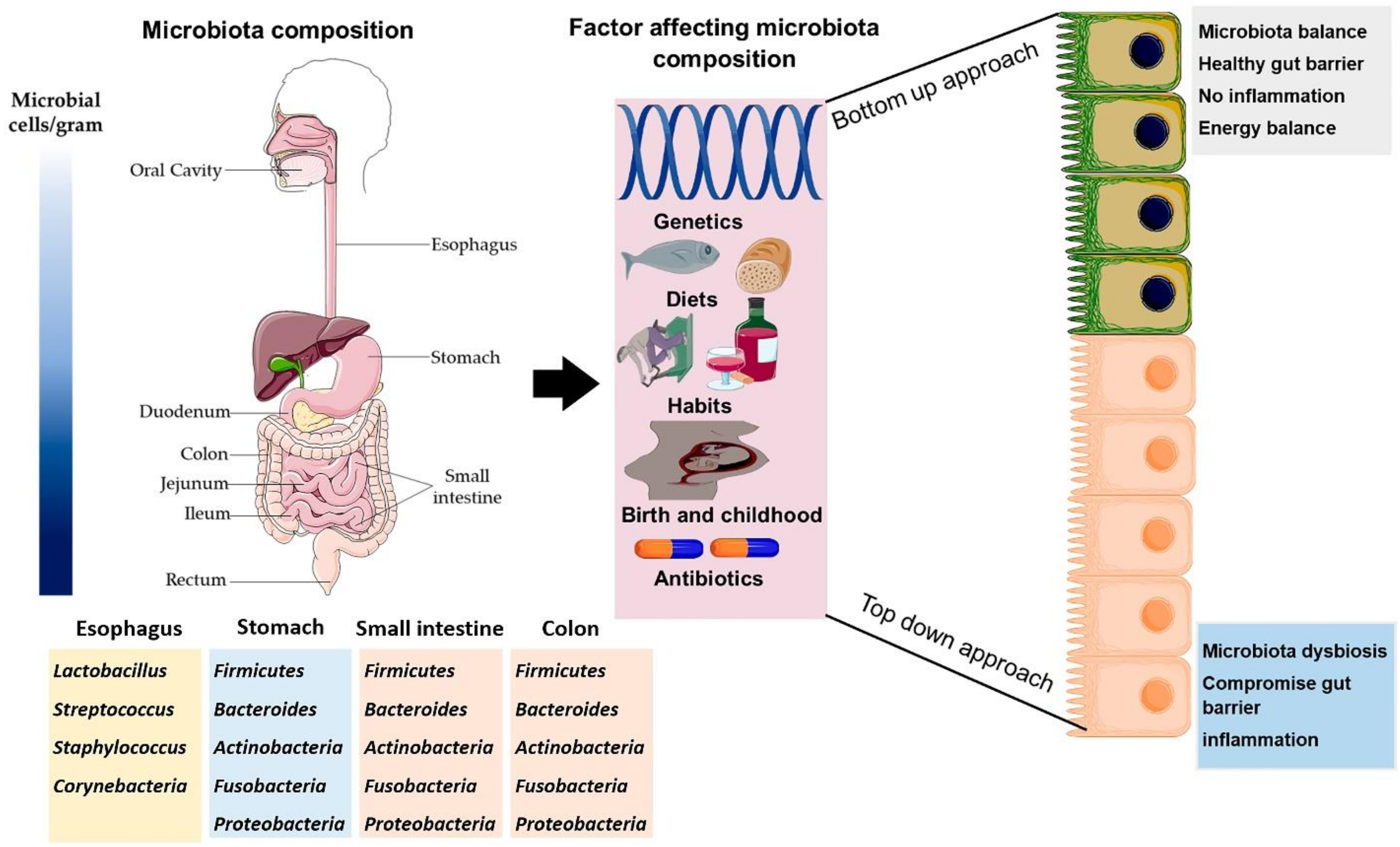
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

Extracellular superoxide dismutase, a molecular transducer of health benefits of exercise - ScienceDirect
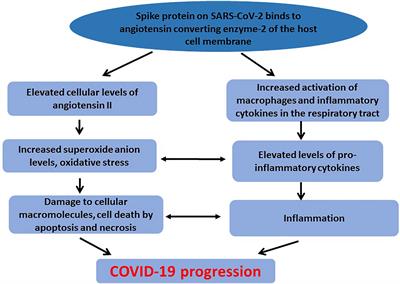
Frontiers Metabolic Implications of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Process in SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis: Therapeutic Potential of Natural Antioxidants

Isoliquiritigenin attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal damage by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and through activating Nrf2 - ScienceDirect

MDA, GSH, NO levels and SOD, CAT, and TF activities of lung tissue.

Effects of dietary treatments on tissue antioxidant enzyme activities

Expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the kidney after gene
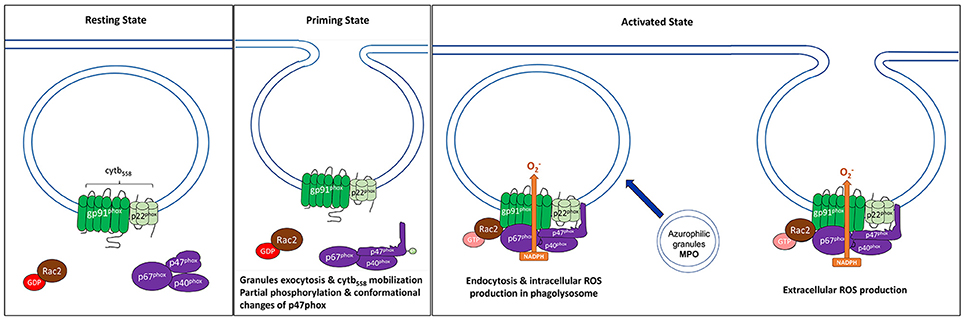
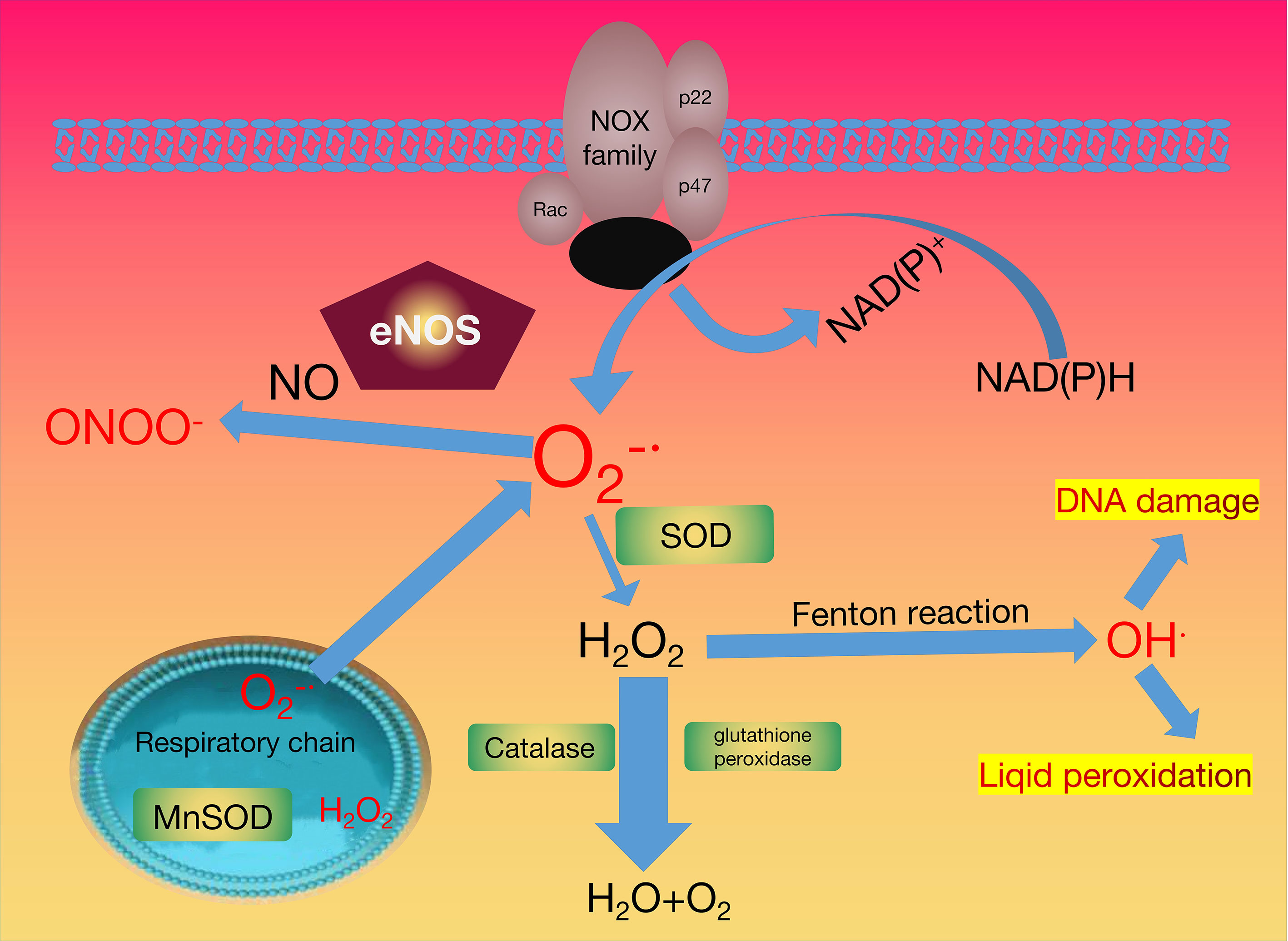
Frontiers Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH Oxidase Activation and Bacterial Resistance
Recomendado para você
-
TIME CONTROL CONTABILIDADE30 março 2025
-
Fabiano Sarzi Sartori - Diretor - TIME CONTROL AUDITORIA E30 março 2025
-
 CONTROL DESK30 março 2025
CONTROL DESK30 março 2025 -
 Arquivos vagas de emprego - Instituto Internacional Arayara30 março 2025
Arquivos vagas de emprego - Instituto Internacional Arayara30 março 2025 -
 Junta-te a nós! - BOLSA DE EMPREGO - SJ Têxteis30 março 2025
Junta-te a nós! - BOLSA DE EMPREGO - SJ Têxteis30 março 2025 -
 Vagas Disponíveis30 março 2025
Vagas Disponíveis30 março 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/j/L/hdHHZKSGSrh23nTIZDtw/electrician-2755683-1920.jpg) Veja as vagas de emprego do SineBahia para Salvador e Lauro de30 março 2025
Veja as vagas de emprego do SineBahia para Salvador e Lauro de30 março 2025 -
 Six Tips for Stress Reduction: Exercising Your Vagus Nerve to Heal30 março 2025
Six Tips for Stress Reduction: Exercising Your Vagus Nerve to Heal30 março 2025 -
 RAIDERS PATCH 12” BACK PATCH30 março 2025
RAIDERS PATCH 12” BACK PATCH30 março 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2022/u/Z/e4BCemR9K1Joi88ZKATA/nicolas-personagem.jpeg) Jovem relata dificuldades na busca do 1º emprego: 'Preciso de30 março 2025
Jovem relata dificuldades na busca do 1º emprego: 'Preciso de30 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
-a.png) Ludii Portal30 março 2025
Ludii Portal30 março 2025 -
 Brookhaven RP Hack: Kill All, Kick All, Teleports & More30 março 2025
Brookhaven RP Hack: Kill All, Kick All, Teleports & More30 março 2025 -
 Mocks without roadblocks: the magic of mswjs+faker.js, by Victor A Shataev, Mitgo30 março 2025
Mocks without roadblocks: the magic of mswjs+faker.js, by Victor A Shataev, Mitgo30 março 2025 -
 ArtStation - Heimdall30 março 2025
ArtStation - Heimdall30 março 2025 -
PFC Ludogorets Razgrad - Wikipedia30 março 2025
-
![Evowars.io - Invisible Hack 27/27 Max Level Mod [Cheat Tutorial] Top 9.9m+](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1LGK28ruWOY/sddefault.jpg) Evowars.io - Invisible Hack 27/27 Max Level Mod [Cheat Tutorial] Top 9.9m+30 março 2025
Evowars.io - Invisible Hack 27/27 Max Level Mod [Cheat Tutorial] Top 9.9m+30 março 2025 -
 London: The London Eye - Standard Admission Ticket30 março 2025
London: The London Eye - Standard Admission Ticket30 março 2025 -
Lifetime Movie Club - Apps on Google Play30 março 2025
-
 Thor: Ragnarok Launches With 100% Positive Score On Rotten Tomatoes30 março 2025
Thor: Ragnarok Launches With 100% Positive Score On Rotten Tomatoes30 março 2025 -
 Download do APK de Como desenhar Beyblade para Android30 março 2025
Download do APK de Como desenhar Beyblade para Android30 março 2025


