Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 fevereiro 2025

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, dopaminergic neuron loss, and alpha-synuclein (αSyn) inclusion…
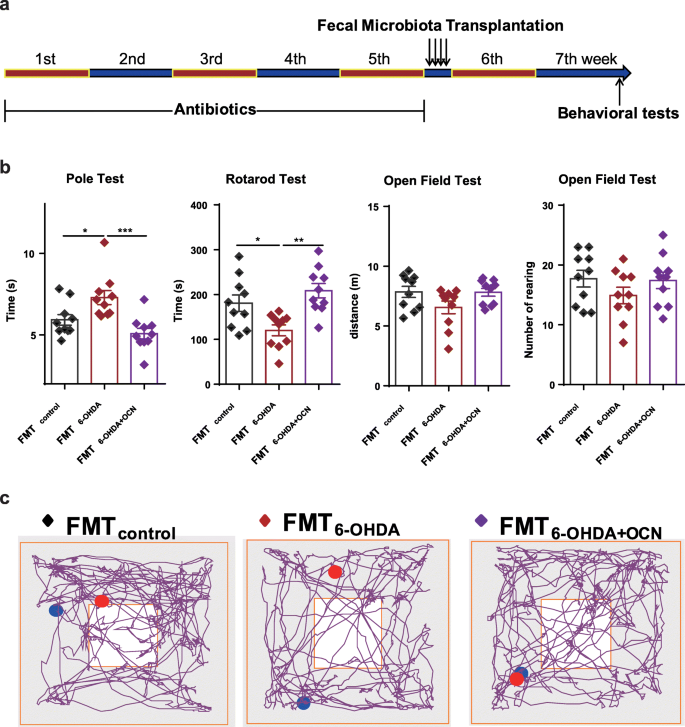
Gut microbiota-derived propionate mediates the neuroprotective effect of osteocalcin in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, Microbiome

Emerging insights between gut microbiome dysbiosis and Parkinson's disease: Pathogenic and clinical relevance - ScienceDirect
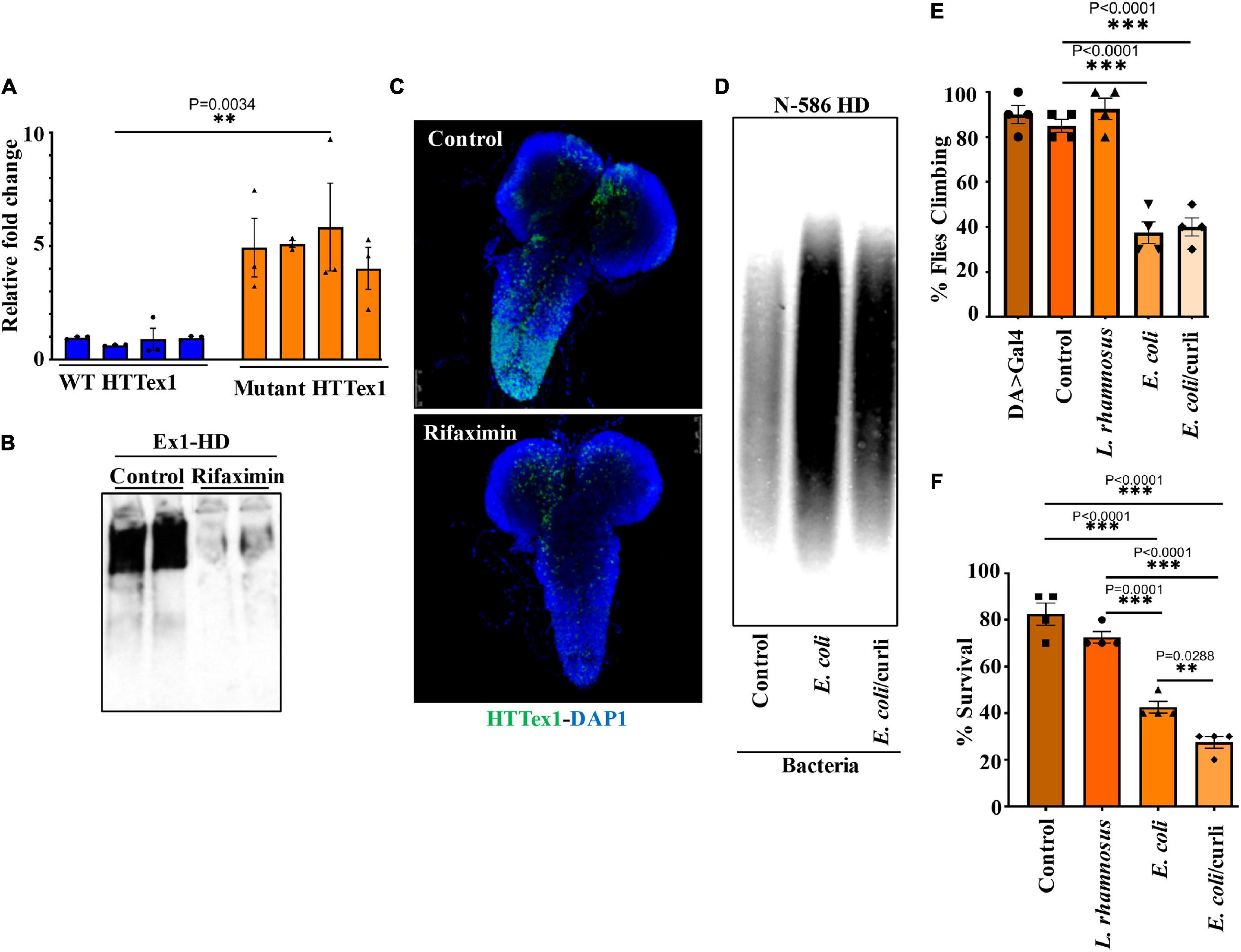
Frontiers Gut Bacteria Regulate the Pathogenesis of Huntington's Disease in Drosophila Model
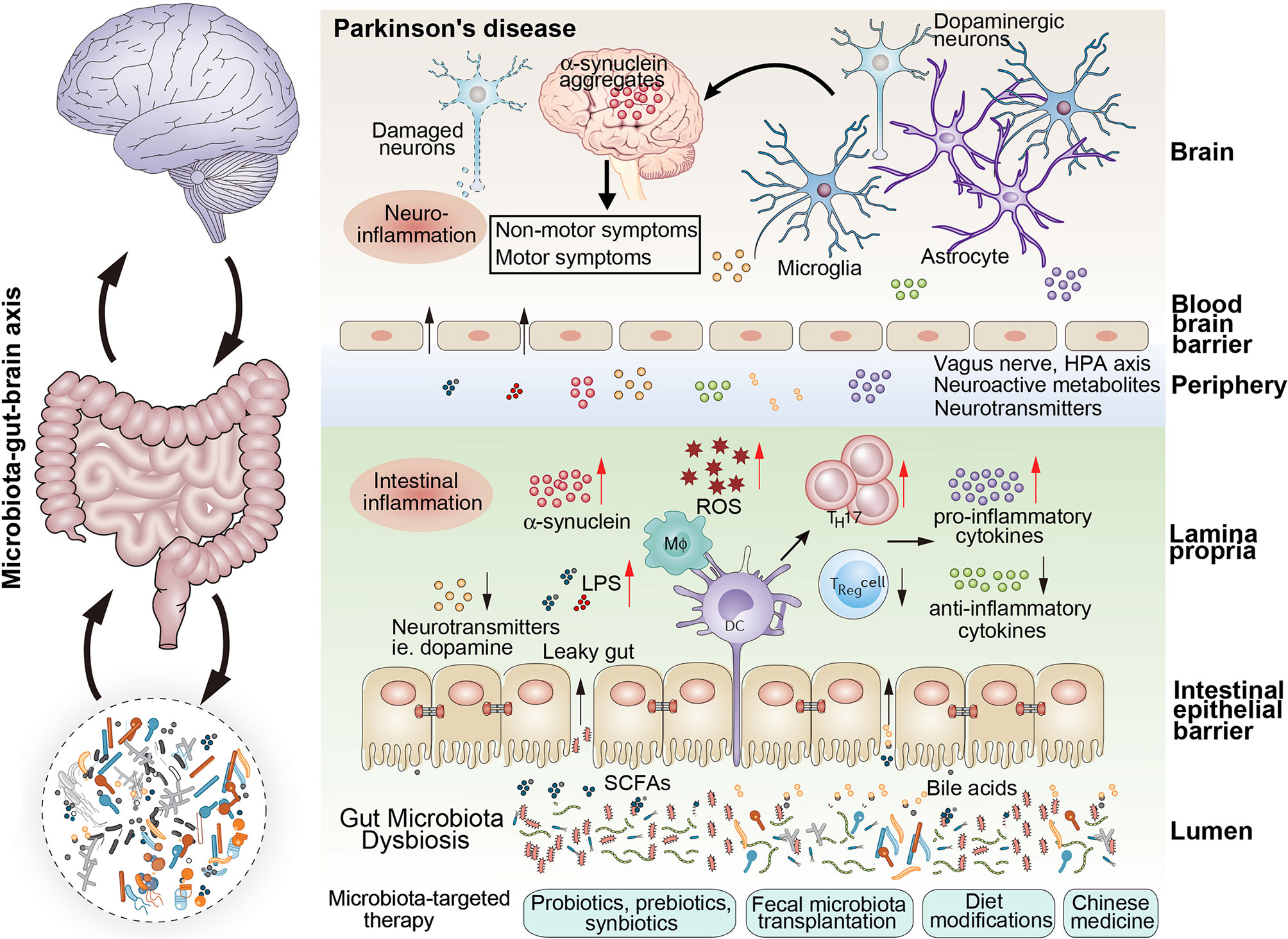
Frontiers Gut Microbiota: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Parkinson's Disease

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine

Neuroprotective effects of an engineered commensal bacterium in the 1‐methyl‐4‐phenyl‐1, 2, 3, 6‐tetrahydropyridine Parkinson disease mouse model via producing glucagon‐like peptide‐1 - Fang - 2019 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
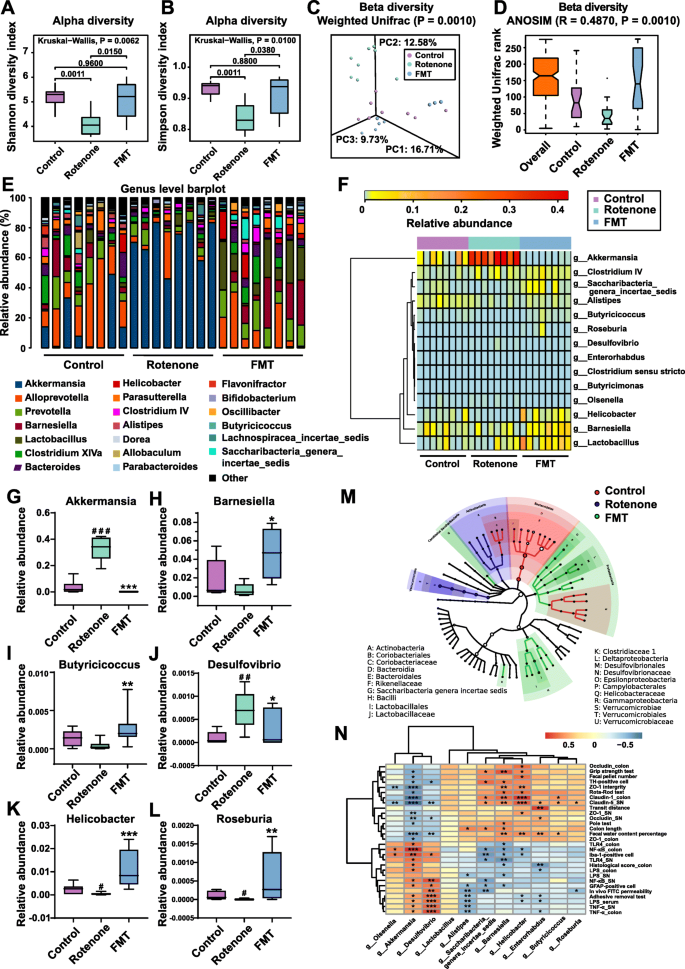
Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, Microbiome

The role of Locus Coeruleus in neuroinflammation occurring in Alzheimer's disease - ScienceDirect

PDF) Peripheral Lewy body pathology in Parkinson's disease and incidental Lewy body disease: Four cases

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect
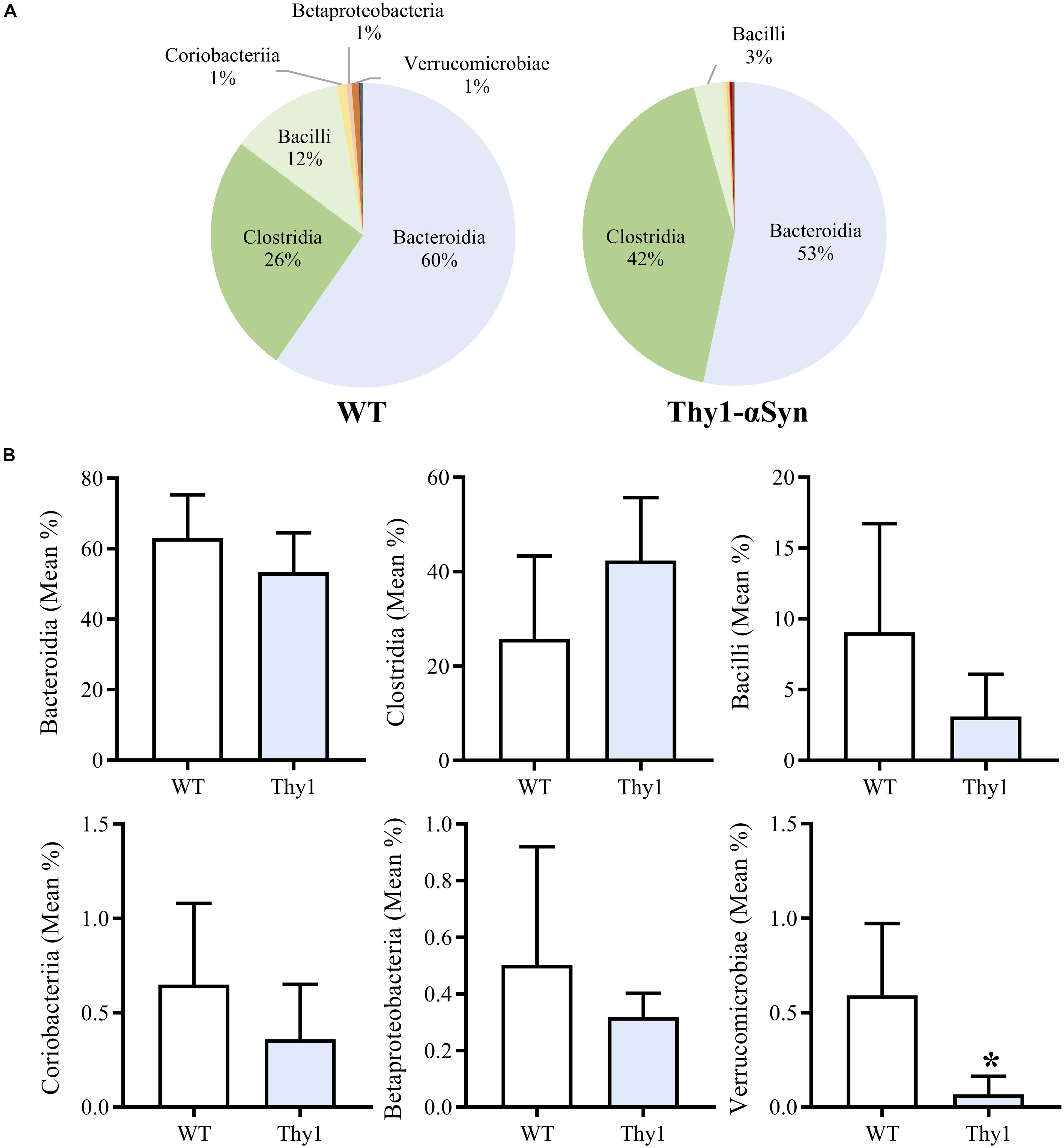
Frontiers Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model

Cell Reports, Vol 42, Issue 9, 26 September 2023
Recomendado para você
-
SOLTEIRA E GADA. Iris gta rp!, gta rp!, By DUDÀ GAMES06 fevereiro 2025
-
 duda games gta rp06 fevereiro 2025
duda games gta rp06 fevereiro 2025 -
 BK REAGIND0 A TRETA DA DUDA GAMES E GABI06 fevereiro 2025
BK REAGIND0 A TRETA DA DUDA GAMES E GABI06 fevereiro 2025 -
 COLOMBIA NA FUGA DE MOTO X DUDA UMA DAS MELHORES GTM / GTAV RP / CIDADE ALTA06 fevereiro 2025
COLOMBIA NA FUGA DE MOTO X DUDA UMA DAS MELHORES GTM / GTAV RP / CIDADE ALTA06 fevereiro 2025 -
beijo da duda games|Pesquisa do TikTok06 fevereiro 2025
-
VOU CRIAR UMA FAC? IRIS, GTA RP!, By DUDÀ GAMES06 fevereiro 2025
-
 PODEROSO BAGUAL PEGANDO DUDA GAMES NA RESENHA DO LUQUET4 POS CAMPEONATO DENDELES06 fevereiro 2025
PODEROSO BAGUAL PEGANDO DUDA GAMES NA RESENHA DO LUQUET4 POS CAMPEONATO DENDELES06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Bye bye xQc : r/h3h3productions06 fevereiro 2025
Bye bye xQc : r/h3h3productions06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Las rebajas de primavera de PlayStation en juegos físicos ya están aquí06 fevereiro 2025
Las rebajas de primavera de PlayStation en juegos físicos ya están aquí06 fevereiro 2025 -
Pack Cp Discord06 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 CONSTRUINDO a SKIN do GELEIA - #minecraft #geleia #geleiaplays #shorts06 fevereiro 2025
CONSTRUINDO a SKIN do GELEIA - #minecraft #geleia #geleiaplays #shorts06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Another Day in Paradise Lyric Song Art Print06 fevereiro 2025
Another Day in Paradise Lyric Song Art Print06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Veja onde assistir jogos de Tênis (12 a 18/6/2023)06 fevereiro 2025
Veja onde assistir jogos de Tênis (12 a 18/6/2023)06 fevereiro 2025 -
 G1 - Invasão de ratos gigantes assusta moradores na Flórida - notícias em Planeta Bizarro06 fevereiro 2025
G1 - Invasão de ratos gigantes assusta moradores na Flórida - notícias em Planeta Bizarro06 fevereiro 2025 -
 What Mario Casas Films and TV are on Netflix in America06 fevereiro 2025
What Mario Casas Films and TV are on Netflix in America06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Pelúcia Pikachu Squishmallow 25 Cm Super Fofo Macio Pokemon - SUNNY - Pelúcia - Magazine Luiza06 fevereiro 2025
Pelúcia Pikachu Squishmallow 25 Cm Super Fofo Macio Pokemon - SUNNY - Pelúcia - Magazine Luiza06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Qual é a origem dos piercings?06 fevereiro 2025
Qual é a origem dos piercings?06 fevereiro 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/D/8/o3NkmESgeO7Vwt30hrOg/2014-09-26-the-crew-diferencas-xbox-one-360.jpg) The Crew: versão para Xbox 360 terá número limitado de jogadores06 fevereiro 2025
The Crew: versão para Xbox 360 terá número limitado de jogadores06 fevereiro 2025 -
 PR Bucchigiri Taiga Kougaga Taiga Kougami06 fevereiro 2025
PR Bucchigiri Taiga Kougaga Taiga Kougami06 fevereiro 2025 -
 Hitmonchan & Hitmonlee Pokemon, Pokemon movies, Pokemon facts06 fevereiro 2025
Hitmonchan & Hitmonlee Pokemon, Pokemon movies, Pokemon facts06 fevereiro 2025


