Relative Selectivity of Covalent Inhibitors Requires Assessment of Inactivation Kinetics and Cellular Occupancy: A Case Study of Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 março 2025


Ibrutinib Inhibits Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 Outside-In Signaling and Thrombus Stability But Not Adhesion to Collagen
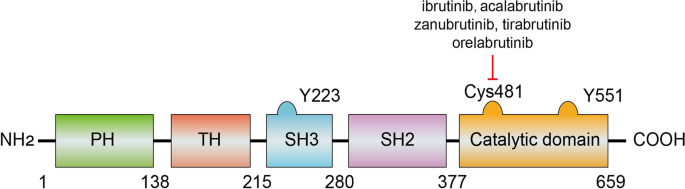
BTK inhibitors in the treatment of hematological malignancies and inflammatory diseases: mechanisms and clinical studies, Journal of Hematology & Oncology
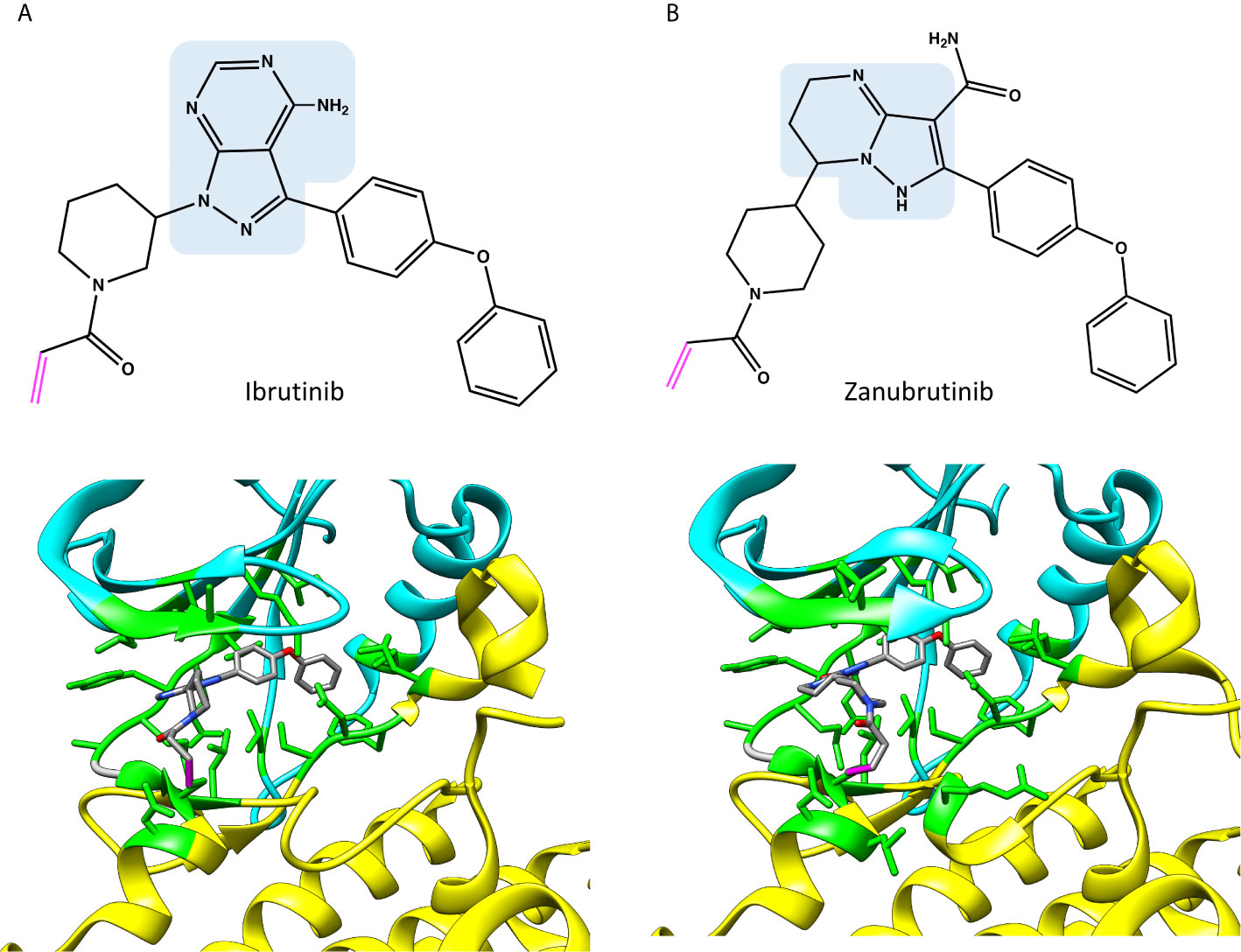
Frontiers Structure-Function Relationships of Covalent and Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitors

Selective Inhibition of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase by a Designed Covalent Ligand Leads to Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Blood Cancers Relative to Clinically Used Inhibitors
Structure of BTK kinase domain with the second-generation inhibitors acalabrutinib and tirabrutinib
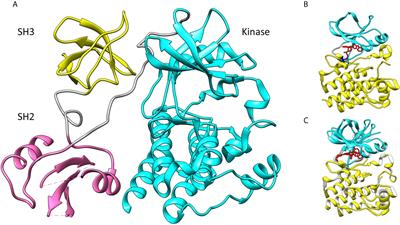
Frontiers Structure-Function Relationships of Covalent and Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitors

Kinetic mechanisms of covalent inhibition - ScienceDirect
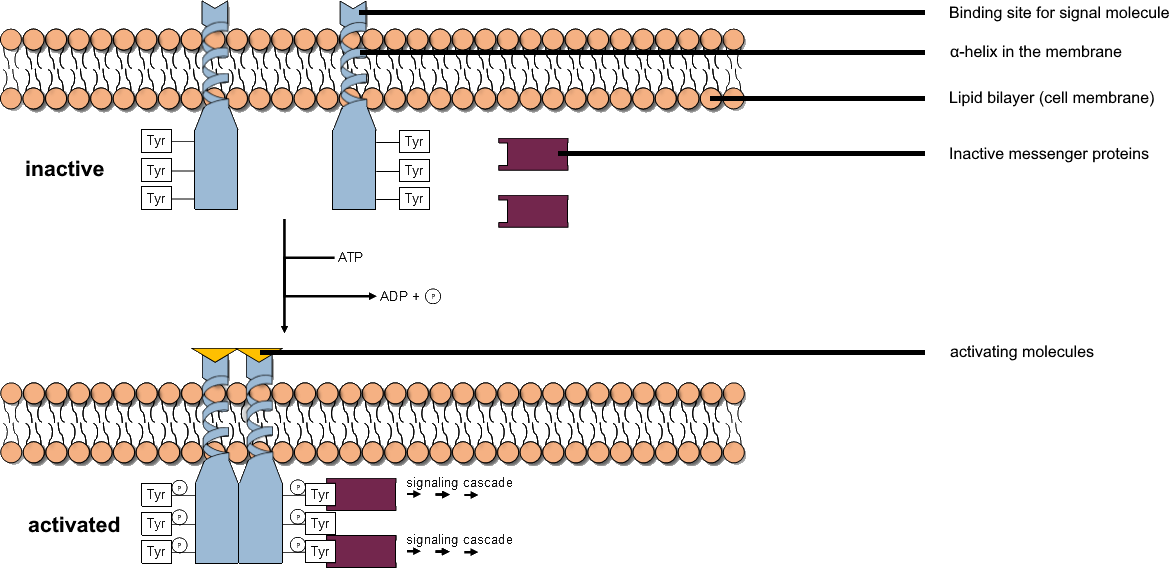
Tyrosine Kinase: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews

PDF] Relative Selectivity of Covalent Inhibitors Requires Assessment of Inactivation Kinetics and Cellular Occupancy: A Case Study of Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib

31st Annual Meeting and Associated Programs of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC 2016): part two

Toward Atomistic Modeling of Irreversible Covalent Inhibitor Binding Kinetics
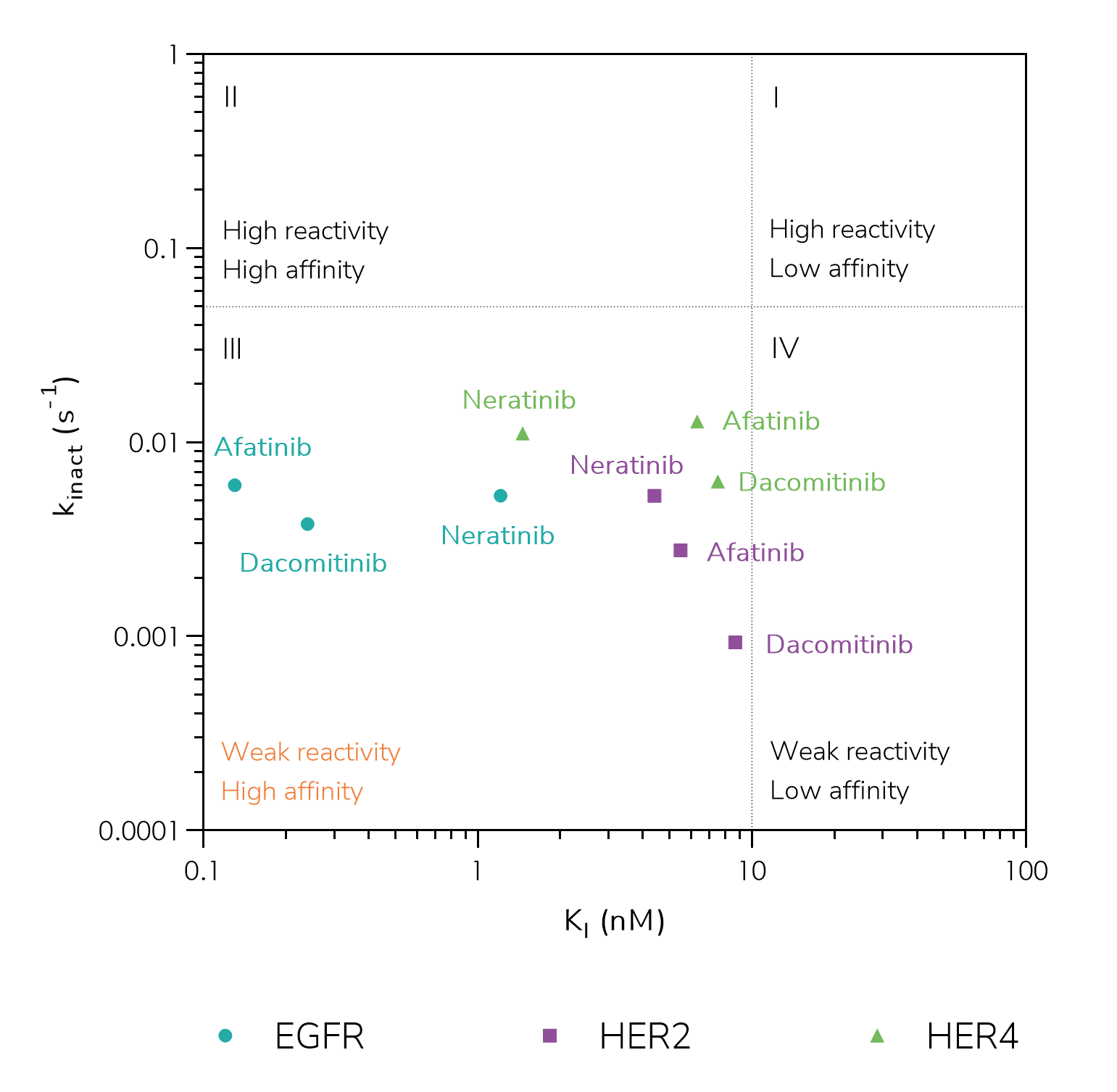
Case Study - COVALfinder to Study Irreversible EGFR Drugs
Recomendado para você
-
 how to do level 372 on brain test|TikTok Search31 março 2025
how to do level 372 on brain test|TikTok Search31 março 2025 -
 Forty - psychology31 março 2025
Forty - psychology31 março 2025 -
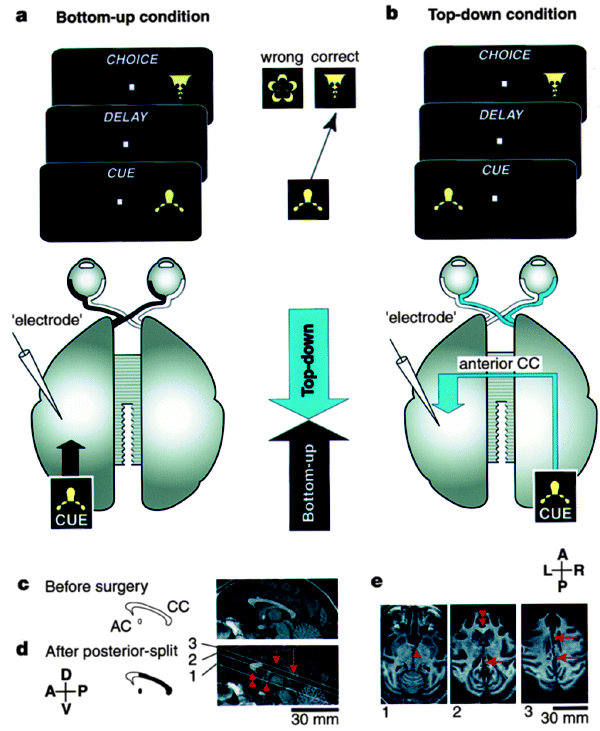 Top-down signal from prefrontal cortex in executive control of memory retrieval31 março 2025
Top-down signal from prefrontal cortex in executive control of memory retrieval31 março 2025 -
 Cube Meet APK for Android Download31 março 2025
Cube Meet APK for Android Download31 março 2025 -
Erase Puzzle for Android - Download the APK from Uptodown31 março 2025
-
Imaging Surrogates of Disease Activity in Neuromyelitis Optica Allow Distinction from Multiple Sclerosis31 março 2025
-
 BEACH. SODA. PUB. FINALLY. : r/CatsAndSoup31 março 2025
BEACH. SODA. PUB. FINALLY. : r/CatsAndSoup31 março 2025 -
 Ischemic Optic Neuropathies31 março 2025
Ischemic Optic Neuropathies31 março 2025 -
 Blood Cancer - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment - Rela Hospital31 março 2025
Blood Cancer - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment - Rela Hospital31 março 2025 -
 IPMI Blog31 março 2025
IPMI Blog31 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 TV Show The Owl House HD Wallpaper by Andy Garner31 março 2025
TV Show The Owl House HD Wallpaper by Andy Garner31 março 2025 -
 Kirby's Adventure ᴴᴰ 100% NO DAMAGE Full Playthrough31 março 2025
Kirby's Adventure ᴴᴰ 100% NO DAMAGE Full Playthrough31 março 2025 -
 How To Redeem Google Play Gift Cards - Nosh31 março 2025
How To Redeem Google Play Gift Cards - Nosh31 março 2025 -
 Wemo Smart Video Doorbell Camera31 março 2025
Wemo Smart Video Doorbell Camera31 março 2025 -
 Pokémon Sword & Shield - Confirmados todos os Pokémon Lendários das expansões The Isle of Armor e The Crown Tundra31 março 2025
Pokémon Sword & Shield - Confirmados todos os Pokémon Lendários das expansões The Isle of Armor e The Crown Tundra31 março 2025 -
Dragon Ball Super e GT crossover. - encontro entre as Dimensões. - Wattpad31 março 2025
-
 News Dragon Ball GT Anime Comic in Saikyō Jump Reaches End31 março 2025
News Dragon Ball GT Anime Comic in Saikyō Jump Reaches End31 março 2025 -
Clickteam France (@ClickteamFrance) / X31 março 2025
-
 ChessBase 17 - Tipps und Tricks' von 'Walter Saumweber' - Buch - '978-3-8328-0605-731 março 2025
ChessBase 17 - Tipps und Tricks' von 'Walter Saumweber' - Buch - '978-3-8328-0605-731 março 2025 -
 🔥 Fantasy Bishoujo Juniku Ojisan to MBTI Personality Type - Anime & Manga31 março 2025
🔥 Fantasy Bishoujo Juniku Ojisan to MBTI Personality Type - Anime & Manga31 março 2025