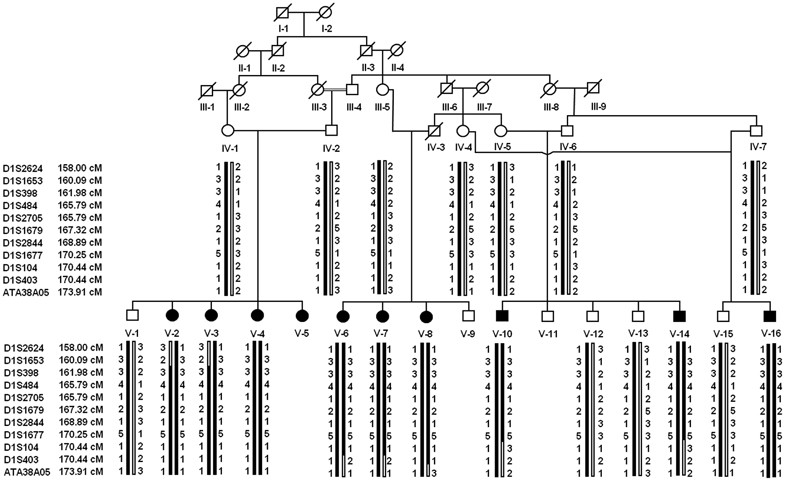
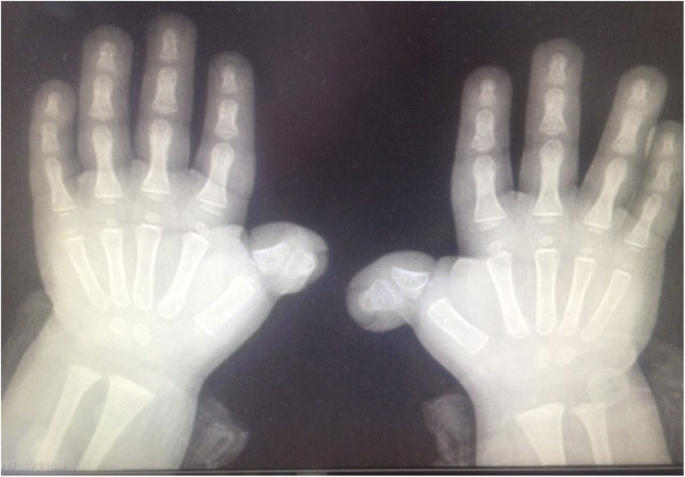
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 março 2025
Mutation in PVRL4 gene encoding nectin-4 underlies ectodermal-dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome (EDSS1)
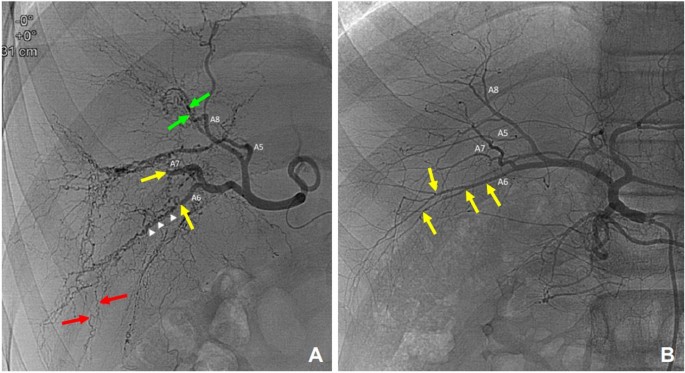
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly

Protein-protein interaction network describes the possible interaction

Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Disease: Revisited: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association

PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly

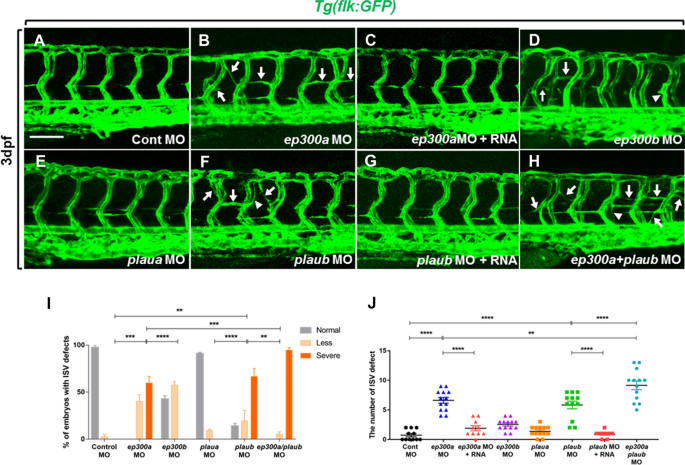
Zebrafish ep300 knockdown models Rubinstein Taybi Syndrome-2. (a-d)

Variant Analysis in Floating-Harbor Syndrome Probands
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: a case report, BMC Medical Genetics

New insights into genetic variant spectrum and genotype–phenotype correlations of Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome in 39 CREBBP‐positive patients - Pérez‐Grijalba - 2019 - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Subclass IgG levels of patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome compared

The EP300/CBP inhibitor, C646 affects normal development of zebrafish

Involvement of LRP and uPA catalytic activity in uPA-induced
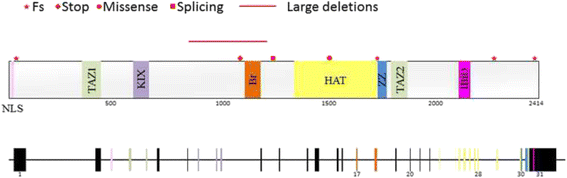
Rubinstein-Taybi 2 associated to novel EP300 mutations: deepening the clinical and genetic spectrum, BMC Medical Genetics

Otopalatodigital Syndrome, Type Ii disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials
Recomendado para você
-
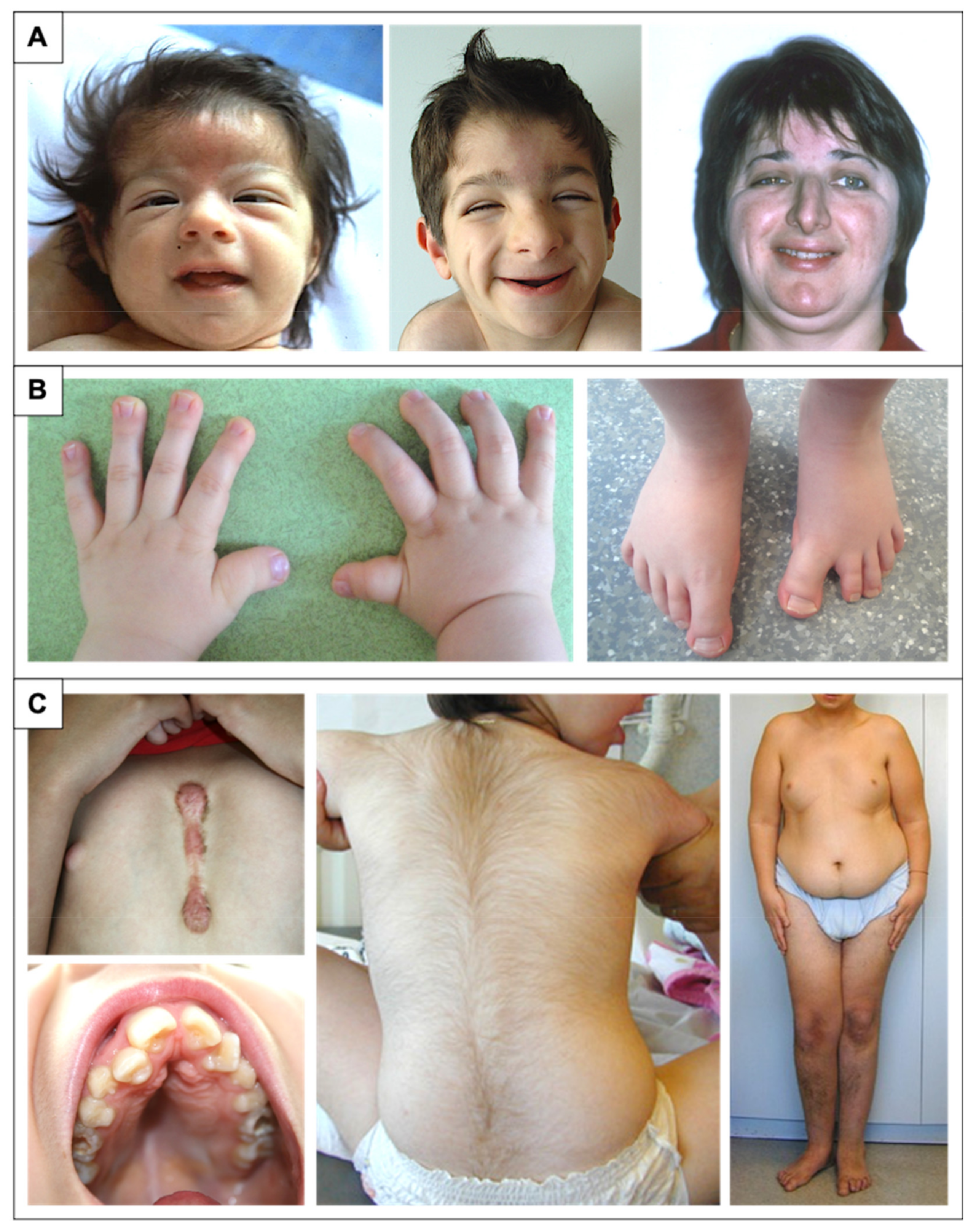 Genes, Free Full-Text31 março 2025
Genes, Free Full-Text31 março 2025 -
 Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension in a neonate with31 março 2025
Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension in a neonate with31 março 2025 -
![Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image001.jpg) Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf31 março 2025
Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf31 março 2025 -
![Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image002.jpg) Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf31 março 2025
Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf31 março 2025 -
 A novel mutation c.4003 G>C in the CREBBP gene in an adult female with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome presenting with subtle dysmorphic features - Li - 2010 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part31 março 2025
A novel mutation c.4003 G>C in the CREBBP gene in an adult female with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome presenting with subtle dysmorphic features - Li - 2010 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part31 março 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials31 março 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials31 março 2025 -
 Clinical and mutational spectrum in Korean patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: The spectrum of brain MRI abnormalities - ScienceDirect31 março 2025
Clinical and mutational spectrum in Korean patients with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: The spectrum of brain MRI abnormalities - ScienceDirect31 março 2025 -
 The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature - Awan - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library31 março 2025
The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature - Awan - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library31 março 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update31 março 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update31 março 2025 -
 (PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly31 março 2025
(PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly31 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
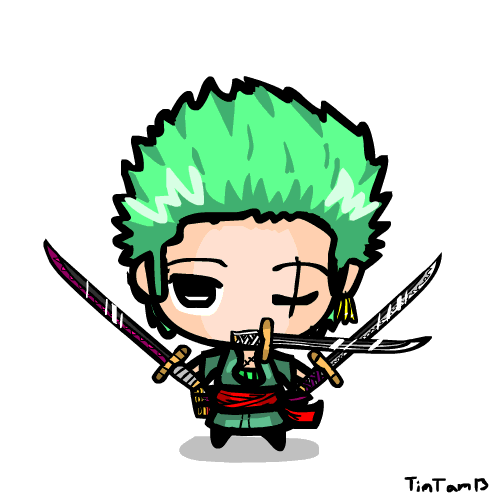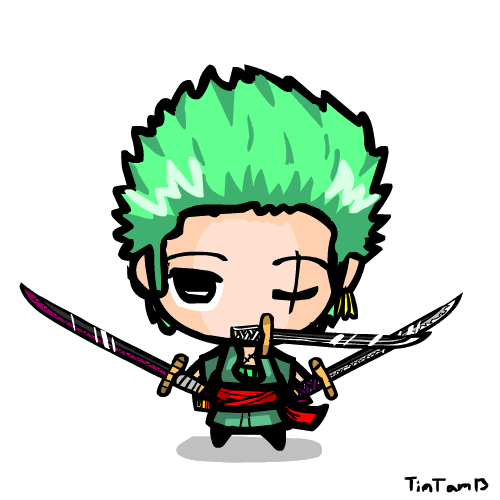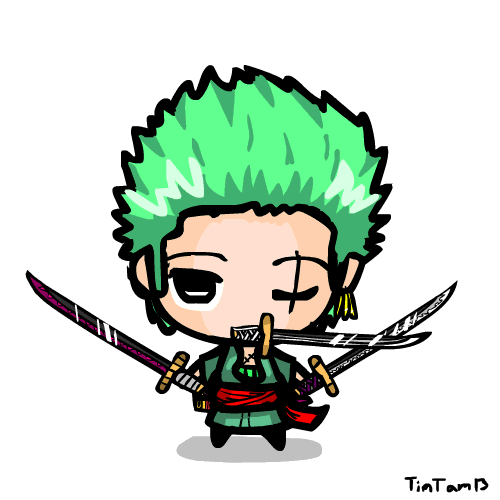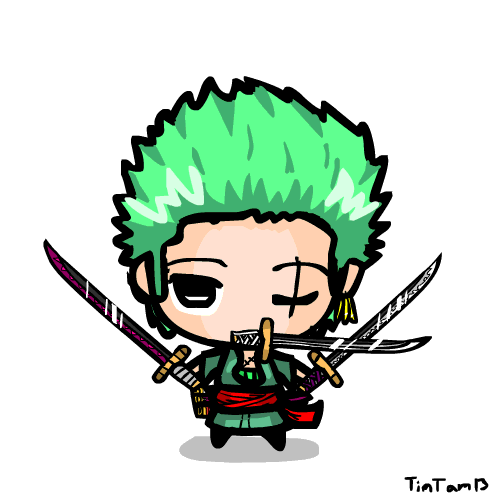 Zoro animation by TimTam13 on DeviantArt31 março 2025
Zoro animation by TimTam13 on DeviantArt31 março 2025 -
 star pets gg is a scam|TikTok Search31 março 2025
star pets gg is a scam|TikTok Search31 março 2025 -
 Instagram, Snapchat, , Facebook, Twitter, Patreon: ban31 março 2025
Instagram, Snapchat, , Facebook, Twitter, Patreon: ban31 março 2025 -
 Dia das Bruxas: 13 ideias assustadoras para decorar sua festa31 março 2025
Dia das Bruxas: 13 ideias assustadoras para decorar sua festa31 março 2025 -
 How to Make a GIF from a Video31 março 2025
How to Make a GIF from a Video31 março 2025 -
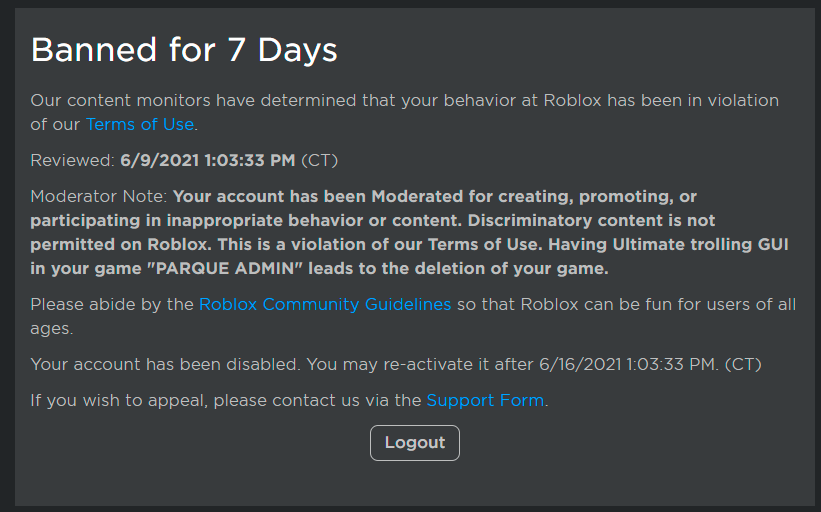 Is the UTG (Ultimate Trolling GUI) allowed to be implemented into31 março 2025
Is the UTG (Ultimate Trolling GUI) allowed to be implemented into31 março 2025 -
 28 IP Chicken Recipes31 março 2025
28 IP Chicken Recipes31 março 2025 -
:quality(75)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/elcomercio/6JV2IMLQS5ACPEMLCUDMZG3PTU.jpg) En qué canal se transmite Nacional vs Peñarol EN VIVO 4K HOY y31 março 2025
En qué canal se transmite Nacional vs Peñarol EN VIVO 4K HOY y31 março 2025 -
 How to Get Free Discord Nitro31 março 2025
How to Get Free Discord Nitro31 março 2025 -
 Caravaggio está na semifinal da Copa Santa Catarina Sub-2131 março 2025
Caravaggio está na semifinal da Copa Santa Catarina Sub-2131 março 2025