Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 21 janeiro 2025
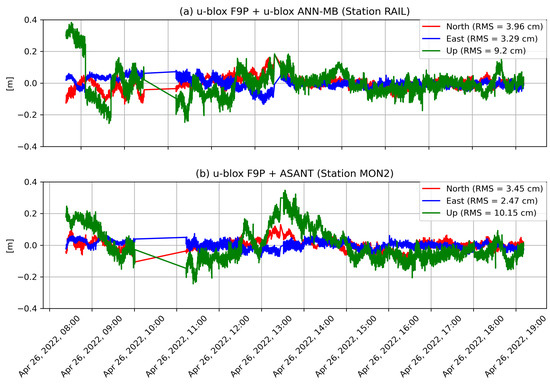
With the availability of low-cost, mass-market dual-frequency GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receivers, standalone processing methods such as Precise Point Positioning (PPP) are no longer restricted to geodetic-grade GNSS equipment only. However, with cheaper equipment, data quality is expected to degrade. This same principle also affects low-cost GNSS antennas, which usually suffer from poorer multipath mitigation and higher antenna noise compared to their geodetic-grade counterparts. This work assesses the quality of a particular piece of low-cost GNSS equipment for real-time PPP and high-rate dynamic monitoring applications, such as strong-motion seismology. We assembled the u-blox ZED-F9P chip in a small and light-weight data logger. With observational data from static experiments—which are processed under kinematic conditions—we assess the precision and stability of the displacement estimates. We tested the impact of different multi-band antenna types, including geodetic medium-grade helical-type (JAVAD GrAnt-G3T), as well as a low-cost helical (Ardusimple AS-ANT2B-CAL) and a patch-type (u-blox ANN-MB) antenna. Besides static tests for the assessment of displacement precision, strong-motion dynamic ground movements are simulated with a robot arm. For cross-validation, we collected measurements with a JAVAD SIGMA G3T geodetic-grade receiver. In terms of precision, we cross-compare the results of three different dual-frequency, real-time PPP solutions: (1) an ambiguity-float solution using the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) open-source software, (2) an ambiguity-float and an AR (ambiguity-resolved) solution using the raPPPid software from TU Vienna, and (3) and a PPP-RTK solution using the u-blox PointPerfect positioning service. We show that, even with low-cost GNSS equipment, it is possible to obtain a precision of one centimeter. We conclude that these devices provide an excellent basis for the densification of existing GNSS monitoring networks, as needed for strong-motion seismology and earthquake-early-warning.
Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Market Analysis Highlights the Impact of COVID-19 (2020-2024), Growing Adoption of UAVs to Boost the Market Growth, Technavio

PDF) PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING by Shefali Aggarwal
Textbook Of Remote Sensing And Geographical Information Systems M Anji Reddy 3e 2008 Book : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Introductory Digital Image Processing A Remote Sensing Perspective Pdf Download - Colaboratory
Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text

Resonance, Journal of Science Education

Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation Third Edition by Lillesand, Thomas M. & Kiefer, Ralph W.: Near Fine Soft Cover (1994) 3rd Edition.

International Journal of Remote Sensing: Vol 44, No 24 (Current issue)

Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text, JAXA Annual Forest Cover Maps for Vietnam during 2015–2018 Using ALOS-2/PALSAR…
13 Free GIS Software Options: Map the World in Open Source - GIS Geography
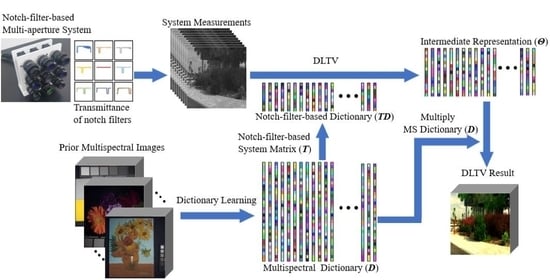
Remote Sensing Dictionary - Colaboratory
Remote Sensing Free Full Text Analysis Of Settlement Expansion And
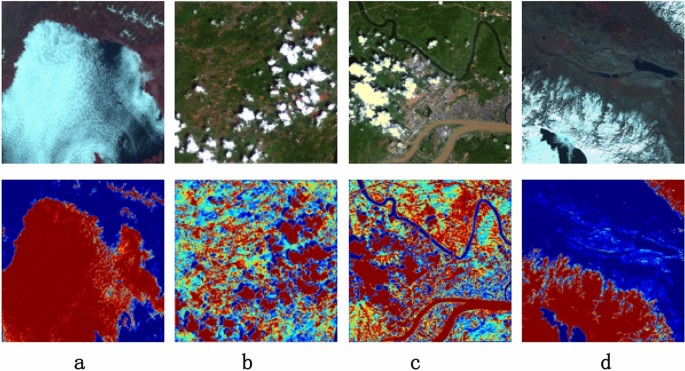
Cloud and snow detection of remote sensing images based on improved Unet3+
Remote sensing of the environment : an earth resource perspective : Jensen, John R., 1949- : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive

Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation by Lillesand, Thomas
Recomendado para você
-
 List of Roblox games - Wikipedia21 janeiro 2025
List of Roblox games - Wikipedia21 janeiro 2025 -
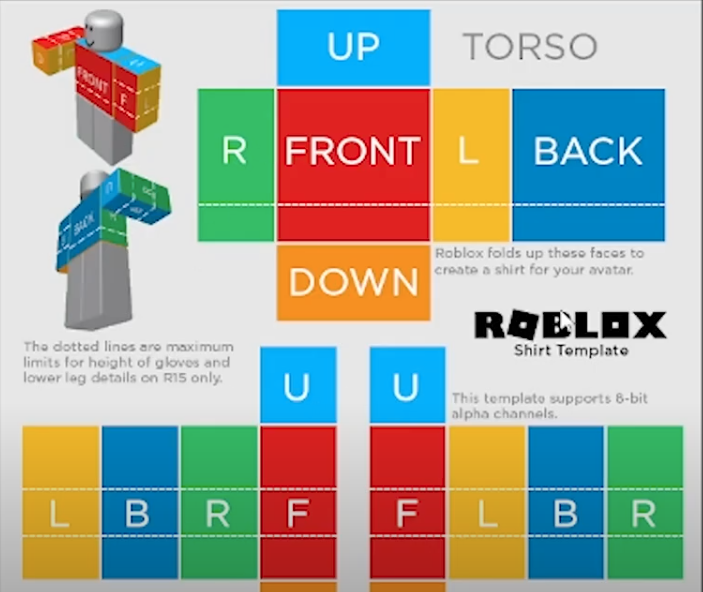 How to Make Avatar Clothing Items & Shirts in Roblox21 janeiro 2025
How to Make Avatar Clothing Items & Shirts in Roblox21 janeiro 2025 -
 All Roblox Blox Fruits Codes (December 2022)21 janeiro 2025
All Roblox Blox Fruits Codes (December 2022)21 janeiro 2025 -
 LeBron James NIKELAND Roblox LeBron 19 Chosen 1 Info21 janeiro 2025
LeBron James NIKELAND Roblox LeBron 19 Chosen 1 Info21 janeiro 2025 -
 Here's what 2 hours as a Roblox avatar in 'Walmart Land' really21 janeiro 2025
Here's what 2 hours as a Roblox avatar in 'Walmart Land' really21 janeiro 2025 -
Games Unlocks21 janeiro 2025
-
 BLOX.LAND on X: 🥊 Today is Giveaway Monday! 🥊 Every Monday, we21 janeiro 2025
BLOX.LAND on X: 🥊 Today is Giveaway Monday! 🥊 Every Monday, we21 janeiro 2025 -
 Press Releases Archives - Page 2 of 6 - DC BLOX21 janeiro 2025
Press Releases Archives - Page 2 of 6 - DC BLOX21 janeiro 2025 -
u-blox Thalwil21 janeiro 2025
-
 NIKELAND Roblox Metaverse NFT Kids' Game21 janeiro 2025
NIKELAND Roblox Metaverse NFT Kids' Game21 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Category:Characters, Toca Life Stories Wiki21 janeiro 2025
Category:Characters, Toca Life Stories Wiki21 janeiro 2025 -
 bushi swiftblade aka afro samurai hon alt avatar Afro samurai, Samurai concept, Illustration character design21 janeiro 2025
bushi swiftblade aka afro samurai hon alt avatar Afro samurai, Samurai concept, Illustration character design21 janeiro 2025 -
 Playstation Plus - Review de jogos21 janeiro 2025
Playstation Plus - Review de jogos21 janeiro 2025 -
 Stranger Things 4': Netflix anuncia cómo se repartirán los capítulos por entrega21 janeiro 2025
Stranger Things 4': Netflix anuncia cómo se repartirán los capítulos por entrega21 janeiro 2025 -
 Carro De Corrida Infantil Em Vermelho Fotografia Editorial21 janeiro 2025
Carro De Corrida Infantil Em Vermelho Fotografia Editorial21 janeiro 2025 -
 Baldur's Gate 3 best class tier list21 janeiro 2025
Baldur's Gate 3 best class tier list21 janeiro 2025 -
 5x5: Wu-Tang Clan Interview Red Bull Music Academy Daily21 janeiro 2025
5x5: Wu-Tang Clan Interview Red Bull Music Academy Daily21 janeiro 2025 -
 The Divine Comedy Vol.1: Inferno: Dante Alighieri-1977 Pb Ed Literature/Classic21 janeiro 2025
The Divine Comedy Vol.1: Inferno: Dante Alighieri-1977 Pb Ed Literature/Classic21 janeiro 2025 -
 A Premium 'Call Of Duty' Is Coming In 2023 After All, But It Isn't What You Think21 janeiro 2025
A Premium 'Call Of Duty' Is Coming In 2023 After All, But It Isn't What You Think21 janeiro 2025 -
 Naruto hatake kakashi uzumaki naruto uchiha itachi uchiha sasuke pequeno pingente boneca pingente chaveiro - AliExpress21 janeiro 2025
Naruto hatake kakashi uzumaki naruto uchiha itachi uchiha sasuke pequeno pingente boneca pingente chaveiro - AliExpress21 janeiro 2025

