Plants, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 janeiro 2025
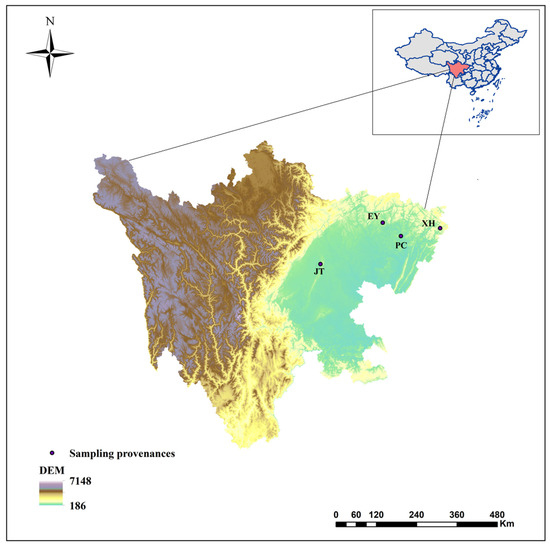
Alnus cremastogyne is a rapidly growing broad-leaved tree species that is widely distributed in southwest China. It has a significant economic and ecological value. However, with the expansion of the planting area, the influence of phenotypic variation and differentiation on Alnus cremastogyne has increased, resulting in a continuous decline in its genetic quality. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate the phenotypic variation of Alnus cremastogyne and select excellent breeding materials for genetic improvement. Herein, four growth-related phenotypic traits (diameter at breast height, the height of trees, volume, height under the branches) and twelve reproductive-related phenotypic traits (fresh weight of single cone, dry weight of single cone, seed weight per plant, thousand kernel weight, cone length, cone width, cone length × cone width, fruit shape index, seed rate, germination rate, germination potential, germination index) of 40 clones from four provenances were measured and analyzed. The phenotypic variation was comprehensively evaluated by correlation analysis, principal component analysis and cluster analysis, and excellent clones were selected as breeding materials. The results revealed that there were abundant phenotypic traits variations among and within provenances. Most of the phenotypic traits were highly significant differences (p < 0.01) among provenances. The phenotypic variation among provenances (26.36%) was greater than that of within provenances clones (24.80%). The average phenotypic differentiation coefficient was accounted for 52.61% among provenances, indicating that the phenotypic variation mainly came from among provenances. The coefficient of variation ranged from 9.41% (fruit shape index) to 97.19% (seed weight per plant), and the repeatability ranged from 0.36 (volume) to 0.77 (cone width). Correlation analysis revealed a significantly positive correlation among most phenotypic traits. In principal component analysis, the cumulative contribution rate of the first three principal components was 79.18%, representing the main information on the measured phenotypic traits. The cluster analysis revealed four groups for the 40 clones. Group I and group II exhibited better performance phenotypic traits as compared with group III and group IV. In addition, the four groups are not clearly clustered following the distance from the provenance. Employing the multi-trait comprehensive evaluation method, 12 excellent clones were selected, and the average genetic gain for each phenotypic trait ranged from 4.78% (diameter at breast height) to 32.05% (dry weight of single cone). These selected excellent clones can serve as candidate materials for the improvement and transformation of Alnus cremastogyne seed orchards. In addition, this study can also provide a theoretical foundation for the genetic improvement, breeding, and clone selection of Alnus cremastogyne.

Aquatic Plants dragonfly-farm

59 Gardening in the Classroom ideas in 2023
Encyclopedia of Plants And Flowers : Umair Mirza : Free Download

Found Things Plant Shop

Indoor Planter with Grow Light, 10 Days Watering-Free

Houseplants On The Balcony Room Full Of Plants View Through The

Sorry I Have Plants This Weekend Svg Funny Plant Svg Plant

I just wet my plants SVG, Vegan SVG

Upcoming Plant Promotion Schedule - Southern Living Plants

Potted Plants Sprouting Love Heart Flowers Black & White Clip Art

SANSI LED Grow Lights for Indoor Plants, 150W Full

Insight into the root growth, soil quality, and assembly of the
Biology, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 SCP-7147 - SCP Foundation19 janeiro 2025
SCP-7147 - SCP Foundation19 janeiro 2025 -
 SCP-7148, SCP Fanon Wiki19 janeiro 2025
SCP-7148, SCP Fanon Wiki19 janeiro 2025 -
![SCP-5812 Ghostyard Safe [SCP Document Reading]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_Y-mRve-GhM/maxresdefault.jpg) SCP-5812 Ghostyard Safe [SCP Document Reading]19 janeiro 2025
SCP-5812 Ghostyard Safe [SCP Document Reading]19 janeiro 2025 -
Terry Hasty - Vice-President - MindSpring Consulting19 janeiro 2025
-
 Physician Recruiter Resume Samples19 janeiro 2025
Physician Recruiter Resume Samples19 janeiro 2025 -
 30.59% OFF on B2S ANITECH เครื่องบดสับอเนกประสงค์ รุ่น SCP300 สีดำ19 janeiro 2025
30.59% OFF on B2S ANITECH เครื่องบดสับอเนกประสงค์ รุ่น SCP300 สีดำ19 janeiro 2025 -
 29479 Woodway Dr, Wickliffe, OH 4409219 janeiro 2025
29479 Woodway Dr, Wickliffe, OH 4409219 janeiro 2025 -
 Cool and Unusual Things to Do in Kilmartin - Atlas Obscura19 janeiro 2025
Cool and Unusual Things to Do in Kilmartin - Atlas Obscura19 janeiro 2025 -
 SCP-7148 Land of Milk and Honey Keter [SCP Document Reading19 janeiro 2025
SCP-7148 Land of Milk and Honey Keter [SCP Document Reading19 janeiro 2025 -
 The role played by alternative splicing in antigenic variability19 janeiro 2025
The role played by alternative splicing in antigenic variability19 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Offers the Ultimate and Most Premium S Series Experience Yet – Samsung Global Newsroom19 janeiro 2025
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Offers the Ultimate and Most Premium S Series Experience Yet – Samsung Global Newsroom19 janeiro 2025 -
 My Talking Tom: AMIGOS / FRIENDS (jogo gameplay) - parte 1 - Todos19 janeiro 2025
My Talking Tom: AMIGOS / FRIENDS (jogo gameplay) - parte 1 - Todos19 janeiro 2025 -
 Calça Feminina Legging Academia Cintura Alta Moda Fitness FIT127 - The Start19 janeiro 2025
Calça Feminina Legging Academia Cintura Alta Moda Fitness FIT127 - The Start19 janeiro 2025 -
Fatal Attraction Season 2 Release Date Rumors: When Is It Coming Out?19 janeiro 2025
-
 Super Mario Odyssey Review – Is it worth playing now?19 janeiro 2025
Super Mario Odyssey Review – Is it worth playing now?19 janeiro 2025 -
 Fantasia Feminina Boneca Barbie Fitness Halloween Carnaval19 janeiro 2025
Fantasia Feminina Boneca Barbie Fitness Halloween Carnaval19 janeiro 2025 -
 Crunchyroll Announces Streaming of Recovery of an MMO Junkie19 janeiro 2025
Crunchyroll Announces Streaming of Recovery of an MMO Junkie19 janeiro 2025 -
![Tibia [where to hunt ED/MS] - MY TOP 5 PLACES FOR MAGES 150+ [Vol. 2 ][2020]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/G_lJZ-dTJyo/maxresdefault.jpg) Tibia [where to hunt ED/MS] - MY TOP 5 PLACES FOR MAGES 150+ [Vol. 2 ][2020]19 janeiro 2025
Tibia [where to hunt ED/MS] - MY TOP 5 PLACES FOR MAGES 150+ [Vol. 2 ][2020]19 janeiro 2025 -
 Eric Clapton: Tears in Heaven (Music Video 1991) - IMDb19 janeiro 2025
Eric Clapton: Tears in Heaven (Music Video 1991) - IMDb19 janeiro 2025 -
 🔥 Fino señores 👨💼 : MAAU19 janeiro 2025
🔥 Fino señores 👨💼 : MAAU19 janeiro 2025

