GMD - A modern-day Mars climate in the Met Office Unified Model: dry simulations
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 fevereiro 2025
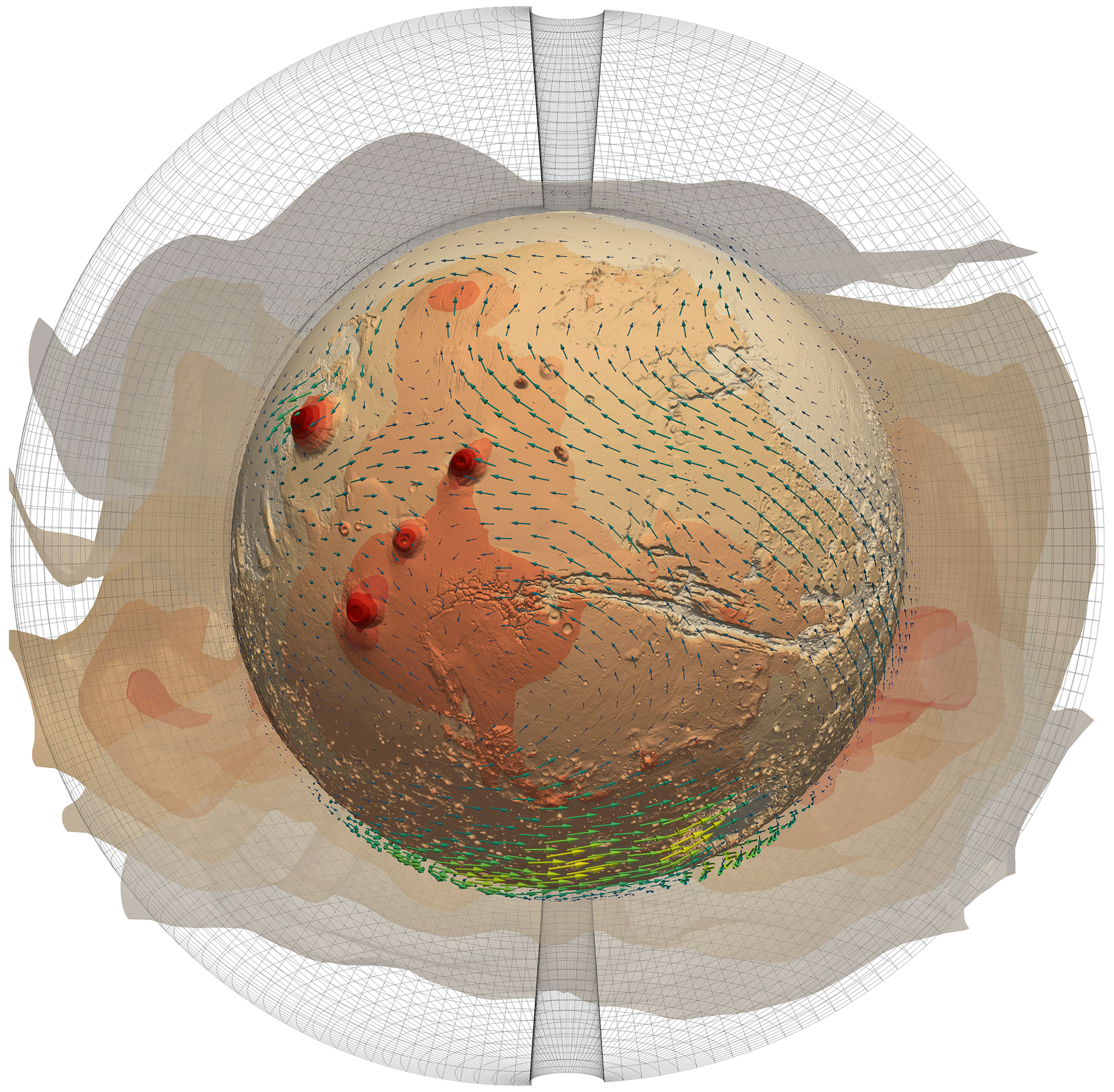
Abstract. We present results from the Met Office Unified Model (UM), a world-leading climate and weather model, adapted to simulate a dry Martian climate. We detail the adaptation of the basic parameterisations and analyse results from two simulations, one with radiatively active mineral dust and one with radiatively inactive dust. These simulations demonstrate how the radiative effects of dust act to accelerate the winds and create a mid-altitude isothermal layer during the dusty season. We validate our model through comparison with an established Mars model, the Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique planetary climate model (PCM), finding good agreement in the seasonal wind and temperature profiles but with discrepancies in the predicted dust mass mixing ratio and conditions at the poles. This study validates the use of the UM for a Martian atmosphere, highlights how the adaptation of an Earth general circulation model (GCM) can be beneficial for existing Mars GCMs and provides insight into the next steps in our development of a new Mars climate model.

GMD - A modern-day Mars climate in the Met Office Unified Model: dry simulations

Sketch of the Michigan Mars Environmental Chamber (MMEC). It can

Observational Evidence for an Active Surface Reservoir of Solid Carbon Dioxide on Mars
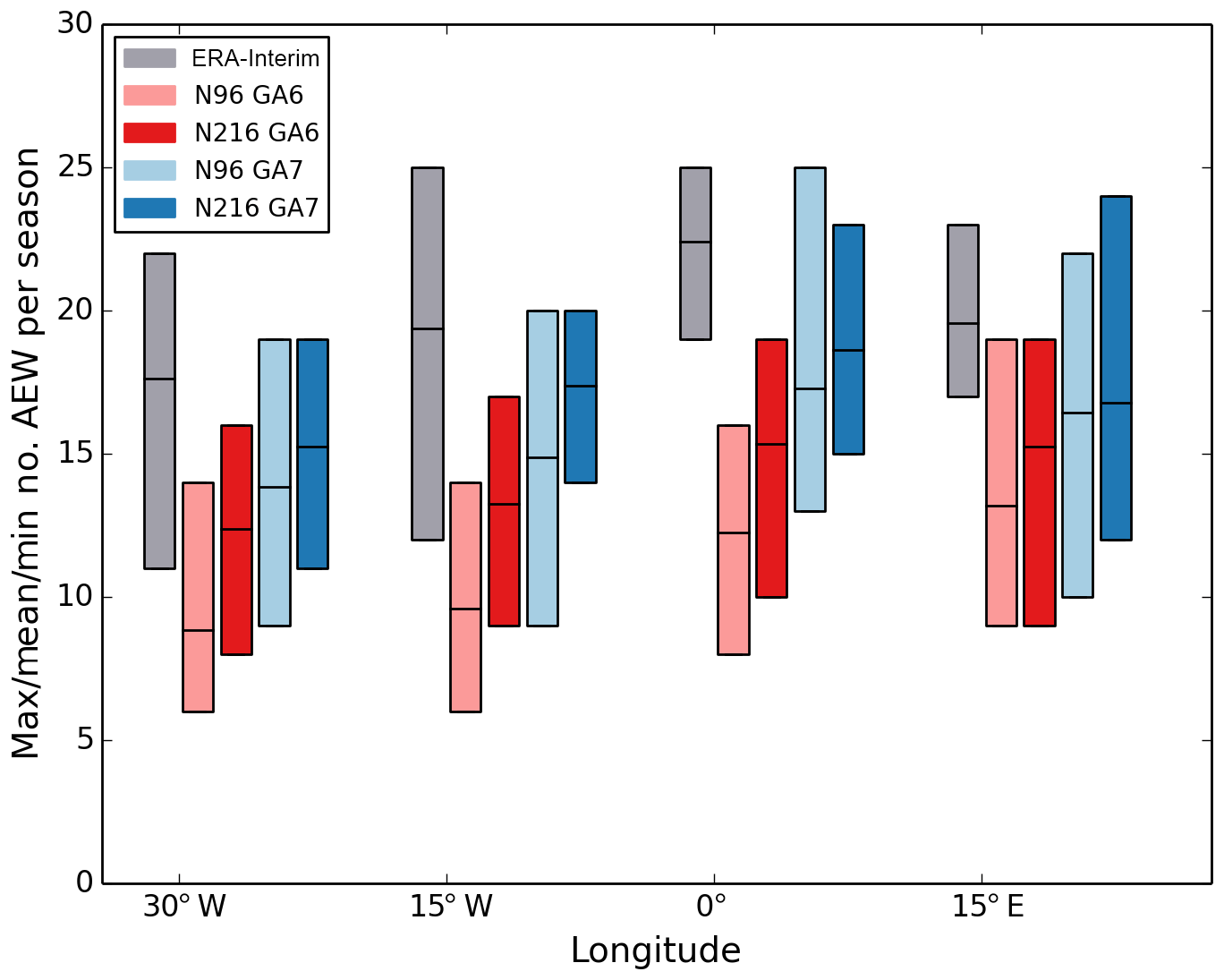
GMD - The Met Office Unified Model Global Atmosphere 7.0/7.1 and JULES Global Land 7.0 configurations

Zonal average temperature (K), produced from dayside retrievals of Mars
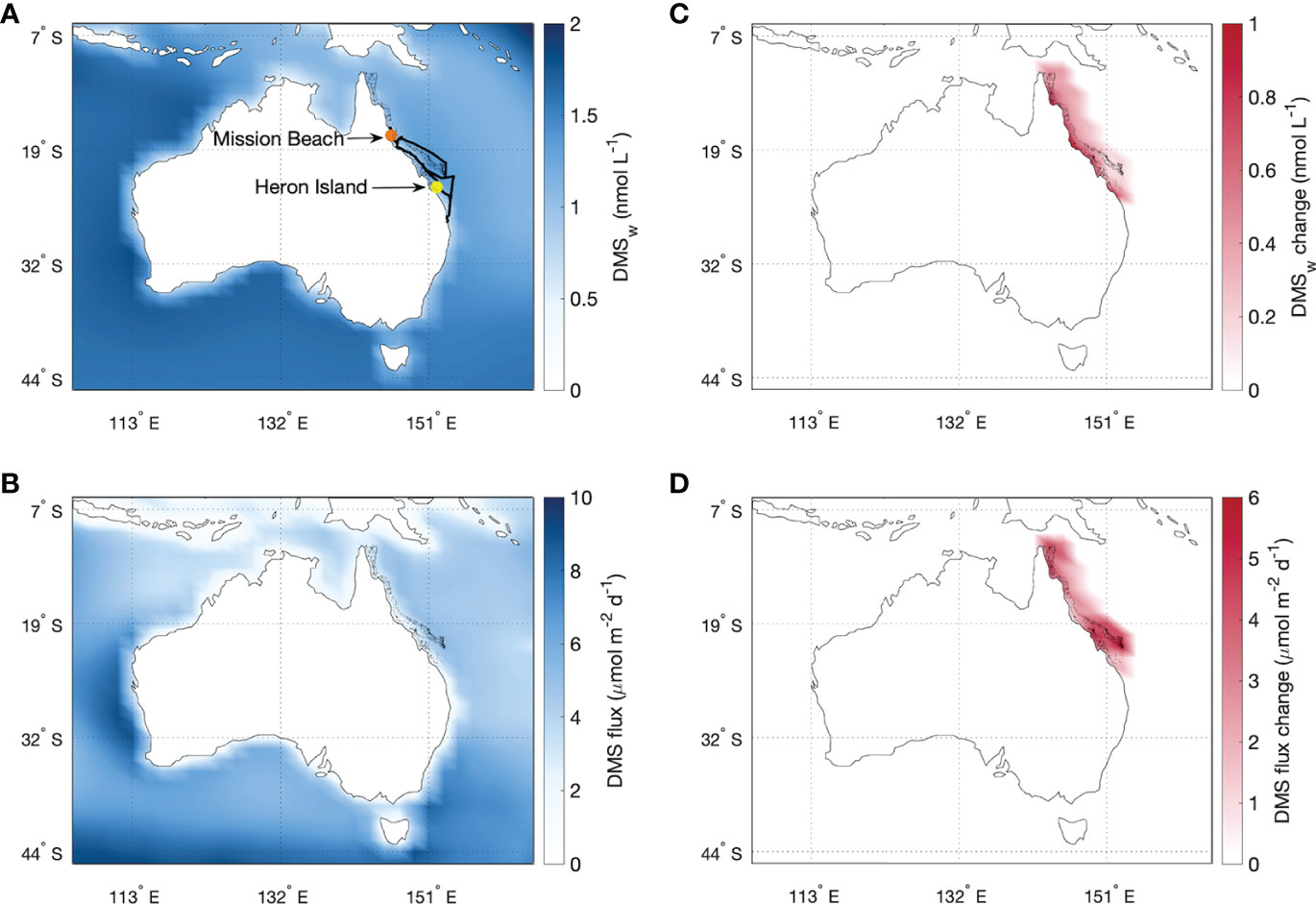
Frontiers Modelling the influence of coral-reef-derived dimethylsulfide on the atmosphere of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia
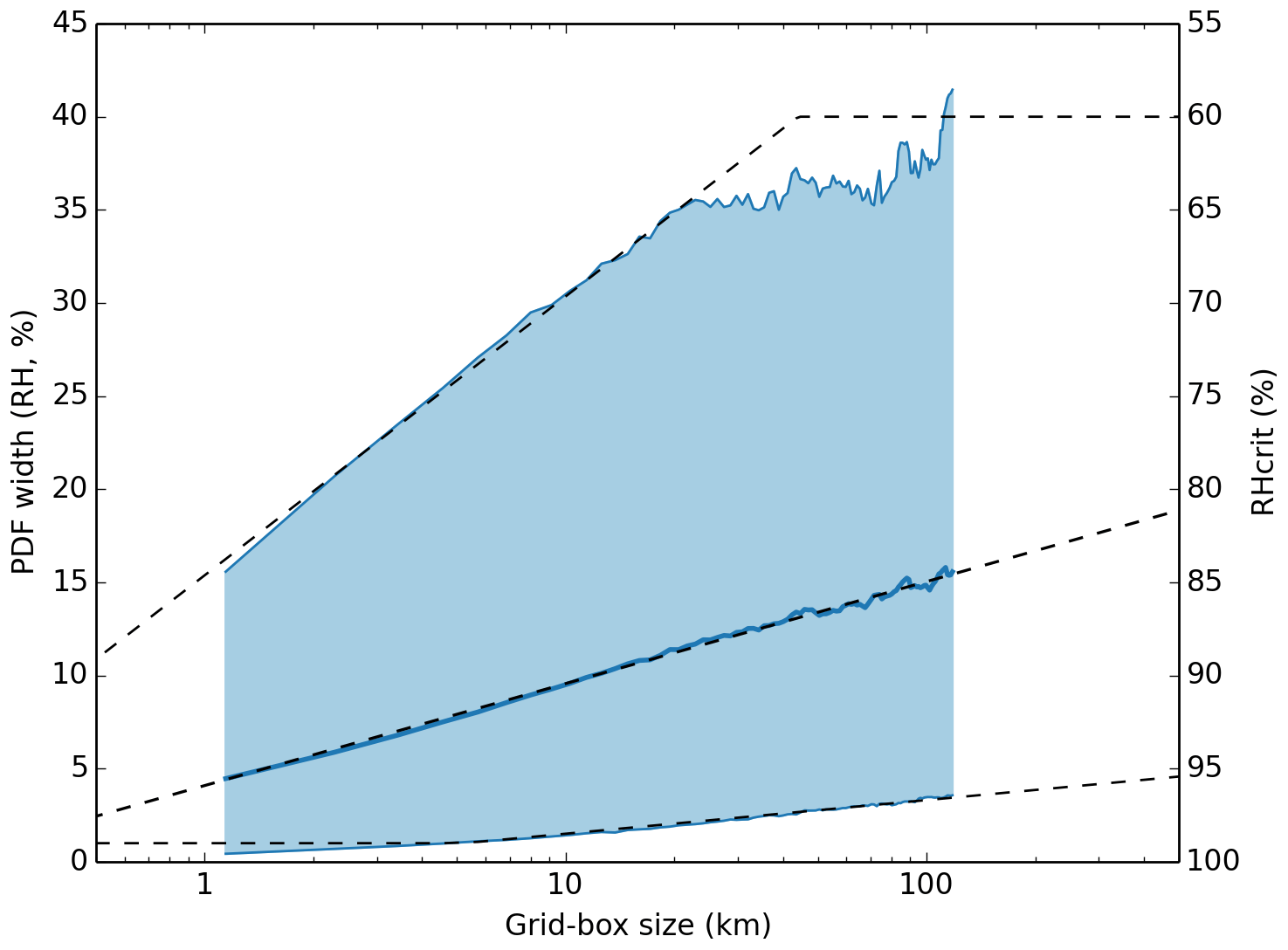
GMD - The Met Office Unified Model Global Atmosphere 7.0/7.1 and JULES Global Land 7.0 configurations
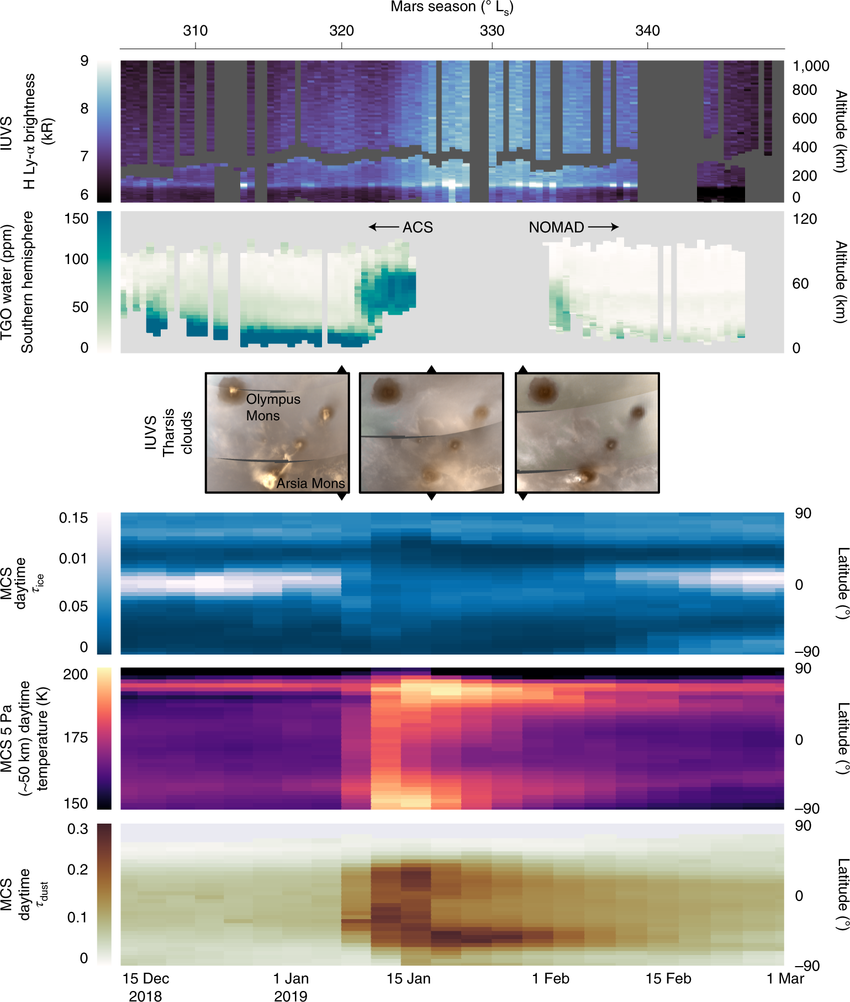
Atmospheric response to the Mars Year 34 C regional dust event From

GMD - A modern-day Mars climate in the Met Office Unified Model: dry simulations

a) Climatological background (black dashed line) and MarsWRF simulated

Explicit Prediction of Continental Convection in a Skillful Variable‐Resolution Global Model - Harris - 2019 - Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems - Wiley Online Library
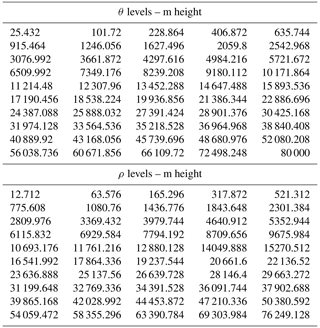
GMD - A modern-day Mars climate in the Met Office Unified Model: dry simulations

Unstructured grid dynamical modeling of planetary atmospheres using planetMPAS: The influence of the rigid lid, computational efficiency, and examples of Martian and Jovian application - ScienceDirect
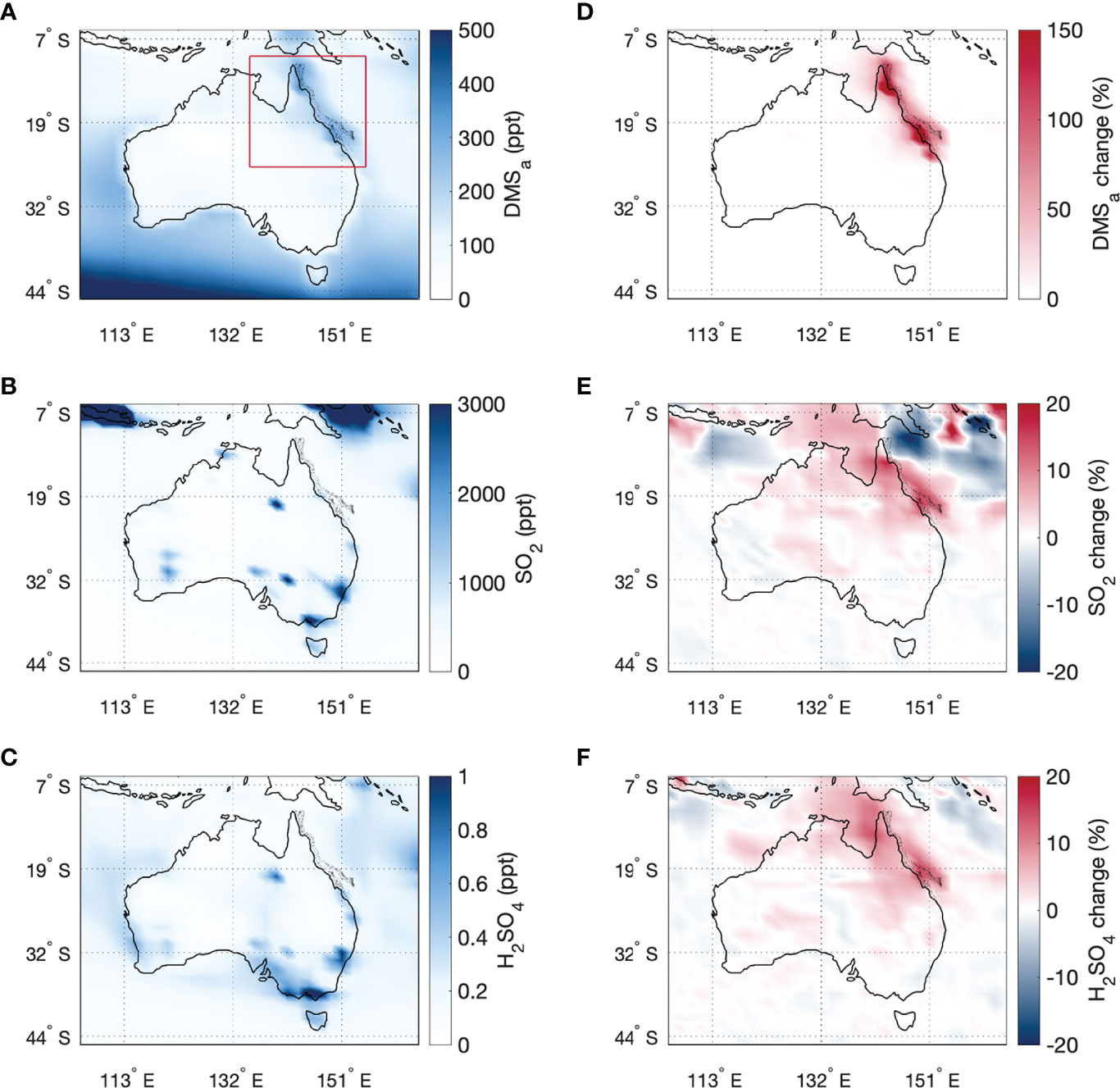
Frontiers Modelling the influence of coral-reef-derived dimethylsulfide on the atmosphere of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia
Recomendado para você
-
 The rise and rise of .io games19 fevereiro 2025
The rise and rise of .io games19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Arras.io, Diep.io Wiki19 fevereiro 2025
Arras.io, Diep.io Wiki19 fevereiro 2025 -
 ARRAS.IO TEST POWERFUL BOSSES - SERVER REVIEW #219 fevereiro 2025
ARRAS.IO TEST POWERFUL BOSSES - SERVER REVIEW #219 fevereiro 2025 -
 arras io moments (by me) : r/Arrasio19 fevereiro 2025
arras io moments (by me) : r/Arrasio19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Arras.io Organ Tier List (Which organ does each tank best resemble?) : r/Arrasio19 fevereiro 2025
Arras.io Organ Tier List (Which organ does each tank best resemble?) : r/Arrasio19 fevereiro 2025 -
Arras:Polygons (Woomy), Diep.io Wiki19 fevereiro 2025
-
 Litt Connector Mechanical Installation Jig19 fevereiro 2025
Litt Connector Mechanical Installation Jig19 fevereiro 2025 -
Battle of Arras (1917) - Wikipedia19 fevereiro 2025
-
 80% Unsouled on19 fevereiro 2025
80% Unsouled on19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Map of the Åland Islands showing the local populations of the Glanville19 fevereiro 2025
Map of the Åland Islands showing the local populations of the Glanville19 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Dragon Ball Z Kakarot Sagas Are the Saiyan, Frieza, Android, Cell, and Buu Sagas in the game? - GameRevolution19 fevereiro 2025
Dragon Ball Z Kakarot Sagas Are the Saiyan, Frieza, Android, Cell, and Buu Sagas in the game? - GameRevolution19 fevereiro 2025 -
![The Legend of Vox Machina (Season 2) Episodes 1-3 [Review] — The Geekly Grind](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/6371c1aaf44e9e0252208a01/1674344343562-BLK74XK57O1AQ4VZ4IPQ/LOVM+2-1.jpg) The Legend of Vox Machina (Season 2) Episodes 1-3 [Review] — The Geekly Grind19 fevereiro 2025
The Legend of Vox Machina (Season 2) Episodes 1-3 [Review] — The Geekly Grind19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Epic Sans + EpicEpic Sans sprite by EpicMkMetaKnight on DeviantArt19 fevereiro 2025
Epic Sans + EpicEpic Sans sprite by EpicMkMetaKnight on DeviantArt19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Superman: Henry Cavill Back for More Movies After Black Adam – The Hollywood Reporter19 fevereiro 2025
Superman: Henry Cavill Back for More Movies After Black Adam – The Hollywood Reporter19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Elden Ring: come battere Malenia19 fevereiro 2025
Elden Ring: come battere Malenia19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Mortal Kombat: Deadly Alliance — StrategyWiki19 fevereiro 2025
Mortal Kombat: Deadly Alliance — StrategyWiki19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Fairy Tail 100 Years Quest Manga Volume 1019 fevereiro 2025
Fairy Tail 100 Years Quest Manga Volume 1019 fevereiro 2025 -
 MCPE But If You Touch Grass You Die19 fevereiro 2025
MCPE But If You Touch Grass You Die19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Sogipa: Doze Décadas De História - Carlos Hofmeister Filho - Traça Livraria e Sebo19 fevereiro 2025
Sogipa: Doze Décadas De História - Carlos Hofmeister Filho - Traça Livraria e Sebo19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Stranger Things Season 4 Soundtrack Exclusive Alternate19 fevereiro 2025
Stranger Things Season 4 Soundtrack Exclusive Alternate19 fevereiro 2025