Binding Force and Site-Determined Desorption and Fragmentation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Metallic Nanomaterials
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 março 2025

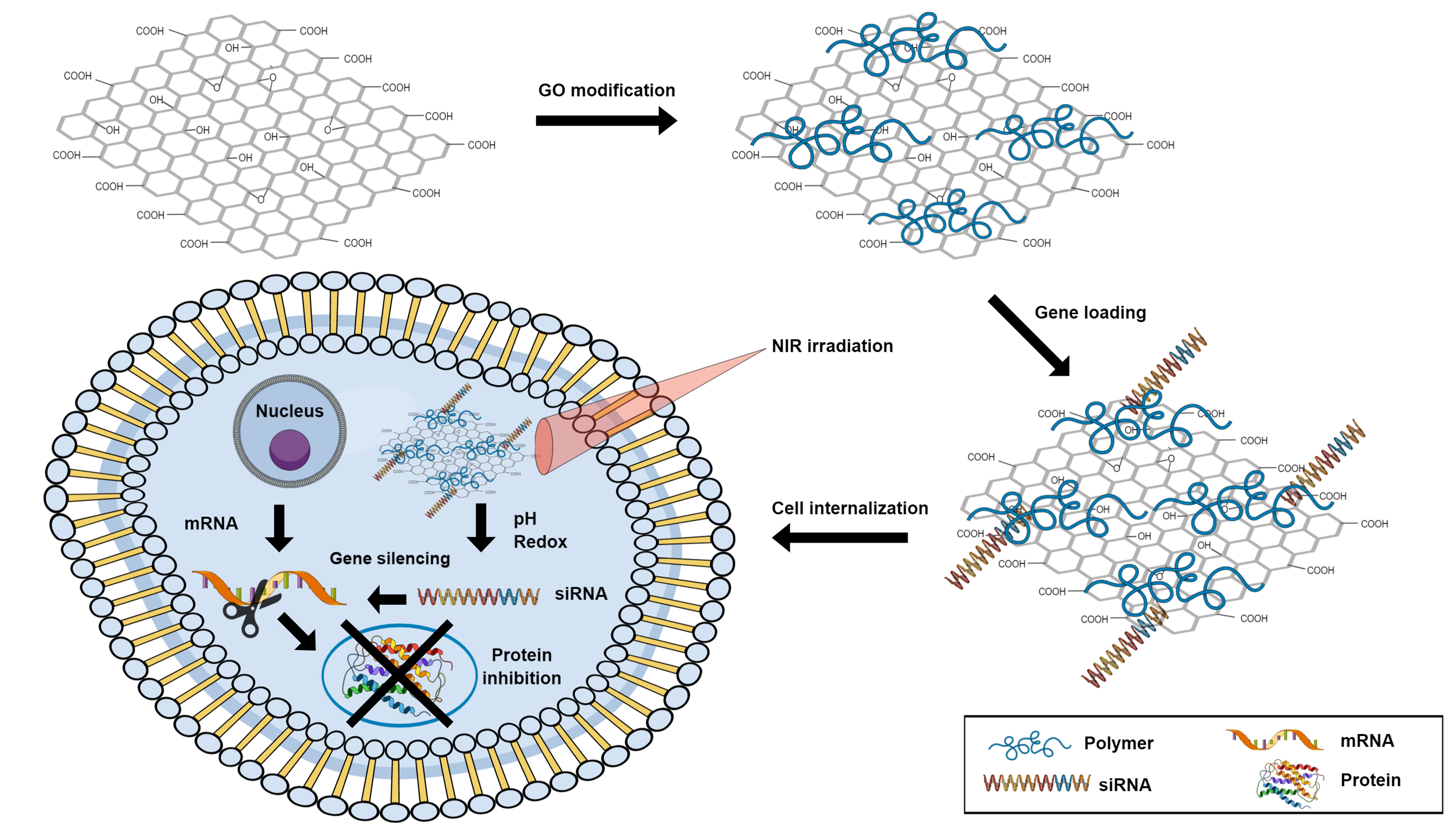
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Single cobalt atoms anchored on Ti3C2Tx with dual reaction sites
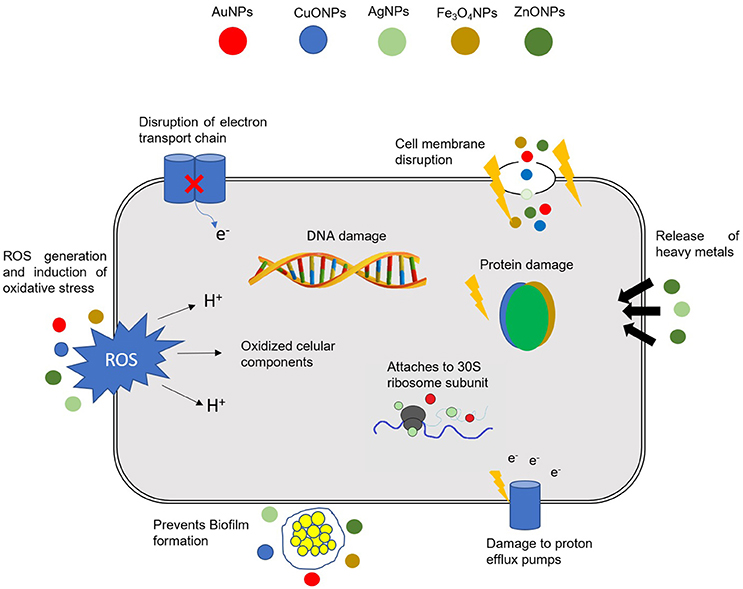
Frontiers Nano-Strategies to Fight Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
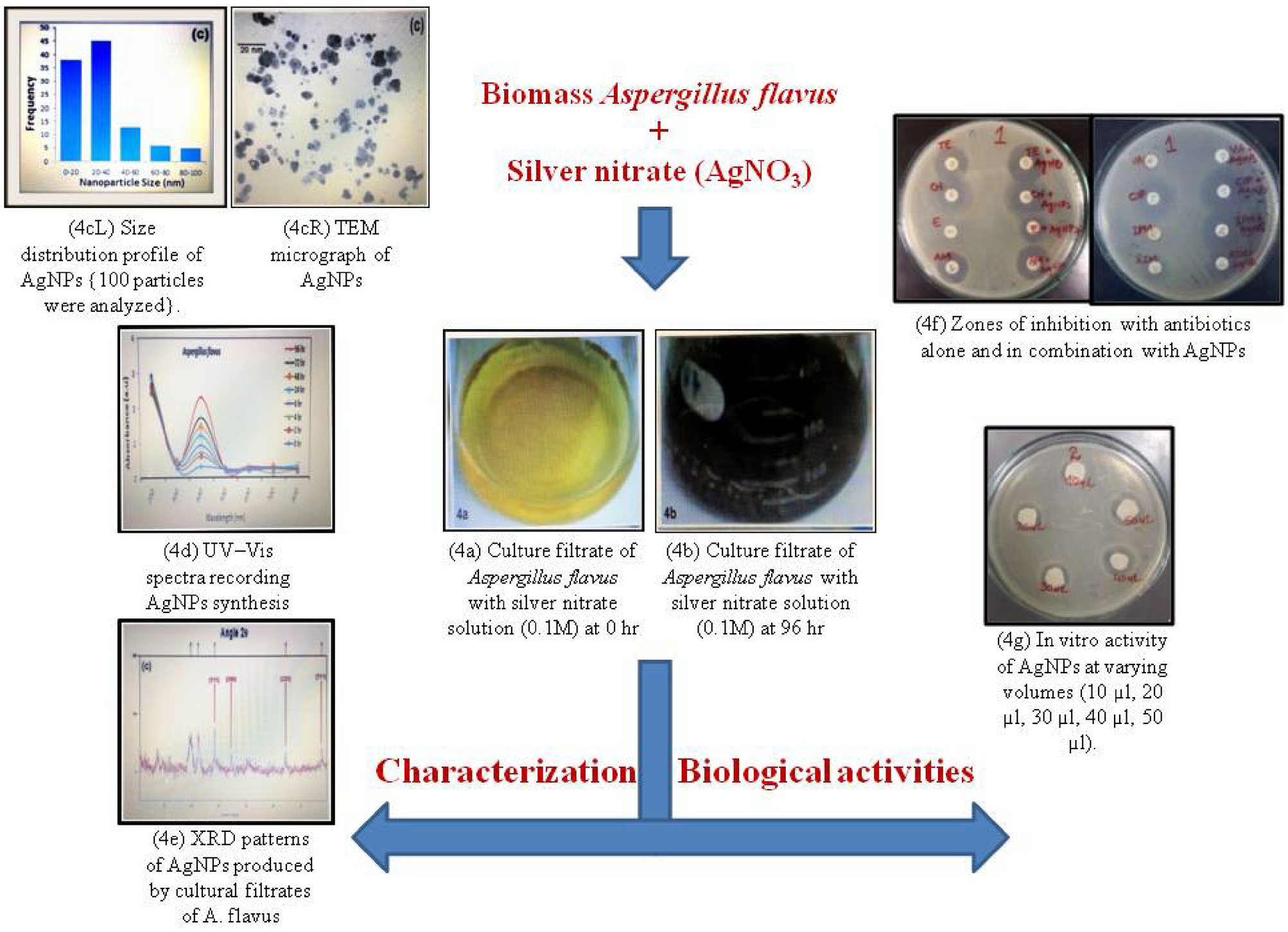
Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against

Nanomaterials: The New Antimicrobial Magic Bullet

The significance of metallic nanoparticles in the emerging

Novel Lignin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug

Using biochar to strengthen the removal of antibiotic resistance

Fate and transport of biological microcontaminants bound to

Binding Force and Site-Determined Desorption and Fragmentation of
Recomendado para você
-
 Final Sea Codes (December 2023): Free Reset Stats, Spins31 março 2025
Final Sea Codes (December 2023): Free Reset Stats, Spins31 março 2025 -
 Tethys Ocean - Wikipedia31 março 2025
Tethys Ocean - Wikipedia31 março 2025 -
 Roblox Sea Piece Codes (March 2023)31 março 2025
Roblox Sea Piece Codes (March 2023)31 março 2025 -
 Sea Piece 2 Codes - Roblox December 202331 março 2025
Sea Piece 2 Codes - Roblox December 202331 março 2025 -
 Roblox Da Piece Codes (December 2023) - Pro Game Guides31 março 2025
Roblox Da Piece Codes (December 2023) - Pro Game Guides31 março 2025 -
 Codes Roblox Sea Piece (janvier 2023) - GameAH31 março 2025
Codes Roblox Sea Piece (janvier 2023) - GameAH31 março 2025 -
 Uniso Ciência - Science @ Uniso v.5, n.10, dez./dec., 2022 by31 março 2025
Uniso Ciência - Science @ Uniso v.5, n.10, dez./dec., 2022 by31 março 2025 -
 Crown-of-thorns starfish - Wikipedia31 março 2025
Crown-of-thorns starfish - Wikipedia31 março 2025 -
 Infinity Sea 2 Codes (July 2023) - Gamer Tweak31 março 2025
Infinity Sea 2 Codes (July 2023) - Gamer Tweak31 março 2025 -
 The 31 Best Motivational Books of All Time (That Will Inspire You)31 março 2025
The 31 Best Motivational Books of All Time (That Will Inspire You)31 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 GitLab Flavored Markdown (GLFM)31 março 2025
GitLab Flavored Markdown (GLFM)31 março 2025 -
 Twitter shares data on the first half of 2020, Animal Crossing: New Horizons the most tweeted-about game globally, The GoNintendo Archives31 março 2025
Twitter shares data on the first half of 2020, Animal Crossing: New Horizons the most tweeted-about game globally, The GoNintendo Archives31 março 2025 -
Total Drama Official31 março 2025
-
 Richmond Hotels, The Jefferson Hotel31 março 2025
Richmond Hotels, The Jefferson Hotel31 março 2025 -
 How to Build a Software Development Team Structure - GraffersID31 março 2025
How to Build a Software Development Team Structure - GraffersID31 março 2025 -
 Friday Night Funkin vs Pibby Corrupted Mod /FNF x Come and Learn with Pibby by Tingly Muffins: Listen on Audiomack31 março 2025
Friday Night Funkin vs Pibby Corrupted Mod /FNF x Come and Learn with Pibby by Tingly Muffins: Listen on Audiomack31 março 2025 -
 a) Qual o sujeito do verbo ficar? Por que esse verbo está no singular?31 março 2025
a) Qual o sujeito do verbo ficar? Por que esse verbo está no singular?31 março 2025 -
 Seagull, Adopt Me! Wiki31 março 2025
Seagull, Adopt Me! Wiki31 março 2025 -
 Pokémon TCG teases a new cross-platform digital application31 março 2025
Pokémon TCG teases a new cross-platform digital application31 março 2025 -
 Cuántas temporadas tiene One Punch Man?31 março 2025
Cuántas temporadas tiene One Punch Man?31 março 2025