Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 julho 2024
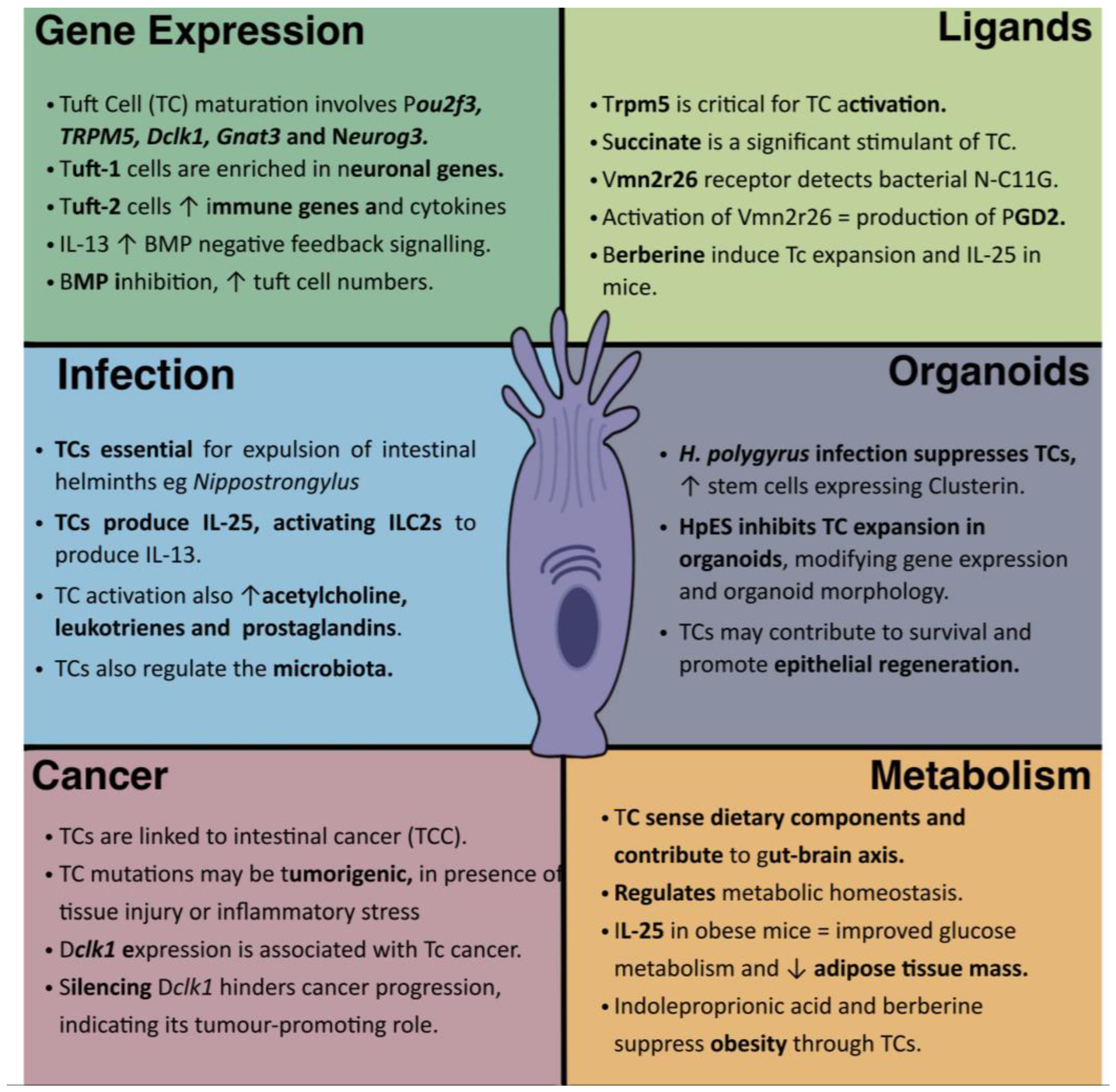
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.

Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Therapy - Gowing Life

Cell-free expression and synthesis of viruses and bacteriophages: applications to medicine and nanotechnology - ScienceDirect
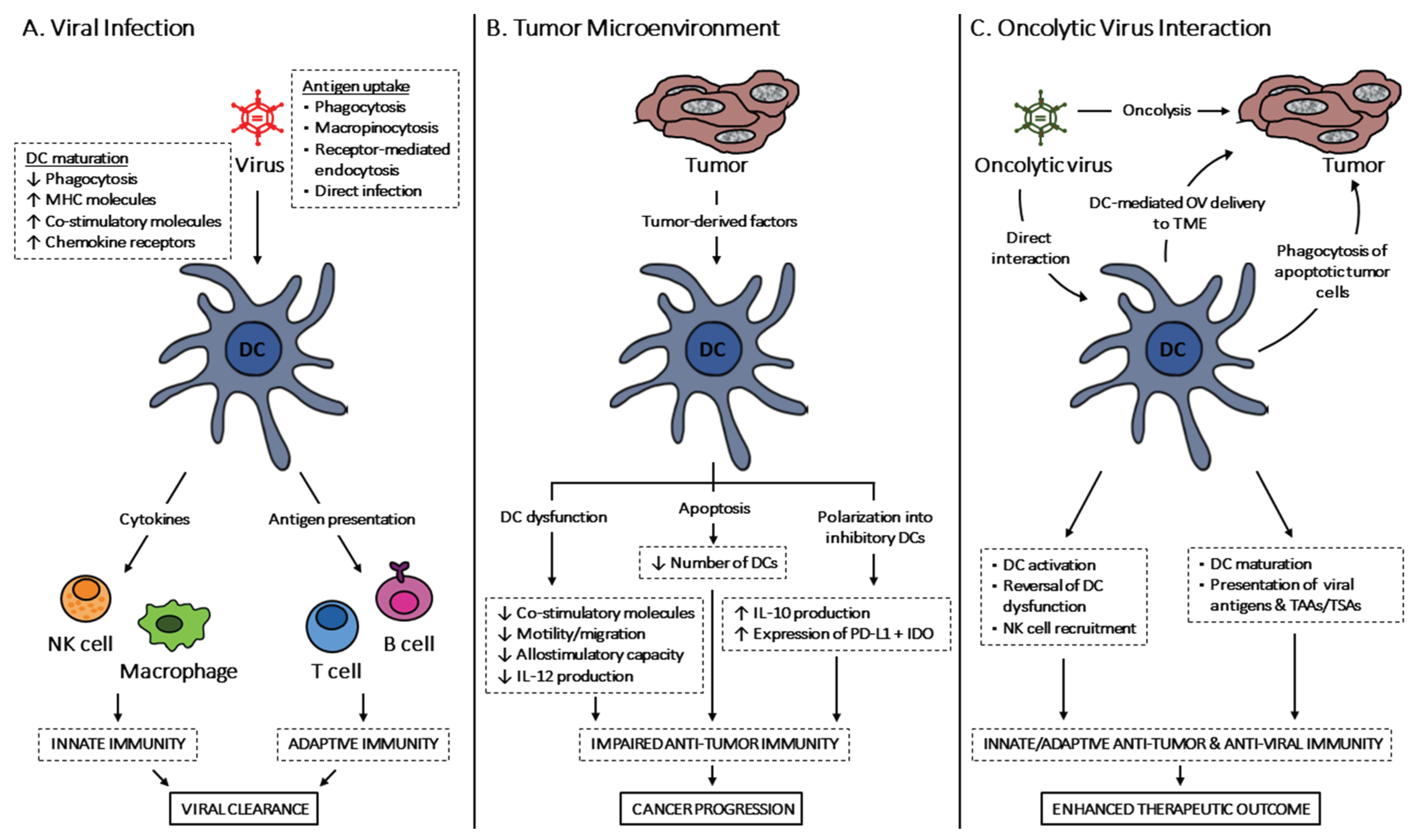
Viruses, Free Full-Text

Towards reproducible cell-free systems
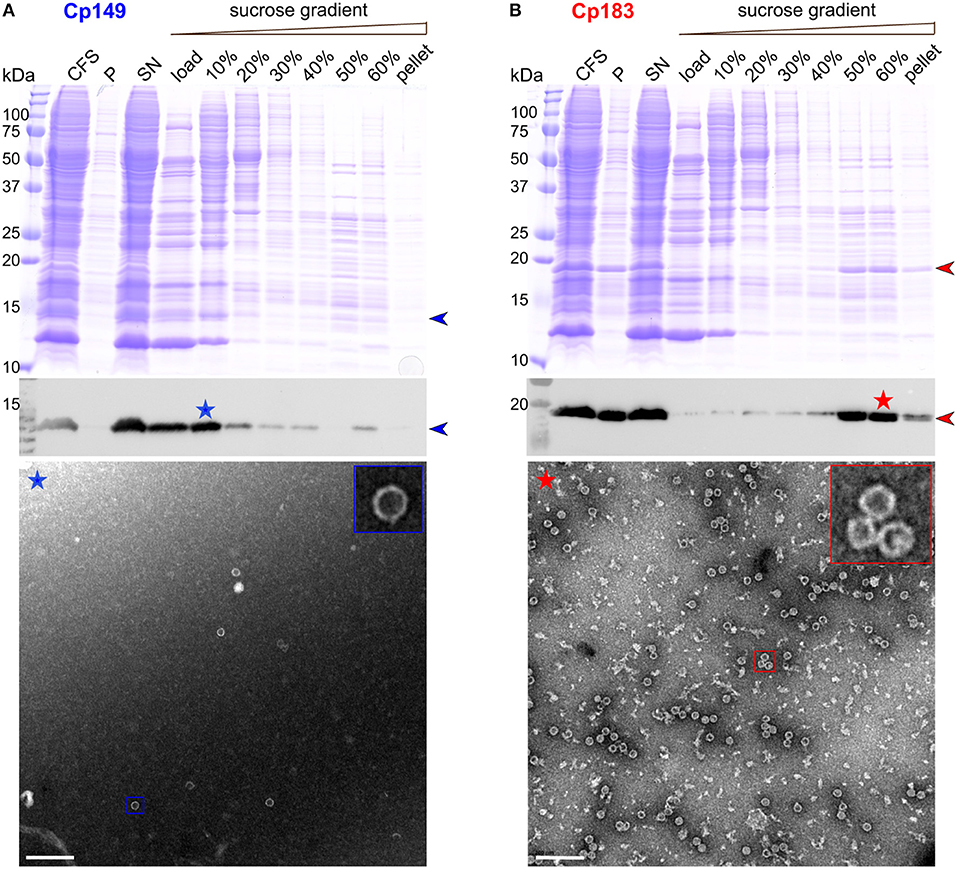
Frontiers Combining Cell-Free Protein Synthesis and NMR Into a Tool to Study Capsid Assembly Modulation
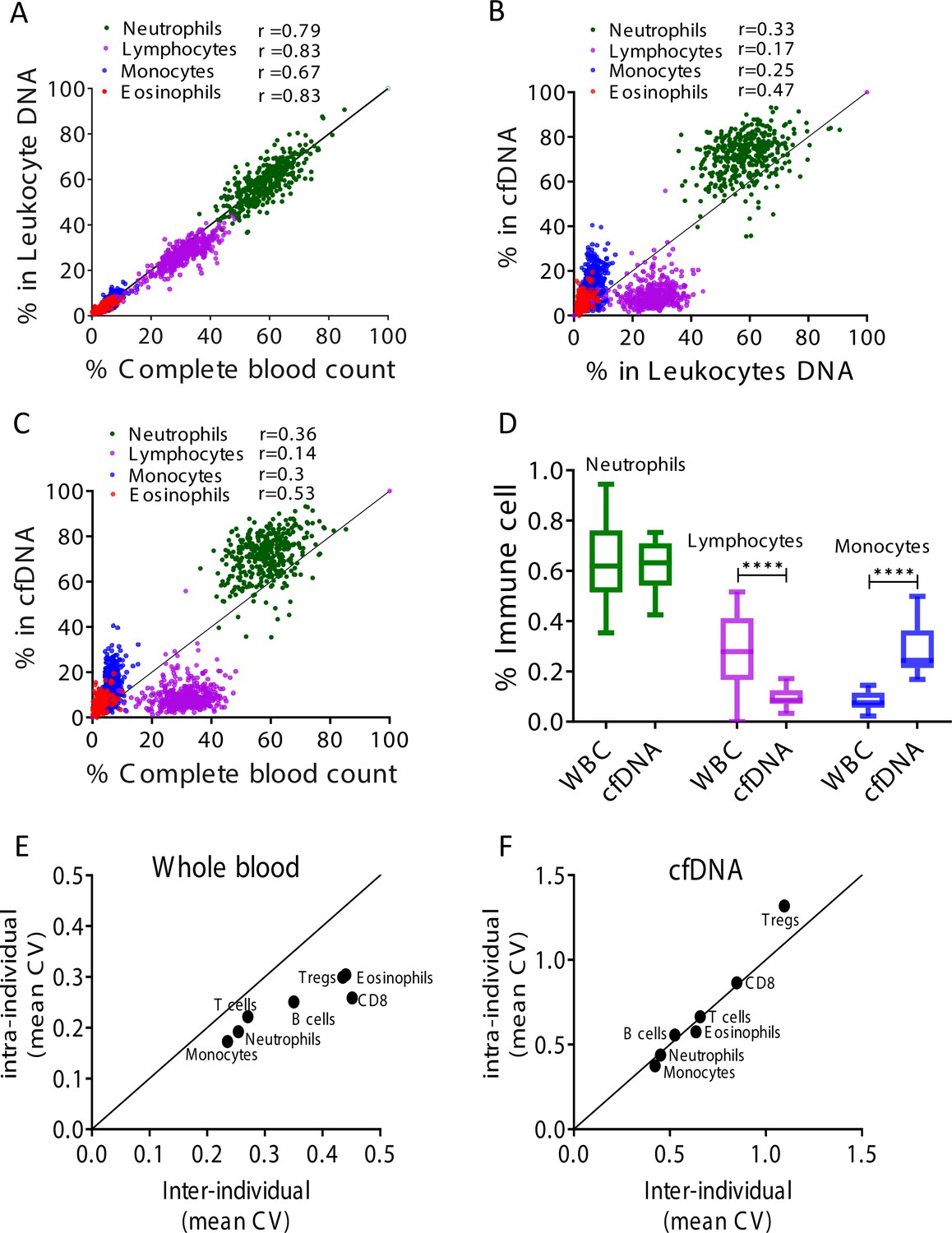
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ

Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-free Macromolecular Synthesis
Recomendado para você
-
 WR GAMES16 julho 2024
WR GAMES16 julho 2024 -
 Wild Rift Patch 3.4b New Content: Vex, Supreme Cells, Bewitching Skins and More16 julho 2024
Wild Rift Patch 3.4b New Content: Vex, Supreme Cells, Bewitching Skins and More16 julho 2024 -
 JavaScript Create 5 Fun Word Games make your own Web Games16 julho 2024
JavaScript Create 5 Fun Word Games make your own Web Games16 julho 2024 -
 Playing as Sam Fisher in Ghost Recon Breakpoint or at least Sam Fisher's skin makes me forget i'm playing Ghost Recon. : r/Splintercell16 julho 2024
Playing as Sam Fisher in Ghost Recon Breakpoint or at least Sam Fisher's skin makes me forget i'm playing Ghost Recon. : r/Splintercell16 julho 2024 -
 iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case16 julho 2024
iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case16 julho 2024 -
 How to Play Agar.io: 11 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow16 julho 2024
How to Play Agar.io: 11 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow16 julho 2024 -
 x alt f4's gtarp : r/LivestreamFail16 julho 2024
x alt f4's gtarp : r/LivestreamFail16 julho 2024 -
 Splinter Cell: Complete Stealth Walkthrough16 julho 2024
Splinter Cell: Complete Stealth Walkthrough16 julho 2024 -
 Timex Men's Indiglo CR2016 Cell WR 30M Stainless Steel Back Leather Watch Band16 julho 2024
Timex Men's Indiglo CR2016 Cell WR 30M Stainless Steel Back Leather Watch Band16 julho 2024 -
 Calvin Ridley stats today: Jaguars WR shines, shows chemistry with Trevor Lawrence in NFL return from suspension16 julho 2024
Calvin Ridley stats today: Jaguars WR shines, shows chemistry with Trevor Lawrence in NFL return from suspension16 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 The Tail (episode), Fukigen na Mononokean Wikia16 julho 2024
The Tail (episode), Fukigen na Mononokean Wikia16 julho 2024 -
 A Gazeta Confrontos das quartas de final da Copa do Brasil são16 julho 2024
A Gazeta Confrontos das quartas de final da Copa do Brasil são16 julho 2024 -
 Scary Teacher Multiplayer - Android Game16 julho 2024
Scary Teacher Multiplayer - Android Game16 julho 2024 -
 Manhas GTA San Andreas PC: veja a lista completa16 julho 2024
Manhas GTA San Andreas PC: veja a lista completa16 julho 2024 -
 Battlefield 2042 Steam reviews make it the 9th lowest rated game ever16 julho 2024
Battlefield 2042 Steam reviews make it the 9th lowest rated game ever16 julho 2024 -
 Enhancing Skills in Gaming: Challenging Positions for Growth — Eightify16 julho 2024
Enhancing Skills in Gaming: Challenging Positions for Growth — Eightify16 julho 2024 -
 Deadly Dinosaur Hunter - Play UNBLOCKED Deadly Dinosaur Hunter on DooDooLove16 julho 2024
Deadly Dinosaur Hunter - Play UNBLOCKED Deadly Dinosaur Hunter on DooDooLove16 julho 2024 -
 SCP 1471-A from SCP Containment Breach Costume, Carbon Costume16 julho 2024
SCP 1471-A from SCP Containment Breach Costume, Carbon Costume16 julho 2024 -
 Maze Runner 4 Already Has An Easy Way To Bring Back Dylan O'Brien16 julho 2024
Maze Runner 4 Already Has An Easy Way To Bring Back Dylan O'Brien16 julho 2024 -
 GothamChess on X: A sneak peek inside my chess book: Easy to read visuals, small arrows indicating which board to focus on, and “last move” highlights. We are modernizing how to read16 julho 2024
GothamChess on X: A sneak peek inside my chess book: Easy to read visuals, small arrows indicating which board to focus on, and “last move” highlights. We are modernizing how to read16 julho 2024