Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 janeiro 2025
The genus Aspergillus, one of the most abundant airborne fungi, is classified into hundreds of species that affect humans, animals, and plants. Among these, Aspergillus nidulans, as a key model organism, has been extensively studied to understand the mechanisms governing growth and development, physiology, and gene regulation in fungi. A. nidulans primarily reproduces by forming millions of asexual spores known as conidia. The asexual life cycle of A. nidulans can be simply divided into growth and asexual development (conidiation). After a certain period of vegetative growth, some vegetative cells (hyphae) develop into specialized asexual structures called conidiophores. Each A. nidulans conidiophore is composed of a foot cell, stalk, vesicle, metulae, phialides, and 12,000 conidia. This vegetative-to-developmental transition requires the activity of various regulators including FLB proteins, BrlA, and AbaA. Asymmetric repetitive mitotic cell division of phialides results in the formation of immature conidia. Subsequent conidial maturation requires multiple regulators such as WetA, VosA, and VelB. Matured conidia maintain cellular integrity and long-term viability against various stresses and desiccation. Under appropriate conditions, the resting conidia germinate and form new colonies, and this process is governed by a myriad of regulators, such as CreA and SocA. To date, a plethora of regulators for each asexual developmental stage have been identified and investigated. This review summarizes our current understanding of the regulators of conidial formation, maturation, dormancy, and germination in A. nidulans.
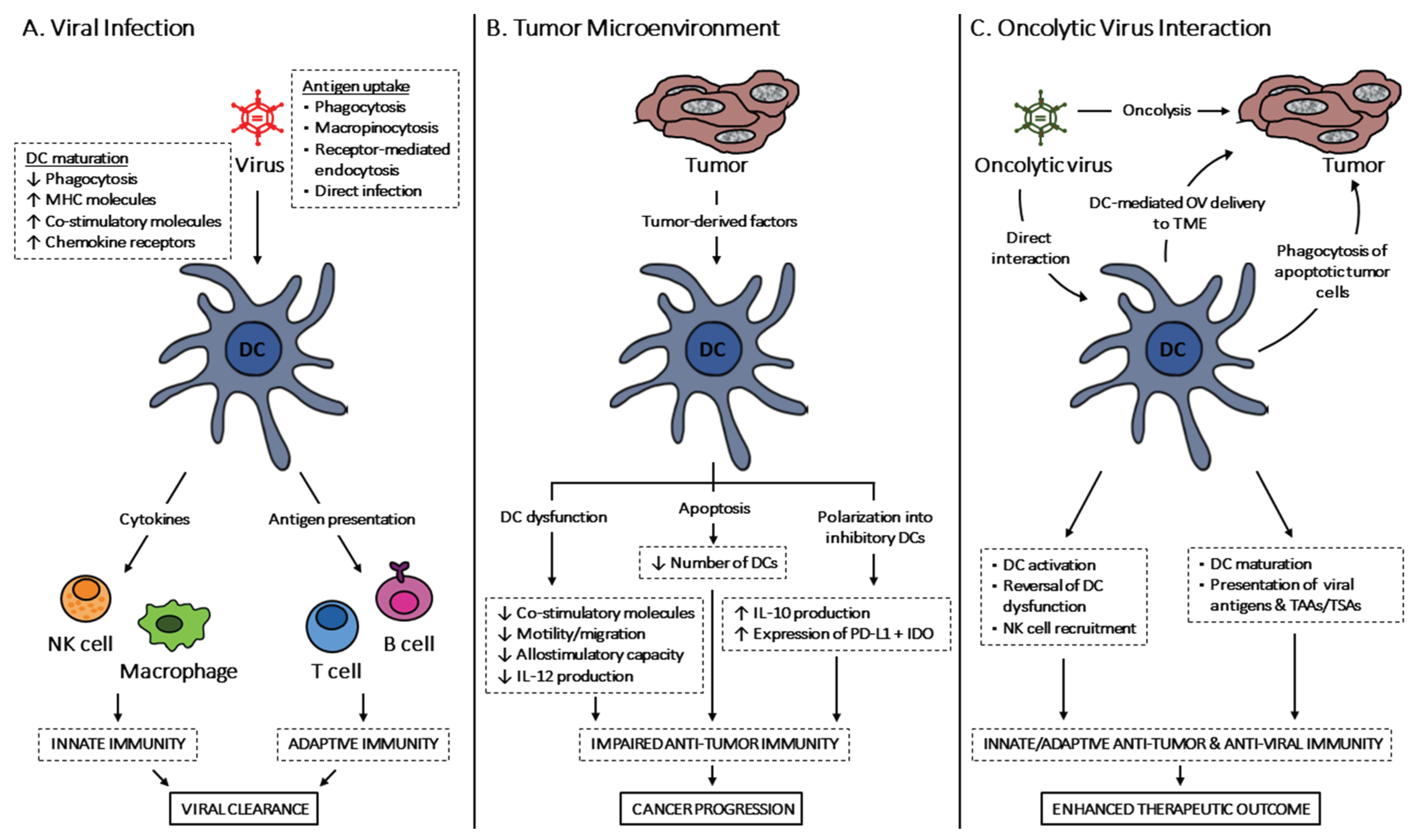
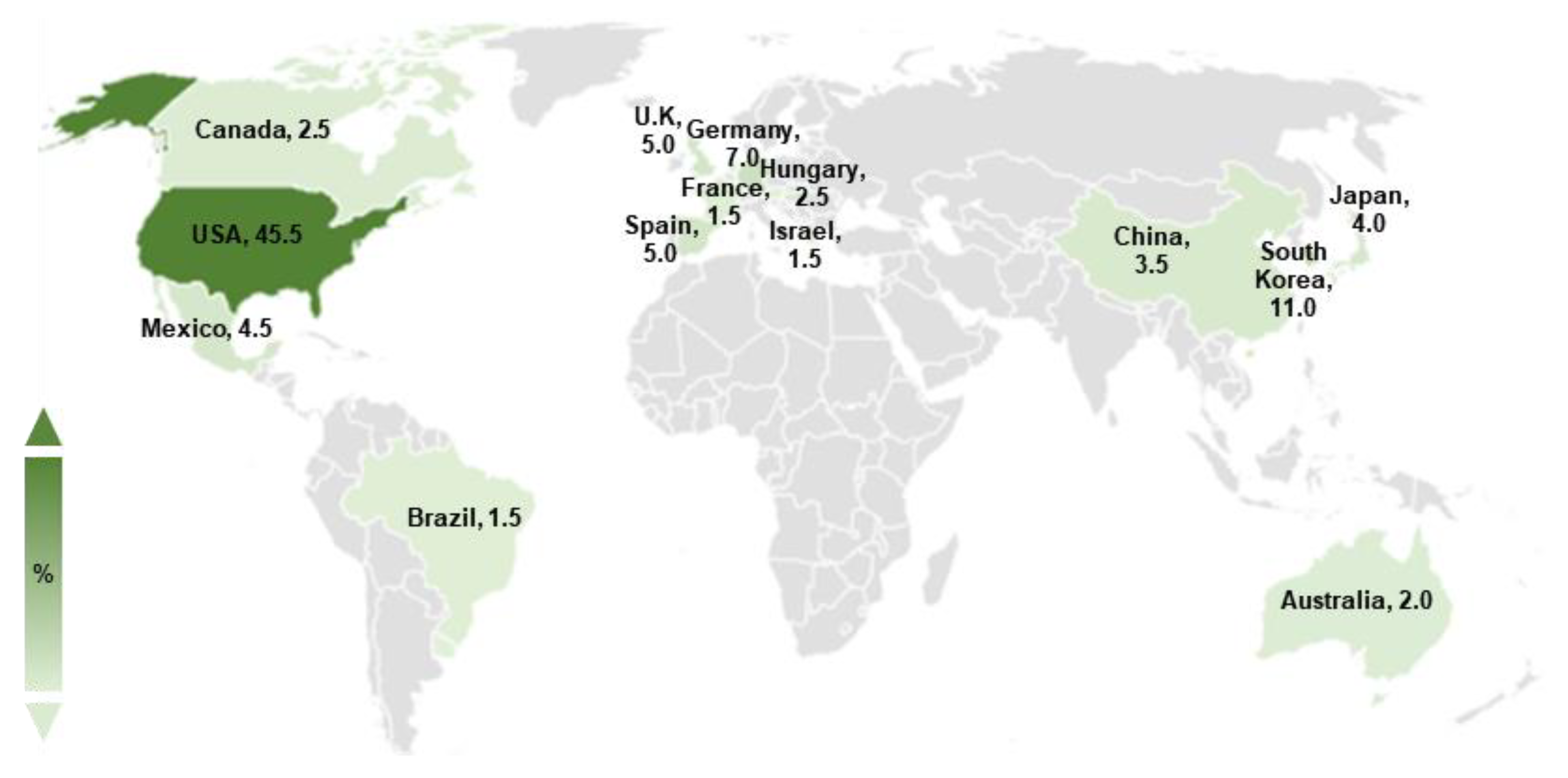
Viruses, Free Full-Text

Advances and applications of cell-free systems for metabolic production - ScienceDirect
Cell-free synthesis of human interferon. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Towards reproducible cell-free systems
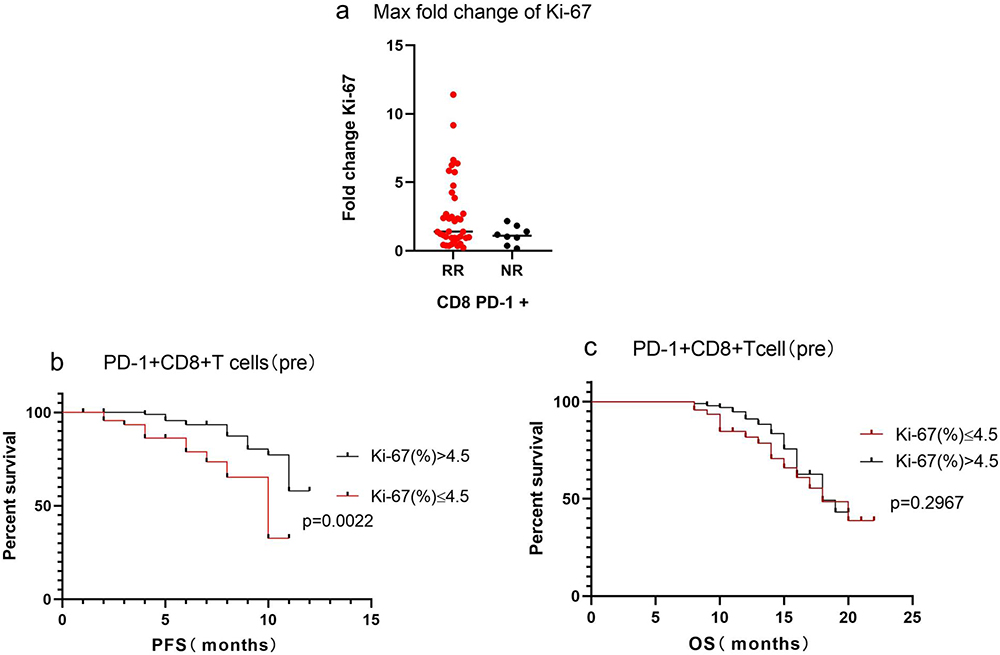
Cells, Free Full-Text

STEM CELLS: Vol 35, No 5

Experimental design of upsidedown, upside-up, and cell-free control
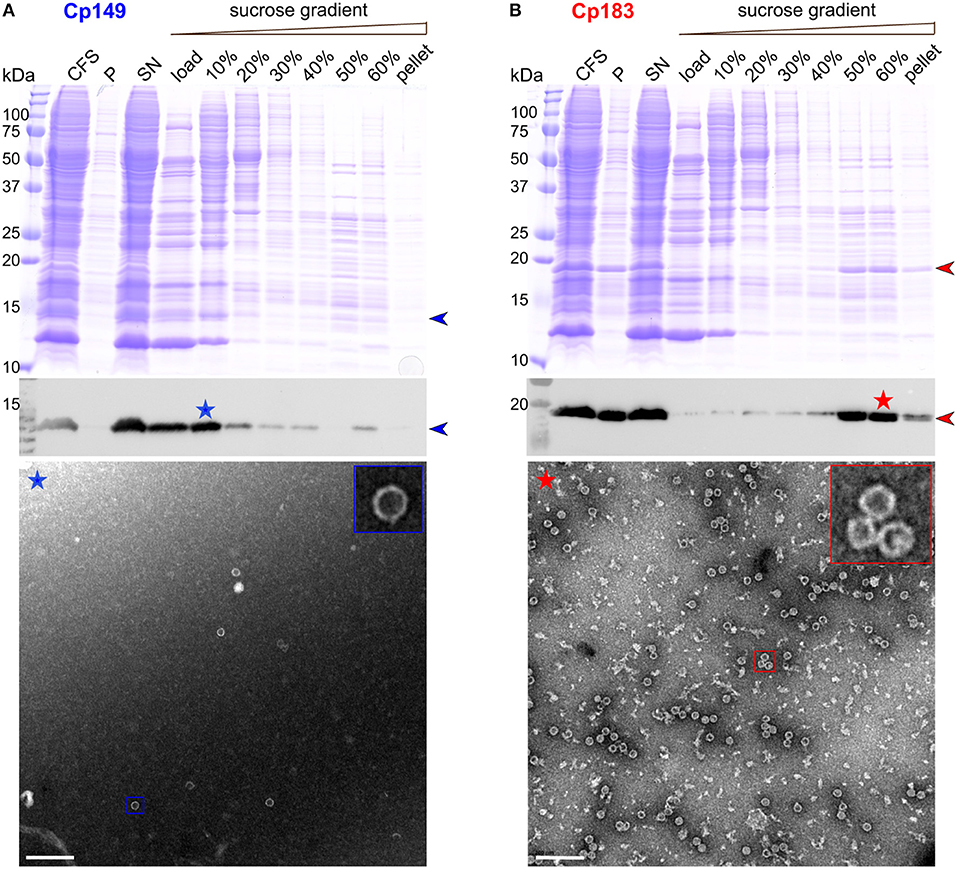
Frontiers Combining Cell-Free Protein Synthesis and NMR Into a Tool to Study Capsid Assembly Modulation

Cells, Free Full-Text
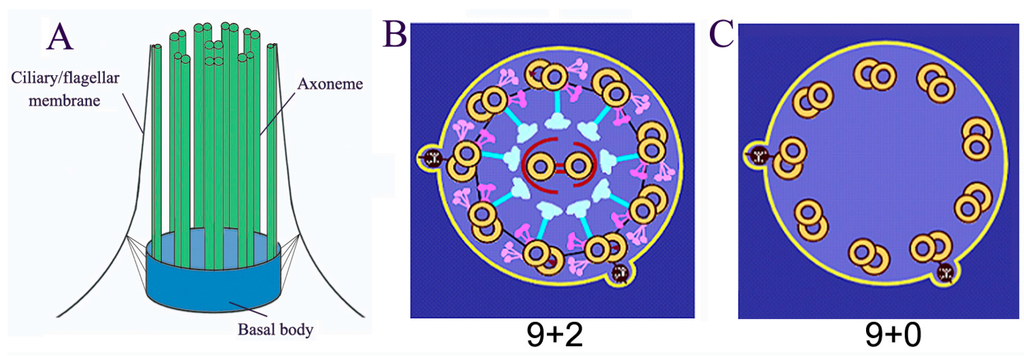
Cells, Free Full-Text
Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus B-30892 can inhibit cytotoxic effects and adhesion of pathogenic Clostridium difficile to Caco-2 cells, Gut Pathogens
THE CELL : PAUL REVERE11 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Recomendado para você
-
 Luffy Vetores, Ícones e Planos de Fundo para Baixar Grátis01 janeiro 2025
Luffy Vetores, Ícones e Planos de Fundo para Baixar Grátis01 janeiro 2025 -
 Son Goku, Heroes Wiki01 janeiro 2025
Son Goku, Heroes Wiki01 janeiro 2025 -
 One piece01 janeiro 2025
One piece01 janeiro 2025 -
Liar Pirate Anime Face Roblox Item - Rolimon's01 janeiro 2025
-
 luffy calvo Minecraft Skins01 janeiro 2025
luffy calvo Minecraft Skins01 janeiro 2025 -
 David Calvo, Minecraft: Story Mode, minecraft Story Mode, r01 janeiro 2025
David Calvo, Minecraft: Story Mode, minecraft Story Mode, r01 janeiro 2025 -
Son Goku, UCF Ultimate Caw Fighting Wiki01 janeiro 2025
-
 Kurozumi Orochi, One Piece Wiki01 janeiro 2025
Kurozumi Orochi, One Piece Wiki01 janeiro 2025 -
 Sanji Print - Norway01 janeiro 2025
Sanji Print - Norway01 janeiro 2025 -
 QuaxoaiTee Shirt MONKEY D LUFFY SUPER CALVO COLORS01 janeiro 2025
QuaxoaiTee Shirt MONKEY D LUFFY SUPER CALVO COLORS01 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Best Ross 'Friends' Episodes and Moments01 janeiro 2025
Best Ross 'Friends' Episodes and Moments01 janeiro 2025 -
 Makeup Kit para Android - Download01 janeiro 2025
Makeup Kit para Android - Download01 janeiro 2025 -
 Eilistraee - Wikipedia01 janeiro 2025
Eilistraee - Wikipedia01 janeiro 2025 -
 Significação - Dicio, Dicionário Online de Português01 janeiro 2025
Significação - Dicio, Dicionário Online de Português01 janeiro 2025 -
 Shadow of the Colossus For PS4 Review - IGN01 janeiro 2025
Shadow of the Colossus For PS4 Review - IGN01 janeiro 2025 -
 Doomer Girl Sticker - Sticker Graphic - Auto, Wall, Laptop, Cell, Truck Sticker for Windows, Cars, Trucks01 janeiro 2025
Doomer Girl Sticker - Sticker Graphic - Auto, Wall, Laptop, Cell, Truck Sticker for Windows, Cars, Trucks01 janeiro 2025 -
 Privacy Policy for iOS Apps - Free Privacy Policy01 janeiro 2025
Privacy Policy for iOS Apps - Free Privacy Policy01 janeiro 2025 -
Eu Vou Jogar a Sua Calcinha Na Casa da Vizinha ou No Fio do Poste - song and lyrics by Mc Fazano, DJ Biel Beats01 janeiro 2025
-
 Convite online arabescos editar grátis01 janeiro 2025
Convite online arabescos editar grátis01 janeiro 2025 -
Paciência Solitário Clássico – Apps no Google Play01 janeiro 2025

