Block caving: A new mining method arises
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 março 2025

Block caving is a new alternative method of developing new mines or extending the operation of open pits. Block caving is an underground hard rock mining metho
Block caving is a new alternative method of developing new mines or extending the operation of open pits. Block caving is an underground hard rock mining method that involves undermining an ore body, allowing it to progressively collapse under its own weight. It is the underground version of open pit mining. In block caving, a large section of rock is undercut, creating an artificial cavern that fills with its own rubble as it collapses. This broken ore falls into a pre-constructed series of funnels and access tunnels underneath the broken ore mass. These mineworks are sheltered from the collapsing ore inside bunker-like mass of rock, and miners extract it continuously from here. The collapse progresses upward through the ore body, eventually causing large areas of the surface to subside into sinkholes. The cost of block cave mining is about 1/10 of the correspondent cost of conventional methods. The production rates can reach 30,000 to 100,000 tons per day. Moreover, drilling and blasting costs are far less, and there are no backfilling costs. Another benefit of block caving is the large reduction in surface waste disposal needs. As open pits get deeper, their ratios of waste rock to ore often get higher and the waste must be placed in surface storage areas. The amount of waste rock generated from underground methods like block caving is a fraction of this, reducing surficial land impacts. The key factors for selecting block caving method are: A region with a massive deposit that has sufficient height and footprint area to initiate and propagate the natural caving of the rock mass. Beneficial geomechanical characteristics such as in-situ rock fractures to encourage fragmentation during the caving process, sufficient rock mass strength to support long life drawpoints and excavation tunnels, and manageable ground stresses. Ore value that is not only able to cover operating costs, but also the relatively high initial capital costs, and extended pre-production periods, as compared to most other methods. As a minimum, the ore value should be two to three times the site operating costs (mining, processing, and general and administration costs). The acceptance of surface disturbance above the cave. This zone of disturbance must be accounted for when considering existing or planned infrastructure and environmental considerations. As large open pit mines come to the end of their lives, many companies are examining the feasibility of transitioning to low-cost, large-scale underground operations. Block cave mining is the only underground method that can offer comparable open pit production rates and operating costs. For new developments, block cave mining offers the further advantage of a smaller surface footprint with significantly less waste disposal requirements.
Block caving is a new alternative method of developing new mines or extending the operation of open pits. Block caving is an underground hard rock mining method that involves undermining an ore body, allowing it to progressively collapse under its own weight. It is the underground version of open pit mining. In block caving, a large section of rock is undercut, creating an artificial cavern that fills with its own rubble as it collapses. This broken ore falls into a pre-constructed series of funnels and access tunnels underneath the broken ore mass. These mineworks are sheltered from the collapsing ore inside bunker-like mass of rock, and miners extract it continuously from here. The collapse progresses upward through the ore body, eventually causing large areas of the surface to subside into sinkholes. The cost of block cave mining is about 1/10 of the correspondent cost of conventional methods. The production rates can reach 30,000 to 100,000 tons per day. Moreover, drilling and blasting costs are far less, and there are no backfilling costs. Another benefit of block caving is the large reduction in surface waste disposal needs. As open pits get deeper, their ratios of waste rock to ore often get higher and the waste must be placed in surface storage areas. The amount of waste rock generated from underground methods like block caving is a fraction of this, reducing surficial land impacts. The key factors for selecting block caving method are: A region with a massive deposit that has sufficient height and footprint area to initiate and propagate the natural caving of the rock mass. Beneficial geomechanical characteristics such as in-situ rock fractures to encourage fragmentation during the caving process, sufficient rock mass strength to support long life drawpoints and excavation tunnels, and manageable ground stresses. Ore value that is not only able to cover operating costs, but also the relatively high initial capital costs, and extended pre-production periods, as compared to most other methods. As a minimum, the ore value should be two to three times the site operating costs (mining, processing, and general and administration costs). The acceptance of surface disturbance above the cave. This zone of disturbance must be accounted for when considering existing or planned infrastructure and environmental considerations. As large open pit mines come to the end of their lives, many companies are examining the feasibility of transitioning to low-cost, large-scale underground operations. Block cave mining is the only underground method that can offer comparable open pit production rates and operating costs. For new developments, block cave mining offers the further advantage of a smaller surface footprint with significantly less waste disposal requirements.
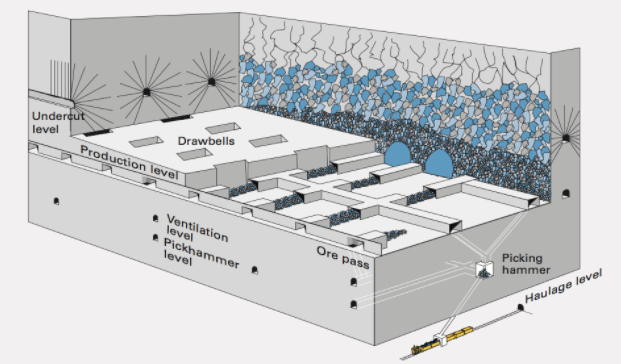
8.4.2a Block Caving

Capital (a) and operating (b) costs for open pit and caving mines

Block caving mining method - Epiroc

Illustration of typical (a) block caving mining and (b) sublevel caving

ISE-Mining - 📊⛏ Caving Methods ✓ Sublevel Caving ✓ Block
Block caving mining method with Elfen software, explained by Rockfield

Beginners Guide to Stope Mining
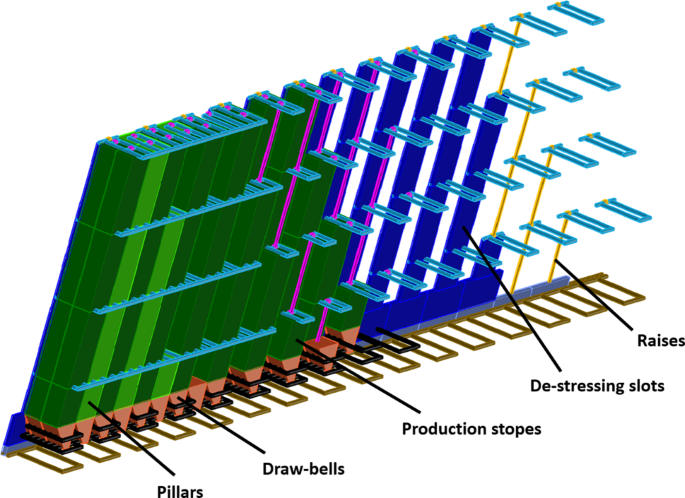
Critical Issues of Ore Flow for the Raise Caving Method

Block caving: A new mining method arises

Full article: Optimisation of life-of-mine production scheduling for block-caving mines under mineral resource and material mixing uncertainty
Recomendado para você
-
 Cryptojacking: Digging for your own Treasure22 março 2025
Cryptojacking: Digging for your own Treasure22 março 2025 -
 Ad Network Uses DGA Algorithm to Bypass Ad Blockers and Deploy In-Browser Miners22 março 2025
Ad Network Uses DGA Algorithm to Bypass Ad Blockers and Deploy In-Browser Miners22 março 2025 -
 My Early Bitcoin ASIC Miners (2013-2014) - Pictures / History22 março 2025
My Early Bitcoin ASIC Miners (2013-2014) - Pictures / History22 março 2025 -
 AdBlock and Authedmine.com cryptocurrency miners – AdBlock22 março 2025
AdBlock and Authedmine.com cryptocurrency miners – AdBlock22 março 2025 -
 Listen to NASA Helps Design Rescue Capsule for Chilean Miners22 março 2025
Listen to NASA Helps Design Rescue Capsule for Chilean Miners22 março 2025 -
 Cryptomining uses as much electricity as Houston, Congress finds22 março 2025
Cryptomining uses as much electricity as Houston, Congress finds22 março 2025 -
 Stablecoin Issuer Tether (USDT/BTC) Wants to Become a Major Bitcoin Miner - Bloomberg22 março 2025
Stablecoin Issuer Tether (USDT/BTC) Wants to Become a Major Bitcoin Miner - Bloomberg22 março 2025 -
 How to Eat Like a 19th Century Colorado Gold-Miner - Gastro Obscura22 março 2025
How to Eat Like a 19th Century Colorado Gold-Miner - Gastro Obscura22 março 2025 -
 Bitcoin Miners Building Rigs Must Navigate World of Crypto Power-Hunting - Bloomberg22 março 2025
Bitcoin Miners Building Rigs Must Navigate World of Crypto Power-Hunting - Bloomberg22 março 2025 -
 How to stop websites from using your computer to mine Bitcoin (and more) - CNET22 março 2025
How to stop websites from using your computer to mine Bitcoin (and more) - CNET22 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Norwegian stockfish in Nigerian meals22 março 2025
Norwegian stockfish in Nigerian meals22 março 2025 -
 Ender Dragon, Minecraft: Legacy Console Edition Wiki22 março 2025
Ender Dragon, Minecraft: Legacy Console Edition Wiki22 março 2025 -
 Sombra e Ossos é cancelada na Netflix junto de mais 4 séries - Mix22 março 2025
Sombra e Ossos é cancelada na Netflix junto de mais 4 séries - Mix22 março 2025 -
 Resumão #150: Abertura de Sun & Moon no Ocidente, Pokémon Gerações dublado e mais!22 março 2025
Resumão #150: Abertura de Sun & Moon no Ocidente, Pokémon Gerações dublado e mais!22 março 2025 -
 Medallero Juegos Panamericanos 2023 actualizado: cuántas lleva México 28 de octubre 202322 março 2025
Medallero Juegos Panamericanos 2023 actualizado: cuántas lleva México 28 de octubre 202322 março 2025 -
 Novos canais estreiam no serviço de streaming Pluto TV; confira22 março 2025
Novos canais estreiam no serviço de streaming Pluto TV; confira22 março 2025 -
 Fino senhores - meme post - Imgur22 março 2025
Fino senhores - meme post - Imgur22 março 2025 -
 Kit 2 Cadernos Espiral Minecraft + Caderno Desenho Minecraft22 março 2025
Kit 2 Cadernos Espiral Minecraft + Caderno Desenho Minecraft22 março 2025 -
 SAIU! Truck Simulator Europe 3 Novo Jogo de Caminhões Para ANDROID22 março 2025
SAIU! Truck Simulator Europe 3 Novo Jogo de Caminhões Para ANDROID22 março 2025 -
 PH Meow Meow Linear Switch 5 pin Switch for Mechanical Keyboard22 março 2025
PH Meow Meow Linear Switch 5 pin Switch for Mechanical Keyboard22 março 2025