Biology, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 fevereiro 2025
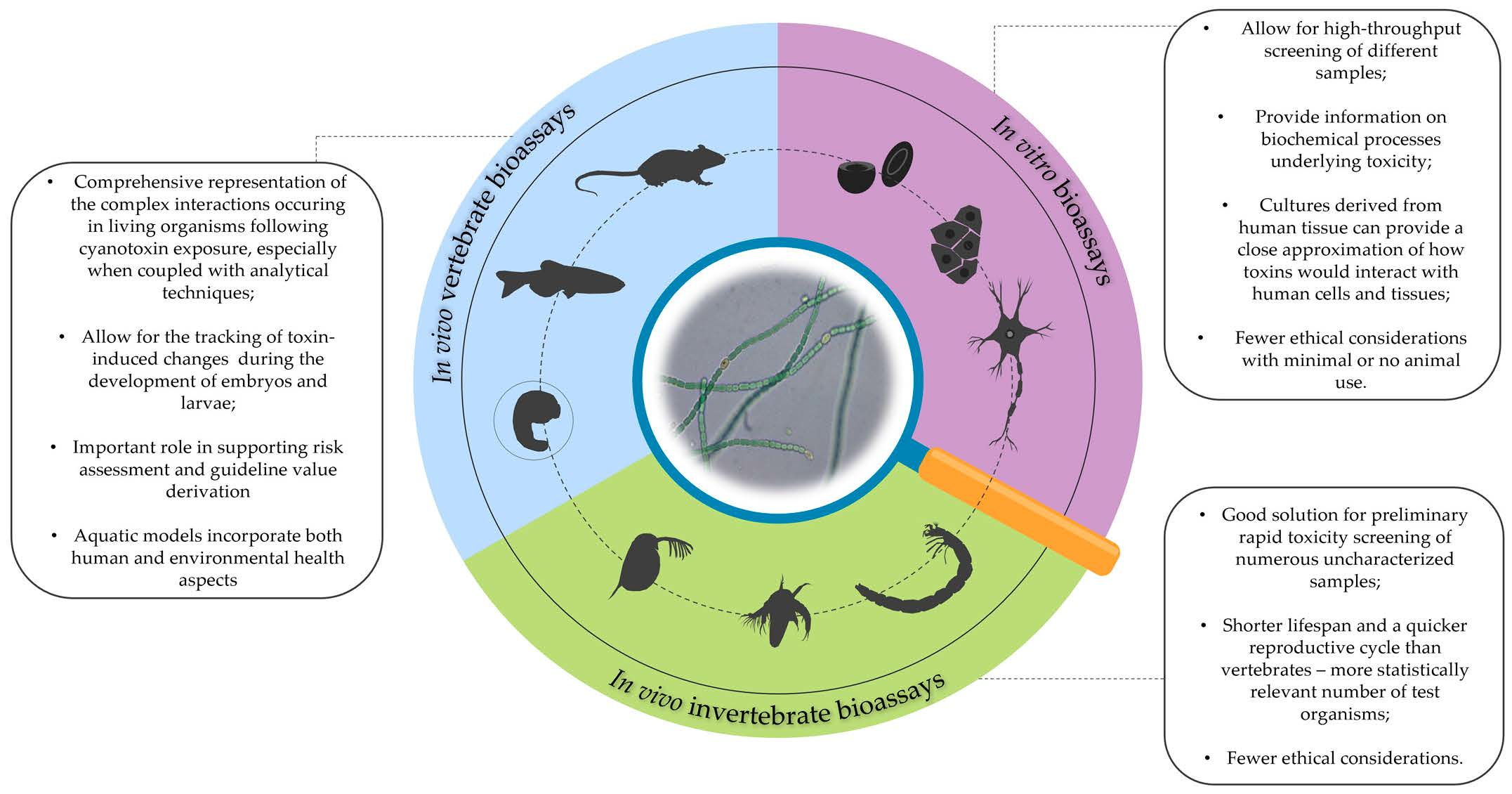
Cyanobacteria are a diverse group of organisms known for producing highly potent cyanotoxins that pose a threat to human, animal, and environmental health. These toxins have varying chemical structures and toxicity mechanisms and several toxin classes can be present simultaneously, making it difficult to assess their toxic effects using physico-chemical methods, even when the producing organism and its abundance are identified. To address these challenges, alternative organisms among aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates are being explored as more assays evolve and diverge from the initially established and routinely used mouse bioassay. However, detecting cyanotoxins in complex environmental samples and characterizing their toxic modes of action remain major challenges. This review provides a systematic overview of the use of some of these alternative models and their responses to harmful cyanobacterial metabolites. It also assesses the general usefulness, sensitivity, and efficiency of these models in investigating the mechanisms of cyanotoxicity expressed at different levels of biological organization. From the reported findings, it is clear that cyanotoxin testing requires a multi-level approach. While studying changes at the whole-organism level is essential, as the complexities of whole organisms are still beyond the reach of in vitro methodologies, understanding cyanotoxicity at the molecular and biochemical levels is necessary for meaningful toxicity evaluations. Further research is needed to refine and optimize bioassays for cyanotoxicity testing, which includes developing standardized protocols and identifying novel model organisms for improved understanding of the mechanisms with fewer ethical concerns. In vitro models and computational modeling can complement vertebrate bioassays and reduce animal use, leading to better risk assessment and characterization of cyanotoxins.
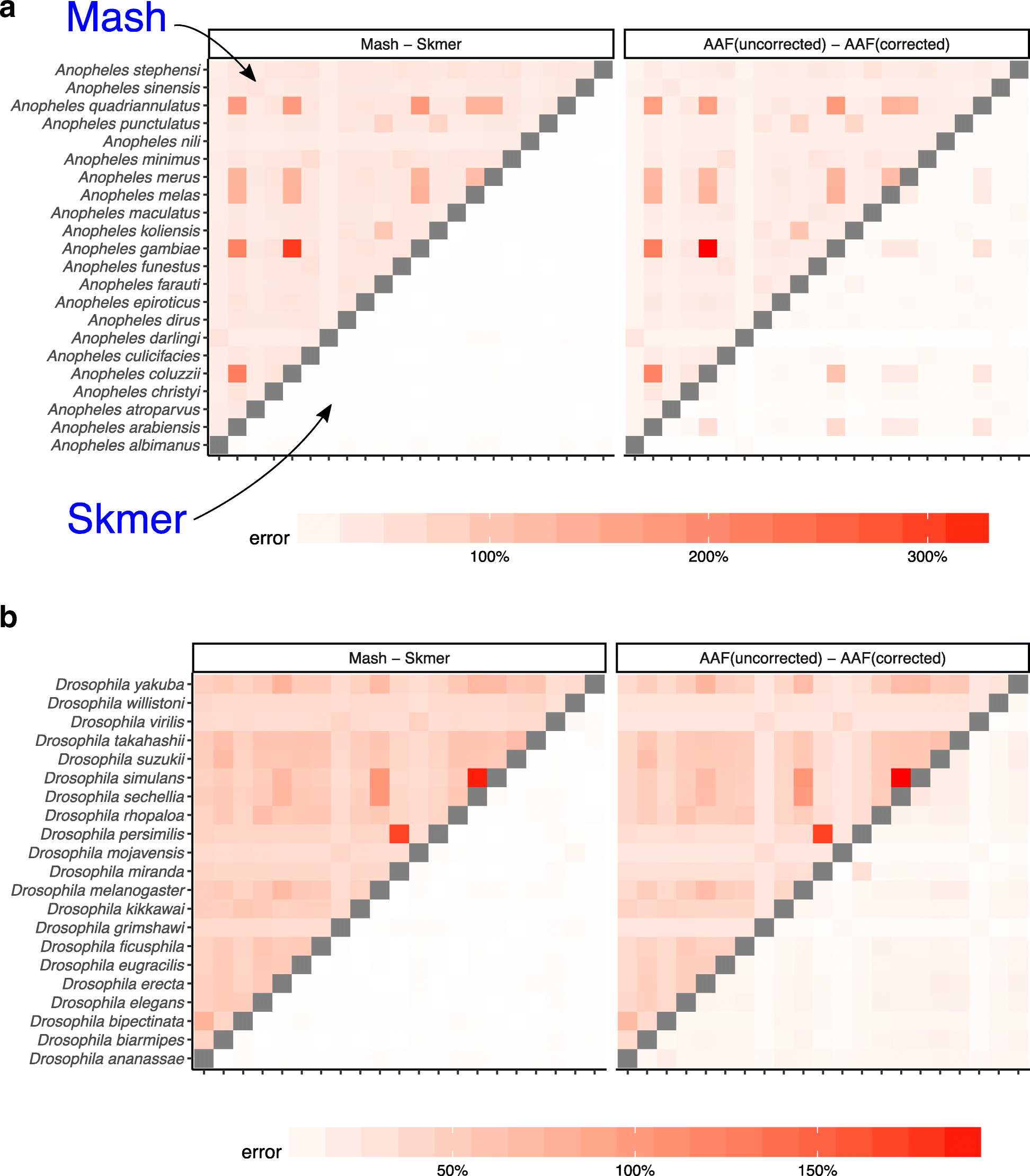
Skmer: assembly-free and alignment-free sample identification using genome skims, Genome Biology

Listen Free to Biology Book: Big Ideas Simply Explained by Tba with a Free Trial.

Unit 1 - Biology Basics - Review Guide ⋆

Free Full Text] RBM 007 - new approach for achondroplasia - Beyond Achondroplasia
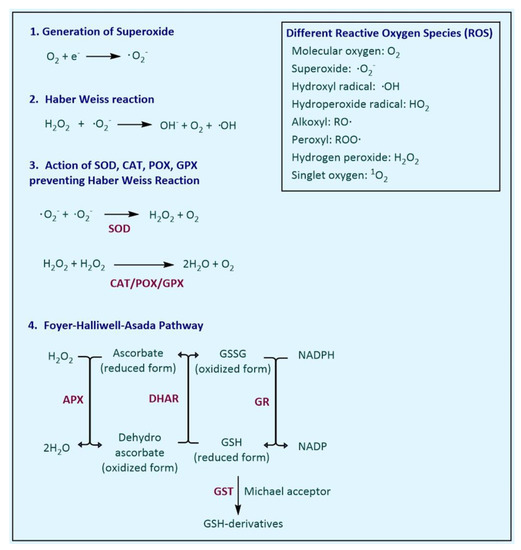
Systems Biology Of Free Radicals And Antioxidants - Colaboratory

biology books Offline APK for Android Download
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ
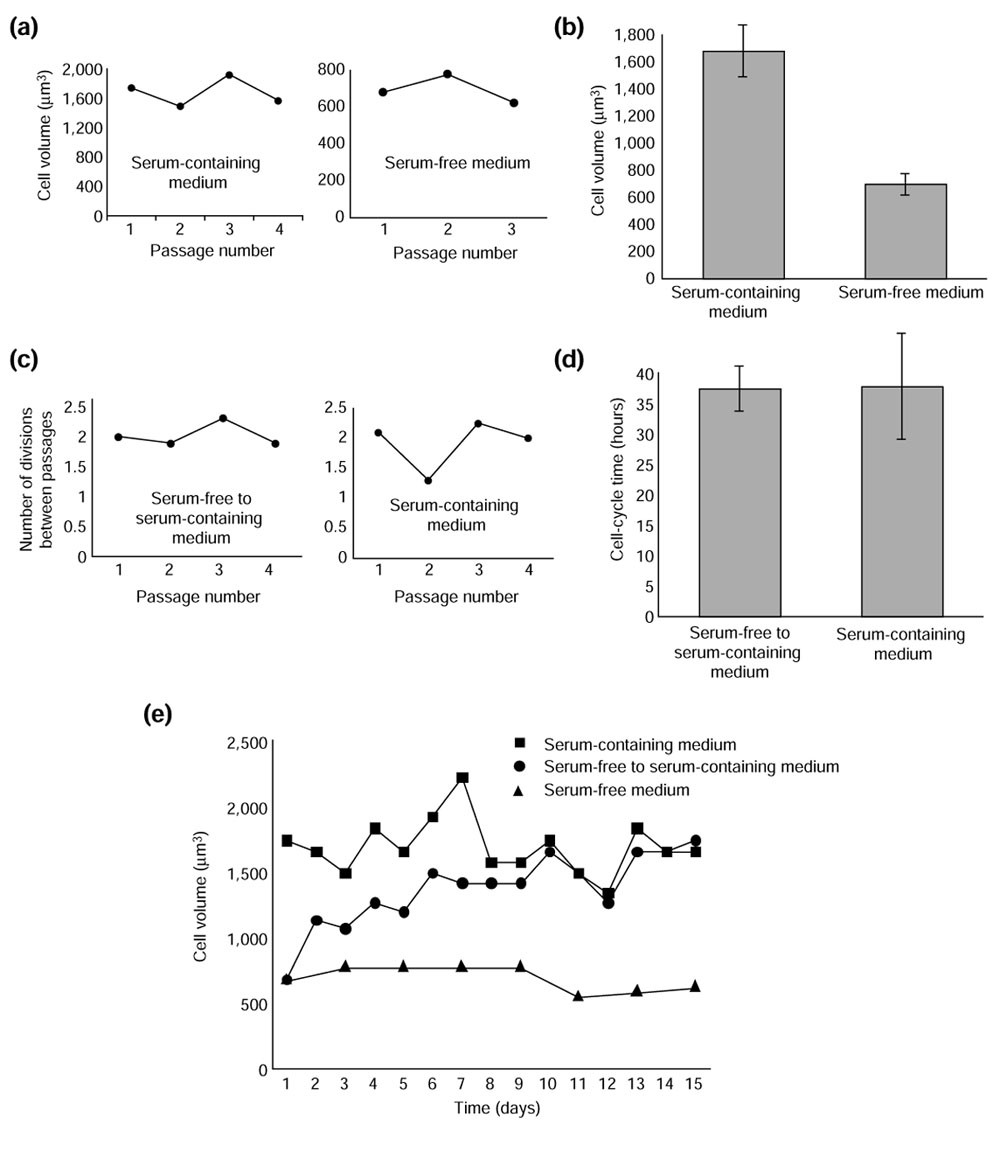
Differences in the way a mammalian cell and yeast cells coordinate cell growth and cell-cycle progression, Journal of Biology

Premium Vector Biology 3d text effect vector download
The flowering plant: as illustrating the first principles of botany : Ainsworth Davis, J. R. (James Richard), 1861-1934 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive

Free Radical Biology and Environmental Toxicity

BioRxiv: a free online archive and distribution service for unpublished preprints in biology
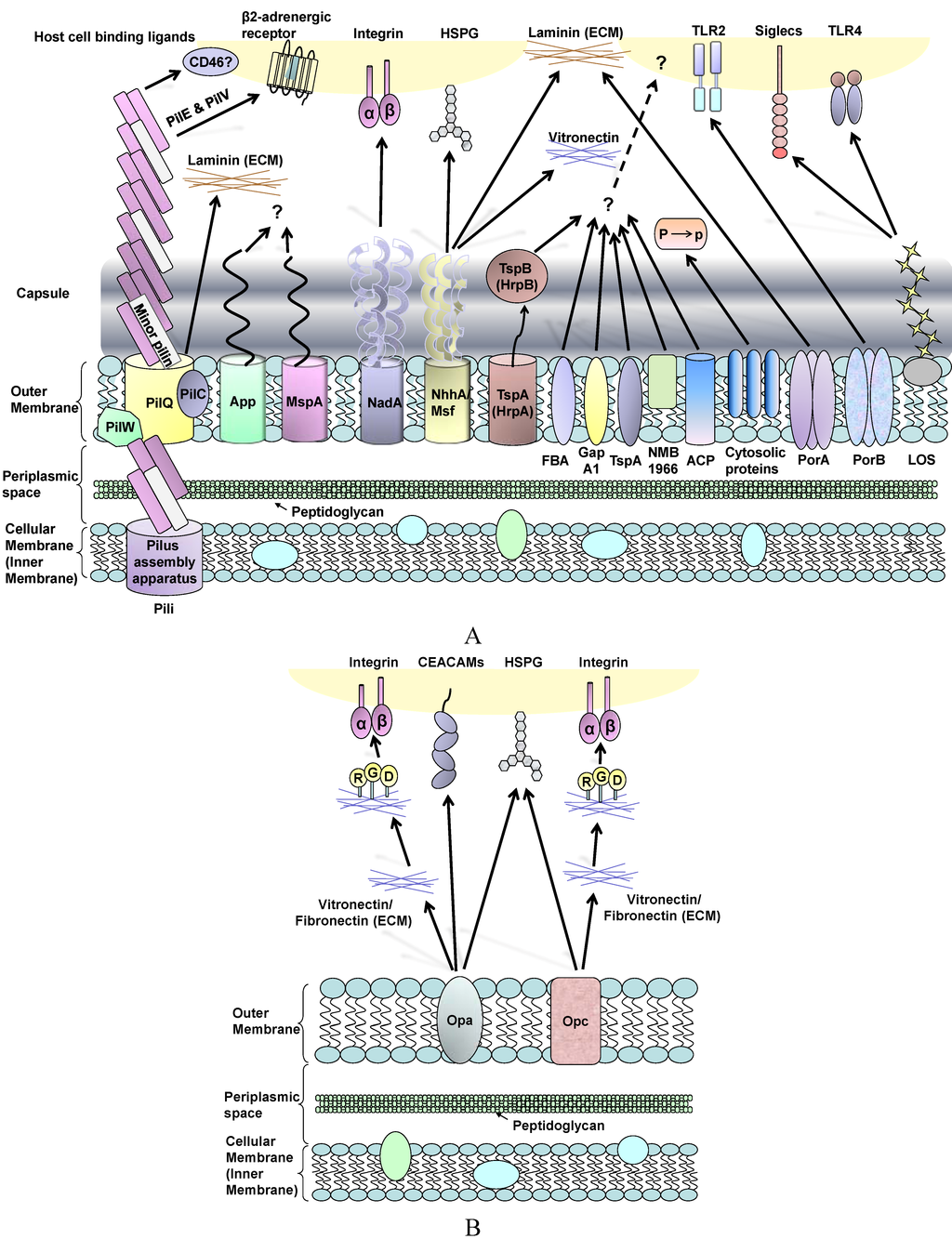
Biology, Free Full-Text

AP Biology For Dummies by Peter J. Mikulecky · OverDrive: ebooks, audiobooks, and more for libraries and schools
Recomendado para você
-
 VENCI O DESAFIO NO CORRIDOR OF HELL19 fevereiro 2025
VENCI O DESAFIO NO CORRIDOR OF HELL19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Duda Ferrão Games19 fevereiro 2025
Duda Ferrão Games19 fevereiro 2025 -
Luquet4 na copa desimpedidos, ferrão nao perdoou kkk #ferraocx19 fevereiro 2025
-
ferrão Nova Skin19 fevereiro 2025
-
 MINECRAFT #17 CONSTRUÍMOS UMA CIDADE SEM MODS. TOUR PELA MINHA19 fevereiro 2025
MINECRAFT #17 CONSTRUÍMOS UMA CIDADE SEM MODS. TOUR PELA MINHA19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Petición · Have the Peppa Pig Videogame be the Game of the Year19 fevereiro 2025
Petición · Have the Peppa Pig Videogame be the Game of the Year19 fevereiro 2025 -
ooi gente!! Passando aqui por um motivo nada bom, meu canal foi19 fevereiro 2025
-
 Novo guia londres 2012 small 3 by Luis Ventura - Issuu19 fevereiro 2025
Novo guia londres 2012 small 3 by Luis Ventura - Issuu19 fevereiro 2025 -
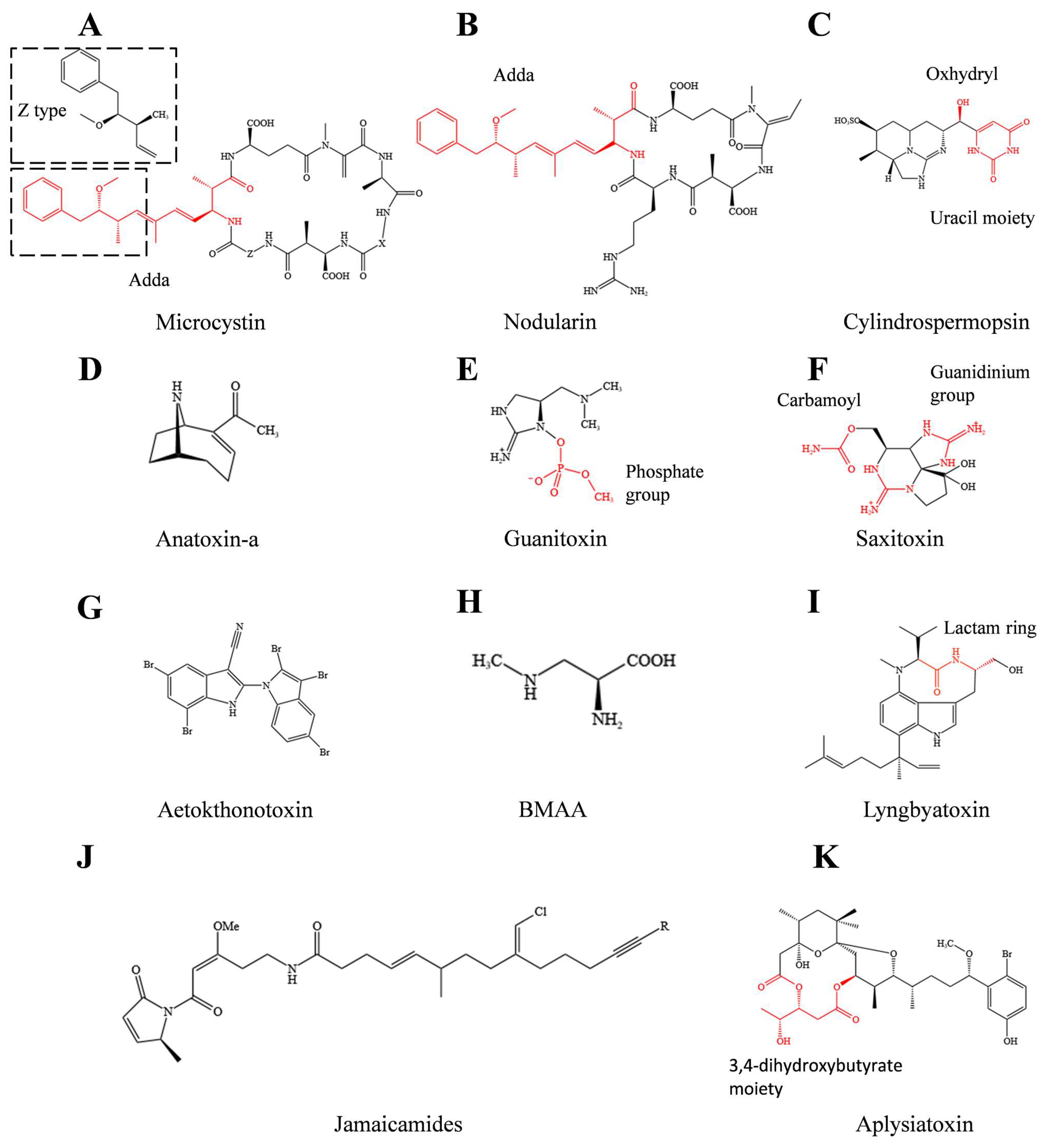 Microorganisms, Free Full-Text19 fevereiro 2025
Microorganisms, Free Full-Text19 fevereiro 2025 -
china nao queria fuga #fivemrp #grotarp #luanz7 #complexorp19 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Rebirth Island - Gallery - Battle Royale, Modern Warfare - Call of Duty Maps19 fevereiro 2025
Rebirth Island - Gallery - Battle Royale, Modern Warfare - Call of Duty Maps19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Página 2 Jogo Dama Slides Imagens – Download Grátis no Freepik19 fevereiro 2025
Página 2 Jogo Dama Slides Imagens – Download Grátis no Freepik19 fevereiro 2025 -
Bola Basquete Spalding Lay Up Baby Borracha Infantil19 fevereiro 2025
-
 Battle Angel (TV Mini Series 1993) - IMDb19 fevereiro 2025
Battle Angel (TV Mini Series 1993) - IMDb19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Need for Speed Most Wanted Remake Might be in The Works : r19 fevereiro 2025
Need for Speed Most Wanted Remake Might be in The Works : r19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Revived my psp 3000. Where to start with games in 2023? Tnx : r/PSP19 fevereiro 2025
Revived my psp 3000. Where to start with games in 2023? Tnx : r/PSP19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Game Station - Grande Rio19 fevereiro 2025
Game Station - Grande Rio19 fevereiro 2025 -
 Boys' Swimming: Long Beach Poly Wins Moore League Title, Ends Wilson's Historic Streak –19 fevereiro 2025
Boys' Swimming: Long Beach Poly Wins Moore League Title, Ends Wilson's Historic Streak –19 fevereiro 2025 -
 emperrando Tradução de emperrando no Dicionário Infopédia de Português - Inglês19 fevereiro 2025
emperrando Tradução de emperrando no Dicionário Infopédia de Português - Inglês19 fevereiro 2025 -
 How to Remove Microsoft Account from Windows 10/1119 fevereiro 2025
How to Remove Microsoft Account from Windows 10/1119 fevereiro 2025


