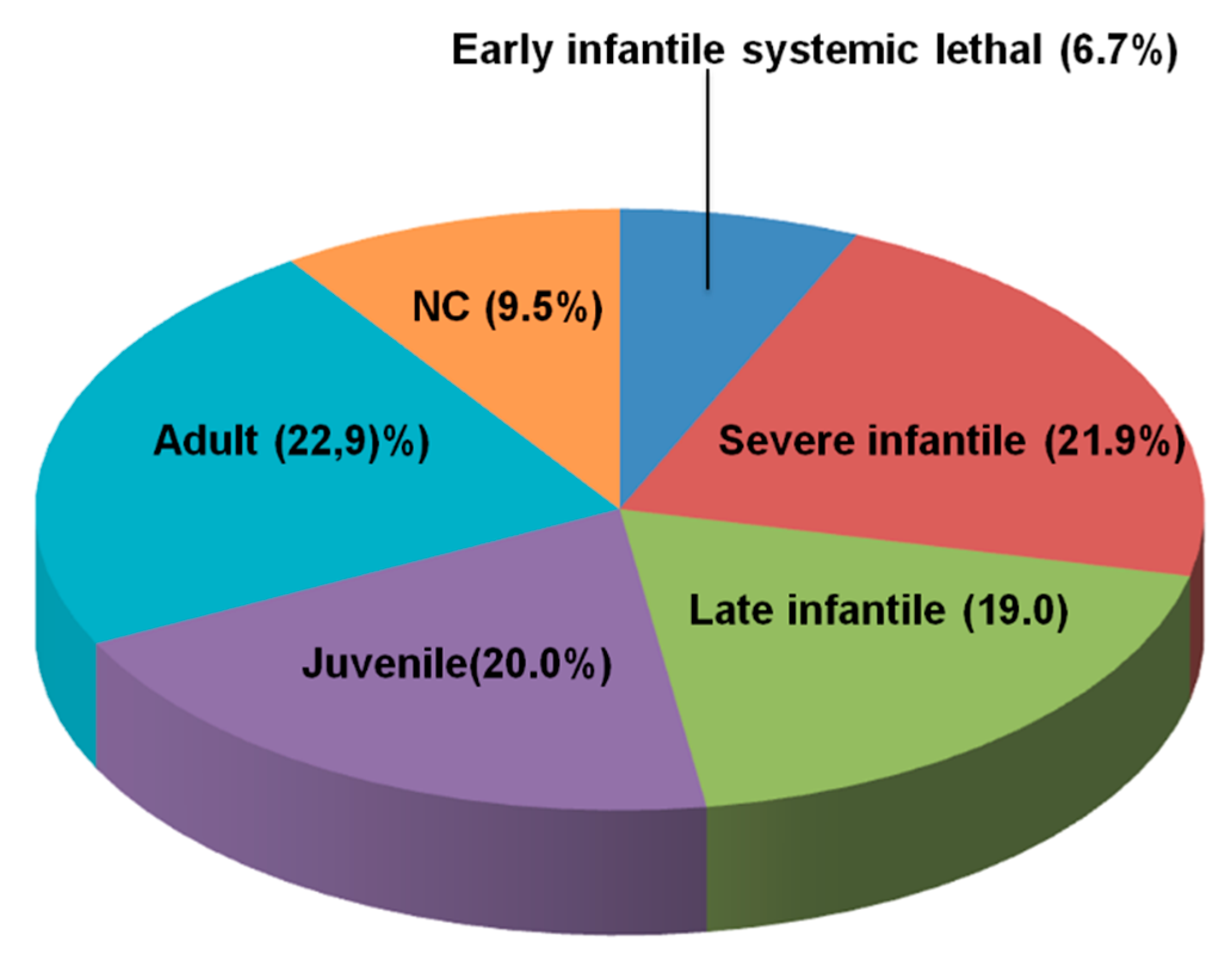
10: Types A and B Niemann–Pick Disease
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 março 2025
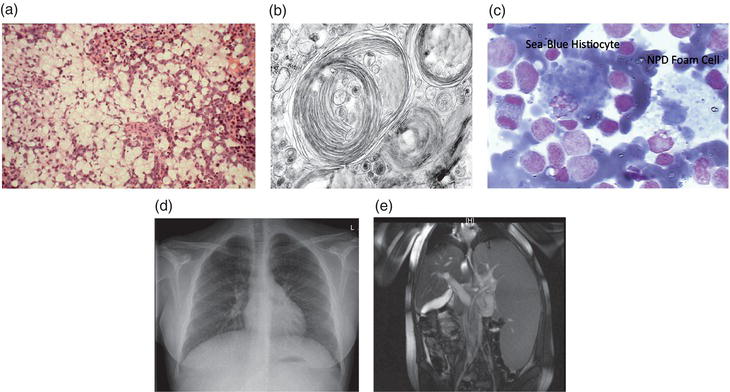
Type A A 3-month-old previously well boy was noted to have hepatosplenomegaly during a routine pediatric visit. Over the next several months, the infant acquired developmental milestones appropriately and learned how to roll over, vocalize, and sit with support. By 10 months of age his abdomen was markedly enlarged, and the extremities appeared thin. Over…
Niemann-Pick Disease Concise Medical Knowledge
JCM, Free Full-Text

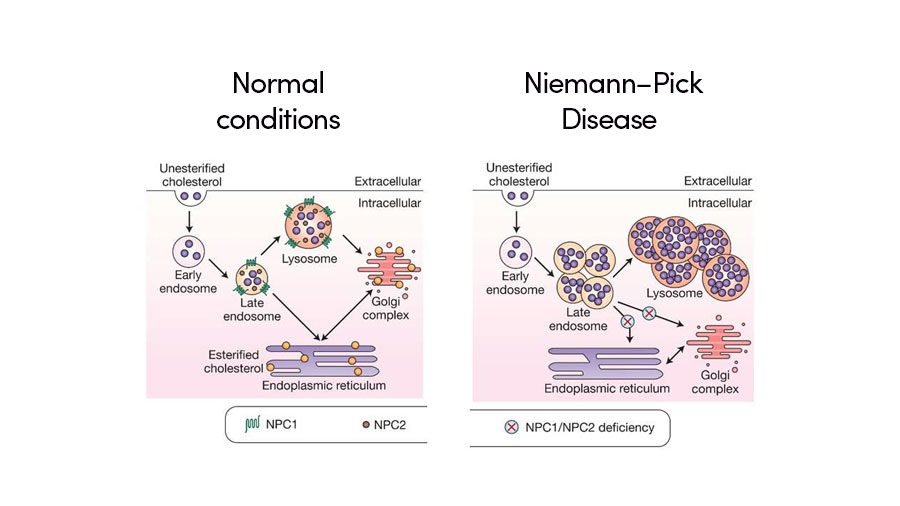
Niemann-Pick disease type C as a neurovisceral disease. Schematic
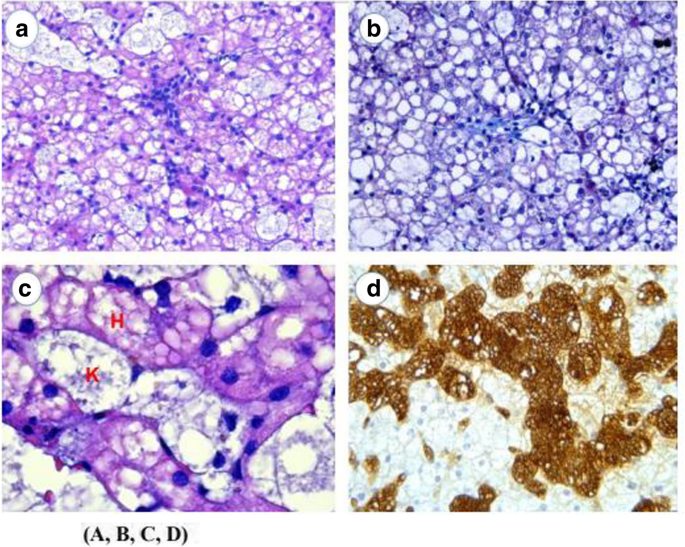
Niemann-Pick disease type-B: a unique case report with compound heterozygosity and complicated lipid management, BMC Medical Genetics
From genes to hope

Imaging manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type B.

Niemann-Pick disease types A and B (NORD): Video

Niemann-Pick disease type C as a neurovisceral disease. Schematic
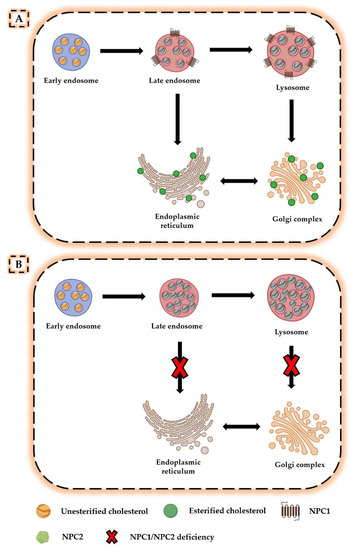
IJMS, Free Full-Text
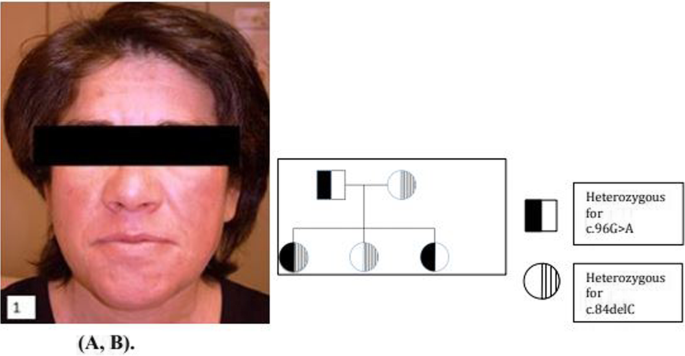
Niemann-Pick disease type-B: a unique case report with compound heterozygosity and complicated lipid management, BMC Medical Genetics

TYPE B NIEMANN-PICK DISEASE: REPORT OF A CASE WITH

Diagnostic workup and management of patients with suspected Niemann-Pick type C disease - Apostolos Papandreou, Paul Gissen, 2016
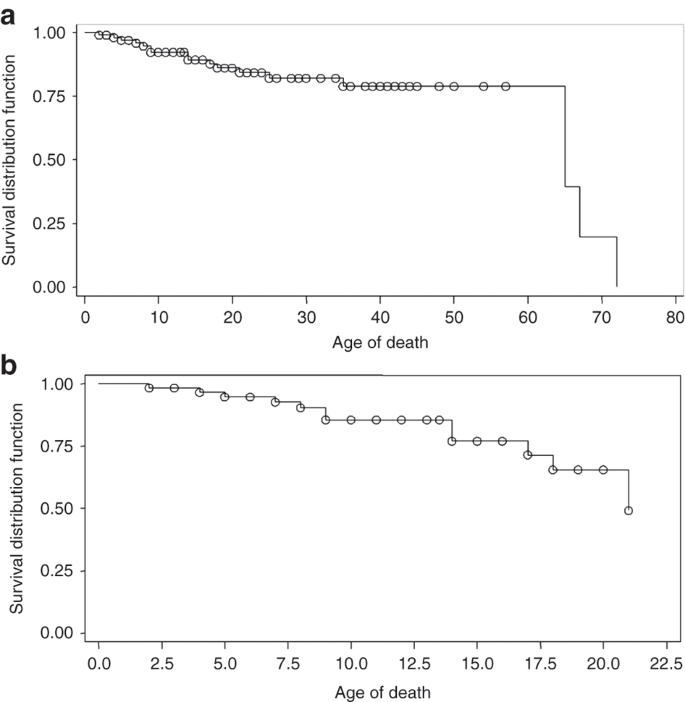
Morbidity and mortality in type B Niemann–Pick disease
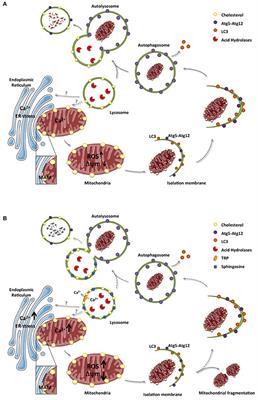
Frontiers Lysosomal and Mitochondrial Liaisons in Niemann-Pick Disease

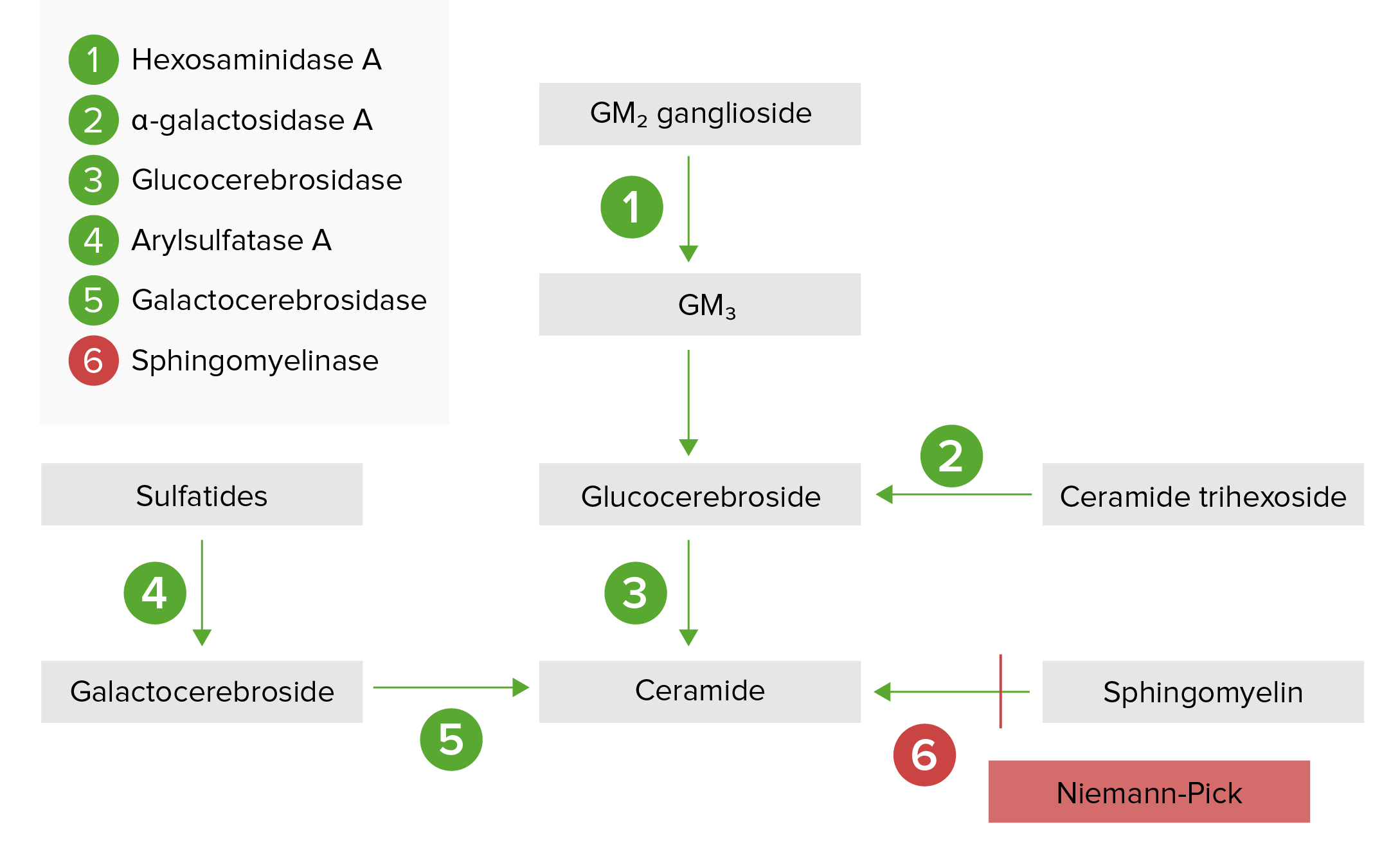
MedRewind - #132 Niemann-Pick disease (Types A and B) : caused by the inability to degrade sphingomyelin due to a deficiency of sphingomyelinase, a type of phospholipase C. In the severe infantile
Recomendado para você
-
 Potential treatment for Niemann-Pick type C, a rare neurodegenerative disease26 março 2025
Potential treatment for Niemann-Pick type C, a rare neurodegenerative disease26 março 2025 -
National Niemann-Pick Disease Foundation, Inc. - October is26 março 2025
-
 Niemann-Pick disease Information26 março 2025
Niemann-Pick disease Information26 março 2025 -
 Niemann-Pick disease type C. The diagram represents subtypes and26 março 2025
Niemann-Pick disease type C. The diagram represents subtypes and26 março 2025 -
 University College London begins preclinical studies to develop a26 março 2025
University College London begins preclinical studies to develop a26 março 2025 -
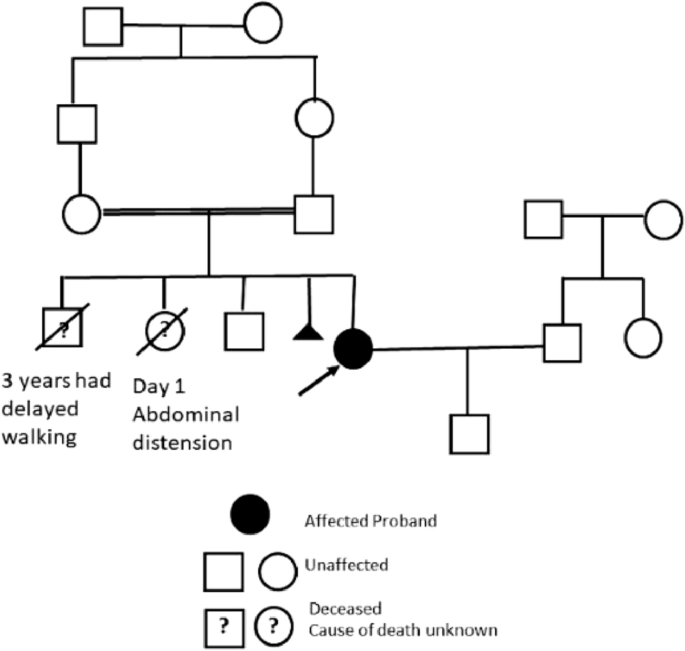 Successful Outcome of Pregnancy in Niemann–Pick Disease Type B: A26 março 2025
Successful Outcome of Pregnancy in Niemann–Pick Disease Type B: A26 março 2025 -
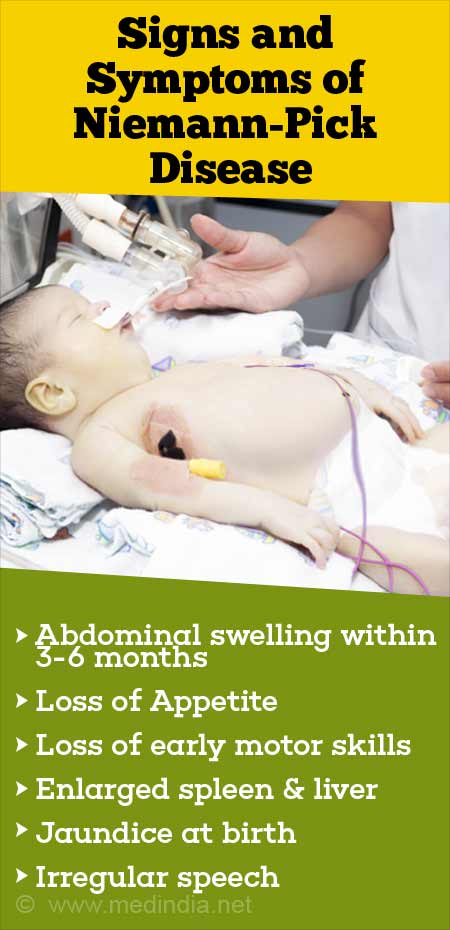 Niemann-Pick Disease - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment26 março 2025
Niemann-Pick Disease - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment26 março 2025 -
 White and gray matter alterations in adults with Niemann-Pick26 março 2025
White and gray matter alterations in adults with Niemann-Pick26 março 2025 -
 Baby With Niemann-Pick Disease — Marian McGlocklin Story26 março 2025
Baby With Niemann-Pick Disease — Marian McGlocklin Story26 março 2025 -
 Niemann-Pick disease type C-presenting as persistent neonatal26 março 2025
Niemann-Pick disease type C-presenting as persistent neonatal26 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 MasterOfSuits - Hobbyist, Artist26 março 2025
MasterOfSuits - Hobbyist, Artist26 março 2025 -
 OOZARU MACACO GIGANTE VS GOKU BLACK NO ROBLOX!! (Dragon Ball)26 março 2025
OOZARU MACACO GIGANTE VS GOKU BLACK NO ROBLOX!! (Dragon Ball)26 março 2025 -
 I'm the 1,000,000,000 person to get rick rolled!! - Imgflip26 março 2025
I'm the 1,000,000,000 person to get rick rolled!! - Imgflip26 março 2025 -
 Lançamentos da semana: Scorn, Undecember, Dragon Ball: The26 março 2025
Lançamentos da semana: Scorn, Undecember, Dragon Ball: The26 março 2025 -
 Marvel Legends Series Grandmaster And Korg26 março 2025
Marvel Legends Series Grandmaster And Korg26 março 2025 -
 Jogo De Tabuleiro De Xadrez Ficar Contra Conjunto Completo De Peças De Xadrez. Estratégia, Planejamento E Decisão Conceito De Negócios Foto Royalty Free, Gravuras, Imagens e Banco de fotografias. Image 14760477926 março 2025
Jogo De Tabuleiro De Xadrez Ficar Contra Conjunto Completo De Peças De Xadrez. Estratégia, Planejamento E Decisão Conceito De Negócios Foto Royalty Free, Gravuras, Imagens e Banco de fotografias. Image 14760477926 março 2025 -
 New Release Jacques the Deinocheirus Scientific Art Model from PNSO Prehistoric Animal Models Series – PNSO26 março 2025
New Release Jacques the Deinocheirus Scientific Art Model from PNSO Prehistoric Animal Models Series – PNSO26 março 2025 -
 TREE CREEPER definition in American English26 março 2025
TREE CREEPER definition in American English26 março 2025 -
Lista Karaoke JFK, PDF, Amor26 março 2025
-
 Comparing Norse Mythology In God Of War: Ragnarok Vs AC: Valhalla26 março 2025
Comparing Norse Mythology In God Of War: Ragnarok Vs AC: Valhalla26 março 2025

